Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 , and H
, and H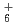 ions produced in irradiated solid hydrogens; An Electron spin resonance study
ions produced in irradiated solid hydrogens; An Electron spin resonance studyKumada, Takayuki; Ushida, Takahiro*; Shimizu, Yuta*; Kumagai, Jun*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(10-12), p.1318 - 1322, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:47.44(Chemistry, Physical)Very recently, we succeeded in observing totally more than 50 sharp ESR lines of H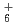 and its isotope substituents H
and its isotope substituents H D
D , H
, H D
D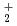 , and H
, and H D
D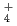 in
in  -ray irradiated solid para-H
-ray irradiated solid para-H (p-H
(p-H ) and p-H
) and p-H -D
-D and p-H
and p-H -HD mixtures. We also observed isotope-substitution reactions such as H
-HD mixtures. We also observed isotope-substitution reactions such as H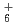 + HD
+ HD  H
H D
D + H
+ H and H
and H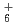 + D
+ D
 H
H D
D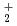 + H
+ H . The H
. The H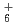 ions diffuse in solid p-H
ions diffuse in solid p-H via the repetition of H
via the repetition of H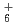 + H
+ H
 H
H + H
+ H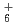 reactions which terminate by the H
reactions which terminate by the H
 + HD or H
+ HD or H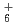 + D
+ D reactions. The H
reactions. The H D
D , H
, H D
D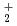 , and H
, and H D
D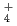 ions, on the other hand, are immobile in solid p-H
ions, on the other hand, are immobile in solid p-H . They decay via geminate recombination with trapped electrons within the time-scale of 5 hours.
. They decay via geminate recombination with trapped electrons within the time-scale of 5 hours.
Kimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Kondo, Takafumi*; Yang, J.*; Yoshida, Yoichi*; Hirota, Koichi
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(10-12), p.1253 - 1257, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:57.45(Chemistry, Physical) cluster ion structure utilizing coulomb explosion imaging
cluster ion structure utilizing coulomb explosion imagingAdachi, Masahiro; Saito, Yuichi; Chiba, Atsuya; Narumi, Kazumasa; Yamada, Keisuke; Kaneko, Toshiaki*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(10-12), p.1328 - 1332, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.70(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
 by 10-keV N
by 10-keV N ion irradiation
ion irradiationKitazawa, Sin-iti; Yamamoto, Shunya; Asano, Masaharu; Saito, Yuichi; Ishiyama, Shintaro
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(10-12), p.1333 - 1336, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.70(Chemistry, Physical)Radiation-induced luminescence (RIL) was generated using 10-keV N irradiation at room temperature to study energy transfer in TiO
irradiation at room temperature to study energy transfer in TiO targets produced by sol-gel and direct-oxidation methods. The RIL spectra in the UV-visible region exhibited numerous atomic lines and three humps; they were deconvolved and proved to be visible bands at 617 and 479 nm from crystalline defects and a UV band at 320 nm from electron transitions between the Ti
targets produced by sol-gel and direct-oxidation methods. The RIL spectra in the UV-visible region exhibited numerous atomic lines and three humps; they were deconvolved and proved to be visible bands at 617 and 479 nm from crystalline defects and a UV band at 320 nm from electron transitions between the Ti 3d and O
3d and O 2s states in the TiO
2s states in the TiO crystal.
crystal.
Yokoya, Akinari; Shikazono, Naoya; Fujii, Kentaro; Urushibara, Ayumi; Akamatsu, Ken; Watanabe, Ritsuko
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(10-12), p.1280 - 1285, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:61 Percentile:95.62(Chemistry, Physical)Ionizing radiation induces a variety of damages in cellular DNA, which is thought to be the critical target of biological effects of radiation, by both direct energy deposition on DNA (direct effect) and reactions with diffusible water radicals (indirect effect). One of the goals of our study is to clarify the nature of DNA damage induced by direct effect. The yields of single- and double-strand breaks, base lesions and clustered damage induced in a plasmid DNA were measured after exposing to various kinds of radiation (ion particles; 20 to 500 keV/  , photons; 0.4 keV to 1.3 MeV). Base excision repair enzymes were used to detect the oxidative base lesions. In order to obtain more detailed insights into the physicochemical mechanism of DNA damage induction, short-lived base radicals by applying an EPR spectrometer at a synchrotron ultrasoft X-ray beamline. Experimental evidences obtained by these methods will be discussed in comparison with the previous plasmid data.
, photons; 0.4 keV to 1.3 MeV). Base excision repair enzymes were used to detect the oxidative base lesions. In order to obtain more detailed insights into the physicochemical mechanism of DNA damage induction, short-lived base radicals by applying an EPR spectrometer at a synchrotron ultrasoft X-ray beamline. Experimental evidences obtained by these methods will be discussed in comparison with the previous plasmid data.
