Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 -ray spectroscopy of neutron-rich nuclei in the uranium region through the heavy-ion transfer reaction
-ray spectroscopy of neutron-rich nuclei in the uranium region through the heavy-ion transfer reactionIshii, Tetsuro; Makii, Hiroyuki; Asai, Masato; Koura, Hiroyuki; Shigematsu, Soichiro*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Matsuda, Makoto; Makishima, Akiyasu*; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 805(1-4), p.257 - 259, 2008/06
no abstracts in English
 Se; Implications for the s-process thermometer
Se; Implications for the s-process thermometerMakinaga, Ayano*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Yamagata, Tamio*; Akimune, Hidetoshi*; Goriely, S.*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Matsumoto, Tetsuro*; Harano, Hideki*; Harada, Hideo; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 805(1-4), p.564 - 566, 2008/06
Photoneutron cross sections were measured for  Se near the neutron threshold energy with quasi-monochromatic
Se near the neutron threshold energy with quasi-monochromatic  rays. Using the
rays. Using the  Se(
Se( ,
, ) cross section as experimental constraints on the E1
) cross section as experimental constraints on the E1  strength function, we estimate the neutron capture rates for
strength function, we estimate the neutron capture rates for  Se. The solar abundance ratio of s-only nuclides
Se. The solar abundance ratio of s-only nuclides  Kr and
Kr and 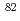 Kr are analyzed in terms of the s-process branching at
Kr are analyzed in terms of the s-process branching at  Se within the local approximation. The corresponding temperature and neutron density regimes are discussed in the light of the s-process scenario in massive stars.
Se within the local approximation. The corresponding temperature and neutron density regimes are discussed in the light of the s-process scenario in massive stars.
 U target nuclei on the fusion probability for the heavy element synthesis
U target nuclei on the fusion probability for the heavy element synthesisNishio, Katsuhisa; Hofmann, S.*; Ikezoe, Hiroshi; He berger, F. P.*; Ackermann, D.*; Antalic, S.*; Comas, V. F.*; Gan, Z.*; Heinz, S.*; Heredia, J. A.*; et al.
berger, F. P.*; Ackermann, D.*; Antalic, S.*; Comas, V. F.*; Gan, Z.*; Heinz, S.*; Heredia, J. A.*; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 805(1-4), p.516 - 518, 2008/06
Ota, Masahisa*; Tatsuda, Sayuki*; Yamamoto, Kazuyuki*; Asano, Tomomasa*; Wada, Takahiro*; Hashizume, Kazuaki*; Sumiyoshi, Kosuke*; Otsuki, Kaori*; Kajino, Toshitaka*; Koura, Hiroyuki; et al.
Nuclear Physics A, 805(2), p.558 - 560, 2008/02
The data base for the fission fragment mass distribution used in the r-process network calculation is constructed. The differences appeared in the final element abundance calculated with and without fission process are demonstrated and the mass region modified by the fission products is presented.
Suzuki, Toshio*; Chiba, Satoshi; Yoshida, Takashi*; Higashijima, Koji*; Homma, Michio*; Kajino, Toshitaka*; Otsuka, Takaharu*
Nuclear Physics A, 805(2), p.579 - 581, 2008/02
Neutrino-nucleus reactions on  C and
C and  He are studied based on new shell model Hamiltonians. The cross sections are found to be enhanced compared with those obtained by conventional Hamiltonians. The production yield of
He are studied based on new shell model Hamiltonians. The cross sections are found to be enhanced compared with those obtained by conventional Hamiltonians. The production yield of  Li and
Li and  B during supernova explosions are pointed out to be enhanced, and a possibility of determining the neutrino mixing angle
B during supernova explosions are pointed out to be enhanced, and a possibility of determining the neutrino mixing angle 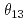 is discussed in case of neutrino oscillations. Neutrino induced reactions on Fe and Ni isotopes are also studied based on recent advances in shell model calculations in the
is discussed in case of neutrino oscillations. Neutrino induced reactions on Fe and Ni isotopes are also studied based on recent advances in shell model calculations in the 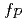 -shell. The reaction crowds sections are found to be enhanced compared with those obtained by a modified KB3 Hamiltonian.
-shell. The reaction crowds sections are found to be enhanced compared with those obtained by a modified KB3 Hamiltonian.