Asano, Akira*; Yang, J.*; Kondo, Takafumi*; Norizawa, Kimihiro*; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Takahashi, Kenji*; Yoshida, Yoichi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(10-12), p.1244 - 1247, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:81.34(Chemistry, Physical)The molar extinction coefficient and the radiolytic yield of solvated electrons in ionic liquid of DEMMA-TFSI were estimated respectively to be 2.3 10
10 L mol
L mol cm
cm and 0.8
and 0.8 10
10 mol J
mol J by observing the reaction and kinetics of solvated electron and dry electron in the ionic liquid. The solvated electron in DEMMA-TFSI has a very broad absorption spectrum peaking at 1100 nm and reacts slowly with pyrene with a rate constant of 3.5
by observing the reaction and kinetics of solvated electron and dry electron in the ionic liquid. The solvated electron in DEMMA-TFSI has a very broad absorption spectrum peaking at 1100 nm and reacts slowly with pyrene with a rate constant of 3.5 10
10 L mol
L mol s
s , while the dry electron is captured rapidly by pyrene with C
, while the dry electron is captured rapidly by pyrene with C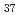 value of 0.065 mol L
value of 0.065 mol L .
.
Yang, J.*; Kondo, Takafumi*; Norizawa, Kimihiro*; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Takahashi, Kenji*; Kato, Ryuji*; Anishchik, S. V.*; Yoshida, Yoichi*; Tagawa, Seiichi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(10-12), p.1233 - 1238, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:81.34(Chemistry, Physical)First observation of picosecond dynamics in ionic liquid of DEMMA-TFSI in radiation chemistry was reported. It is found that the electron produced by ionization is solvated to full solvation in ionic liquid with a rate constant of 3.9 10
10 s
s . The yield of solvated electrons in picosecond time region is 1.2
. The yield of solvated electrons in picosecond time region is 1.2 10
10 mol J
mol J . The dry electron in ionic liquid reacts rapidly with biphenyl and pyrene with a rate constant of 3.8 to 7.9
. The dry electron in ionic liquid reacts rapidly with biphenyl and pyrene with a rate constant of 3.8 to 7.9 10
10 L mol
L mol s
s . The geminate ion recombination in n-dodecane and n-hexane was also observed by monitoring the transient absorptions at 523 nm.
. The geminate ion recombination in n-dodecane and n-hexane was also observed by monitoring the transient absorptions at 523 nm.
Ukai, Masatoshi*; Yokoya, Akinari; Fujii, Kentaro; Saito, Yuji
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(10-12), p.1265 - 1269, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:57.45(Chemistry, Physical)In order to substantiate the hydrated structure of DNA from the view point of the electronic properties, we develop a new spectroscopic technique for the photoelectrons ejected from solutions dissolving biological molecules using a soft X-ray synchrotron radiation (SPring-8, BL23SU) in combination with liquid jet technique in vacuum. In this paper, we present the first evidence of the spectrum of total photoelectron yields for a nucleotide, guanosine-5'-monophosphate, in solution in the energy region of so-called water window around nitrogen K-edge. A liquid nucleotide/water sample is maintained in the form of continuous thin water jet (diameter  20
20  m) in vacuum and is intersected by a highly focused soft X-ray beam. The obtained spectrum in solution shows common features with the spectrum in solid film. Nitrogen atoms only exist in the base site, so that the spectral similarities can be explained by the hydrophobic property of the base site.
m) in vacuum and is intersected by a highly focused soft X-ray beam. The obtained spectrum in solution shows common features with the spectrum in solid film. Nitrogen atoms only exist in the base site, so that the spectral similarities can be explained by the hydrophobic property of the base site.
Nikjoo, H.*; Emifietzoglou, D.*; Watanabe, Ritsuko; Uehara, Shuzo*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(10-12), p.1270 - 1279, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:55 Percentile:94.76(Chemistry, Physical)Microdosimetry and track structure have been applied to scrutinize and understand aspects of radiation damage in biological molecules from a theoretical approach. To this end track structure has provided a basis for understanding the mechanism(s) that shape dose-effect relationships. There is a wealth of information and data accumulated from radiation biology that need to be placed in the framework of a general descriptive theory. While there are many classical radiobiology questions remain unanswered new ideas and challenging question are emerging. Among many, simulation of radiation track at molecular level is an emerging tool in radiobiology and theoretical radiotherapy. In this paper we present recent progress in development of low energy electron tracks in condensed media and high energy proton tracks and discuss progress in characterizing DNA damage in terms of types and complexity.
Kumagai, Yuta; Lin, M.; Lampre, I.*; Mostafavi, M.*; Muroya, Yusa*; Katsumura, Yosuke
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(10-12), p.1198 - 1202, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.82(Chemistry, Physical)The absorption spectra of the hydrated electron in concentrated LiCl, LiClO , Li
, Li SO
SO , MgCl
, MgCl and Mg(ClO
and Mg(ClO )
) deuterated water solutions were measured by pulse radiolysis techniques from room temperature to 300
deuterated water solutions were measured by pulse radiolysis techniques from room temperature to 300  C at a constant pressure of 25 MPa. As salt effects, shifts to shorter wavelengths and broadening of the absorption band of the solvated electron were observed at room temperature. At elevated temperatures, similar spectral shifts were observed. The broadening of the spectrum, on the other hand, becomes smaller with increasing temperature. These result indicate that high concentration of salts not only form an ion atmosphere to cause the spectral shifts, but also affect the solvation structure of an electron. The smaller broadening at elevated temperatures suggest that a decrease in the density expand the distance between solvated electron and surrounding ions, and that therefore the effect on the solvation structure becomes smaller.