Nishinaka, Ichiro; Tanikawa, Masashi*; Goto, Shinichi*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Asai, Masato; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Nagame, Yuichiro; Kudo, Hisaaki*
Nuclear Physics A, 805, p.434 - 436, 2008/00
The aim of this work is to study how shell effects of fissioning nuclei and fission fragments are responsible for deformation and mass division during descent from the saddle point to scission. We studied in detail excitation energy dependence of mass and total kinetic energy distributions in the fission of  +
+ 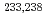 U at incident beam energies of 10.0, 11.5 and 13.0 MeV. For the asymmetric mass division in the fission for both uranium isotopes, the obtained yield at
U at incident beam energies of 10.0, 11.5 and 13.0 MeV. For the asymmetric mass division in the fission for both uranium isotopes, the obtained yield at 
 132 with the spherical shell of
132 with the spherical shell of  = 82 increases more largely with increasing excitation energy than that at
= 82 increases more largely with increasing excitation energy than that at 
 143 with deformed shell of
143 with deformed shell of  = 86-88. The present excitation energy dependence shows the opposite trend observed in the thermal neutron induced fission and cold fission of actinides. We will discuss the shell effects on excitation energy dependence of fragment mass and total kinetic energy distributions in fission.
= 86-88. The present excitation energy dependence shows the opposite trend observed in the thermal neutron induced fission and cold fission of actinides. We will discuss the shell effects on excitation energy dependence of fragment mass and total kinetic energy distributions in fission.
Maruyama, Toshiki; Chiba, Satoshi; Schulze, H.-J.*; Tatsumi, Toshitaka*
Nuclear Physics A, 805, p.588 - 590, 2008/00
no abstracts in English
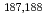 W produced in
W produced in  O-induced transferreactions
O-induced transferreactionsShizuma, Toshiyuki; Ishii, Tetsuro; Makii, Hiroyuki; Hayakawa, Takehito; Shigematsu, Soichiro*; Matsuda, Makoto; Ideguchi, Eiji*; Zheng, Y.*; Liu, M.*; Morikawa, Tsuneyasu*; et al.
no journal, ,
Neutron-rich W-Os nuclei with 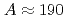 exhibit the various signature of nuclear collective motions such as
exhibit the various signature of nuclear collective motions such as  -softness, triaxiality, and a prolate-oblate shape transition. In addition, the emergence of high-
-softness, triaxiality, and a prolate-oblate shape transition. In addition, the emergence of high- isomers, where
isomers, where  is the angular momentum projection on the nuclear symmetry axis, based on multi-quasiparticle excitation is a characteristic of nuclei in this region. The recent experimental and theoretical studies of the neutron-rich W nuclei have revealed the existence of high-
is the angular momentum projection on the nuclear symmetry axis, based on multi-quasiparticle excitation is a characteristic of nuclei in this region. The recent experimental and theoretical studies of the neutron-rich W nuclei have revealed the existence of high- multi-quasiparticle isomers. Here we report results from the in-beam
multi-quasiparticle isomers. Here we report results from the in-beam  -ray spectroscopic experiments on neutron-rich
-ray spectroscopic experiments on neutron-rich  W and
W and  W.
W.
Hara, Kaoru; Harada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Goko, Shinji*; Hohara, Shinya*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Makinaga, Ayano*; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*; Watanabe, Yukinobu*
no journal, ,
Neutron capture cross sections of the unstable nuclei  Cl (t
Cl (t =3.0
=3.0 10
10 yr) and
yr) and  Sm (t
Sm (t =90 yr) are the fundamental data for the nuclear transmutation. The cross sections of the inverse
=90 yr) are the fundamental data for the nuclear transmutation. The cross sections of the inverse  Cl(
Cl( ,n)
,n) Cl and
Cl and 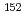 Sm(
Sm( ,n)
,n) Sm reaction were measured with the laser-Compton scattering (LCS)
Sm reaction were measured with the laser-Compton scattering (LCS)  rays at 10.4-12.0 MeV and 8.3-12.4 MeV, respectively. Quasi-monochromatic beams of LCS photons irradiated a natural NaCl sample and an enriched
rays at 10.4-12.0 MeV and 8.3-12.4 MeV, respectively. Quasi-monochromatic beams of LCS photons irradiated a natural NaCl sample and an enriched  Sm
Sm O
O sample. The emitted neutrons were detected with a 4
sample. The emitted neutrons were detected with a 4 neutron detector. The energy distribution of LCS
neutron detector. The energy distribution of LCS  beam was measured with a 120
beam was measured with a 120  Ge detector or the high-resolution high-energy photon spectrometer (HHS). The present data for
Ge detector or the high-resolution high-energy photon spectrometer (HHS). The present data for  Cl,
Cl,  Sm, and
Sm, and  Au are compared with the previous data compiled in the IAEA document and the calculation with a nuclear reaction code TALYS.
Au are compared with the previous data compiled in the IAEA document and the calculation with a nuclear reaction code TALYS.
 -ray spectrometer for neutron capture experiments
-ray spectrometer for neutron capture experimentsOshima, Masumi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Kin, Tadahiro; Kimura, Atsushi; Toh, Yosuke; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Goto, Jun*
no journal, ,
Koura, Hiroyuki; Tachibana, Takahiro*; Chiba, Satoshi
no journal, ,
We have developed an original nuclear mass model based on the macroscopic and mean-field models to describe the global features, called the KTUY (Koura-Tachibana-Uno-Yamada) model. By using the KTUY model, we have studied decay modes for  -decay,
-decay,  -decay, proton emission and spontaneous fission ranging from light nuclei to superheavy nuclei including unknown ones. In this calculation we find that various decay modes coexist and a kind of a periodic structure of the closed shell with
-decay, proton emission and spontaneous fission ranging from light nuclei to superheavy nuclei including unknown ones. In this calculation we find that various decay modes coexist and a kind of a periodic structure of the closed shell with  =126, 184 and 228 near the proton-drip line in the superheavy region. We also calculate total half-lives for nuclei in the "island of stability for the superheavy nuclei" and find a nucleus with the longest half-life on the
=126, 184 and 228 near the proton-drip line in the superheavy region. We also calculate total half-lives for nuclei in the "island of stability for the superheavy nuclei" and find a nucleus with the longest half-life on the  -stability line in the order of 100 years. Furthermore, we also investigate much heavier nuclei beyond the superheavy ones and estimate the next "island of stability" and the limit of existence of nuclei which is given not by proton emission, but by fission.
-stability line in the order of 100 years. Furthermore, we also investigate much heavier nuclei beyond the superheavy ones and estimate the next "island of stability" and the limit of existence of nuclei which is given not by proton emission, but by fission.
Hayakawa, Takehito; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Kajino, Toshitaka*; Ogawa, Kengo*; Nakada, Hitoshi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Maruyama, Toshiki; Chiba, Satoshi; Tatsumi, Toshitaka*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hayakawa, Takehito; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Kajino, Toshitaka*; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Umeda, Hideyuki*; Nomoto, Kenichi*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 Ge detector for Au and Ag
Ge detector for Au and AgHarada, Hideo; Kitatani, Fumito; Toh, Yosuke; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Oshima, Masumi; Mizumoto, Motoharu*; Igashira, Masayuki*; et al.
no journal, ,
The  rays produced by neutron capture reactions for Au and Ag samples were measured using the 4
rays produced by neutron capture reactions for Au and Ag samples were measured using the 4 Ge spectrometer in the resonance region in a time-of-flight (TOF) mode. Two dimensional matrices for TOF and summed Ge pulse heights were produced to analyze the data. From the analyses of the matrices, the origin of each resonance peak is identified. For example, the resonance of Ag-107 and Ag-109 were clearly separated in the measurement of Ag-nat sample by gating at the neutron separation energy for each isotope. Furthermore, the
Ge spectrometer in the resonance region in a time-of-flight (TOF) mode. Two dimensional matrices for TOF and summed Ge pulse heights were produced to analyze the data. From the analyses of the matrices, the origin of each resonance peak is identified. For example, the resonance of Ag-107 and Ag-109 were clearly separated in the measurement of Ag-nat sample by gating at the neutron separation energy for each isotope. Furthermore, the  -ray spectrum for each resonance is deduced from the matrices. The potential of the 4
-ray spectrum for each resonance is deduced from the matrices. The potential of the 4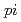 Ge detector as the high-energy-resolution total energy absorption detector is demonstrated using the TOF data obtained for Au and Ag.
Ge detector as the high-energy-resolution total energy absorption detector is demonstrated using the TOF data obtained for Au and Ag.
 absorption for high energy
absorption for high energy  rays
raysKitatani, Fumito; Harada, Hideo; Hara, Kaoru; Utsunomiya, Hiroaki*; Goko, Shinji*; Kaihori, Takeshi*; Toyokawa, Hiroyuki*
no journal, ,
 -rays
-raysKin, Tadahiro; Oshima, Masumi; Kimura, Atsushi; Furutaka, Kazuyoshi
no journal, ,
MA and LLFP neutron capture cross sections are important for nuclear transmutation. Measurements of prompt  are useful method for improvement of accuracy of the data. For the method, ground-state transition
are useful method for improvement of accuracy of the data. For the method, ground-state transition  have to be known. We developed an innovative method for identification of nuclear levels using measured multiple prompt
have to be known. We developed an innovative method for identification of nuclear levels using measured multiple prompt  -ray. For demonstration of the method, we calculated a existing-probability of
-ray. For demonstration of the method, we calculated a existing-probability of  N nuclear levels with measurement of
N nuclear levels with measurement of  N(n,
N(n, )
) N reaction with 4
N reaction with 4 Ge spectrometer at JRR-3. With this demonstration, we verified that the method is useful.
Ge spectrometer at JRR-3. With this demonstration, we verified that the method is useful.
Nagae, Daisuke; Takemuara, Makoto*; Ueno, Hideki*; Kameda, Daisuke*; Asahi, Koichiro*; Yoshimi, Akihiro*; Sugimoto, Takashi*; Nagatomo, Takashi*; Kobayashi, Yoshio*; Uchida, Makoto*; et al.
no journal, ,
An electric quadrupole moment ( moment) is sensitive to collective aspects of nuclear structure. In the
moment) is sensitive to collective aspects of nuclear structure. In the  -moment measurement for unstable nuclei, we employ the
-moment measurement for unstable nuclei, we employ the  -detected nuclear-quadrupole resonance method. In this method, we need to supply
-detected nuclear-quadrupole resonance method. In this method, we need to supply 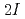 resonance frequencies, where
resonance frequencies, where  denotes the nuclear spin. We have developed a new RF-application system to induced all of the
denotes the nuclear spin. We have developed a new RF-application system to induced all of the 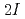 transitions. The application of the
transitions. The application of the 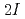 frequencies may be pursued in two different ways; the sequential RF pulse method and the mixed-wave RF pulse method. We confirmed the reversal of polarization for the both methods, from measurements of
frequencies may be pursued in two different ways; the sequential RF pulse method and the mixed-wave RF pulse method. We confirmed the reversal of polarization for the both methods, from measurements of  -ray asymmetry change for polarized
-ray asymmetry change for polarized  B. Using this system, the
B. Using this system, the  moments of
moments of 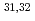 Al have been measured to be
Al have been measured to be 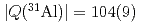
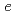
 mb and
mb and 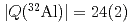
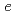
 mb by the sequential RF pulse method.
mb by the sequential RF pulse method.
 La determined by collinear fast-beam laser spectroscopy
La determined by collinear fast-beam laser spectroscopyIimura, Hideki; Schuessler, H. A.*; Buchinger, F.*; Cocolios, T.*; Crawford, J. E.*; Gulick, S.*; Lee, J. K. P.*; Levy, C. D. P.*; Pearson, M.*; Lioubimov, V.*; et al.
no journal, ,
We report measurements of the hyperfine structure constants of  La (N=74) as an initial step to further exploring the neutron deficient rare-earth region where a sudden onset of nuclear deformation is predicted theoretically around N=74. This work is an extension of our earlier off-line experiments on
La (N=74) as an initial step to further exploring the neutron deficient rare-earth region where a sudden onset of nuclear deformation is predicted theoretically around N=74. This work is an extension of our earlier off-line experiments on 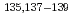 La to on-line laser spectroscopy. The radioactive isotope
La to on-line laser spectroscopy. The radioactive isotope  La (T
La (T =59 min) was produced by means of a spallation reaction using a proton beam from TRIUMF cyclotron. The hyperfine spectra were observed by using the method of collinear fast-beam laser spectroscopy. From the obtained hyperfine constants, the nuclear moments of
=59 min) was produced by means of a spallation reaction using a proton beam from TRIUMF cyclotron. The hyperfine spectra were observed by using the method of collinear fast-beam laser spectroscopy. From the obtained hyperfine constants, the nuclear moments of  La were derived. In order to arrive at an understanding of the nuclear structure of
La were derived. In order to arrive at an understanding of the nuclear structure of  La, we have carried out particle triaxial-rotor calculations. The results from the calculation reproduce well the experimental values when a triaxial shape is assumed for
La, we have carried out particle triaxial-rotor calculations. The results from the calculation reproduce well the experimental values when a triaxial shape is assumed for  La.
La.
 Li
LiMiyatake, Hiroari; Ishiyama, Hironobu*; Watanabe, Yutaka*; Hirayama, Yoshikazu*; Imai, Nobuaki*; Tanaka, Masahiko*; Yoshikawa, Nobuharu*; Jeong, S.-C.*; Fuchi, Yoshihide*; Nomura, Toru*; et al.
no journal, ,
A systematic study of astrophysical reaction rates on light neutron-rich nuclei using low-energy radioactive nuclear beams (RNB) is in progress at the tandem facility of Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). Direct measurements of reaction rates of  Li(
Li( , n)
, n) B,
B,  B(
B( , n)
, n) N and,
N and,  Li(d, p), (d, t), (d,
Li(d, p), (d, t), (d,  ), (p,
), (p,  ) have been carried out. Measured excitation functions and obtained reaction rates will be presented. Possible r-process path via
) have been carried out. Measured excitation functions and obtained reaction rates will be presented. Possible r-process path via  Li at each temperature during r-process and the influence of r-process abundance will be discussed.
Li at each temperature during r-process and the influence of r-process abundance will be discussed.