C at a constant pressure of 25 MPa. As salt effects, shifts to shorter wavelengths and broadening of the absorption band of the solvated electron were observed at room temperature. At elevated temperatures, similar spectral shifts were observed. The broadening of the spectrum, on the other hand, becomes smaller with increasing temperature. These result indicate that high concentration of salts not only form an ion atmosphere to cause the spectral shifts, but also affect the solvation structure of an electron. The smaller broadening at elevated temperatures suggest that a decrease in the density expand the distance between solvated electron and surrounding ions, and that therefore the effect on the solvation structure becomes smaller.
 C; Absorption spectra, kinetics and yield of carboxyl radical CO
C; Absorption spectra, kinetics and yield of carboxyl radical CO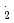

Lin, M.; Katsumura, Yosuke; Muroya, Yusa*; He, H.*; Miyazaki, Toyoaki*; Hiroishi, Daisuke*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(10-12), p.1208 - 1212, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:80.44(Chemistry, Physical)Sodium formate neutral aqueous solutions saturated with N O were studied by pulse radiolysis techniques from room temperature to 400
O were studied by pulse radiolysis techniques from room temperature to 400  C. The absorption spectra of CO
C. The absorption spectra of CO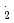
 show a red shift from
show a red shift from 
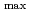 = 235 nm at 25
= 235 nm at 25  C to 280 nm at 400
C to 280 nm at 400  C. The second-order decay of CO
C. The second-order decay of CO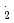
 is not monotonically temperature-dependent: the rate constant (2
is not monotonically temperature-dependent: the rate constant (2 /
/ ) slightly increases with temperature up to 200
) slightly increases with temperature up to 200  C, then decreases to a valley at 300
C, then decreases to a valley at 300  C, and it sharply increases again for temperature
C, and it sharply increases again for temperature  350
350  C.
C. 

 (CO
(CO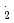
 ) increases with temperature from room temperature to 400
) increases with temperature from room temperature to 400  C. Significant density effect on
C. Significant density effect on 

 (CO
(CO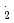
 ) is found at 400
) is found at 400  C. Assumed
C. Assumed  (CO
(CO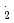
 ) is independent on temperature, at 400
) is independent on temperature, at 400  C, the density dependence of
C, the density dependence of  (CO
(CO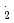
 ) in the presence of N
) in the presence of N O agrees well with that of [
O agrees well with that of [ (e
(e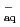 )+
)+ (H
(H )+
)+ (
( OH)].
OH)].
Fu, H.*; Katsumura, Yosuke; Lin, M.; Muroya, Yusa*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(10-12), p.1300 - 1305, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:28.54(Chemistry, Physical)In the present work, laser photolysis techniques have been used to study the transient species of silybin (abbreviated as SLB) in ethanol solutions. It has been demonstrated that the exposure of silybin to 248 nm excimer laser gives rise to monophotonic ionization with a high quantum yield. The transient species have been identified, and a series of related kinetics parameters have also been obtained. For the sake of comparison, we approached the problem using another way to reduce silybin, i.e. attack of solvated electrons, e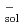 , produced in pulse radiolysis. The rate constant for reaction of e
, produced in pulse radiolysis. The rate constant for reaction of e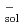 was determined to be 3.8
was determined to be 3.8 10
10 dm
dm mol
mol s
s at 720 nm, which is consistent with 4.6
at 720 nm, which is consistent with 4.6 10
10 dm
dm mol
mol s
s , obtained by laser photolysis.
, obtained by laser photolysis.
Muroya, Yusa*; Lin, M.; Han, Z.*; Kumagai, Yuta; Sakumi, Akira*; Ueda, Toru*; Katsumura, Yosuke
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(10-12), p.1176 - 1182, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:76.19(Chemistry, Physical)In order to study radiation-induced fast phenomena, a new pulse radiolysis system with higher time resolution based on pulse-and-probe method was developed and utilized for practical work. A few picosecond electron beam generated from a linear accelerator, in which a laser photocathode RF-gun is introduced, was synchronized with a femtosecond laser pulse which is employed as the analyzing light. The synchronization precision between them was suppressed within 1.6 ps (rms). Converting the fundamental laser into white light continuum or optical parametric amplification allows to measure in the wide wavelength from visible to infrared region.
Katsumura, Yosuke; Lin, M.; Yokoya, Akinari; Hatano, Yoshihiko
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 77(10-12), P. 1119, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:82.47(Chemistry, Physical)As Guest Editors, we publish a special issue of Radiation Physics and Chemistry in conjunction with the ASR2007 Symposium, an international symposium on "Charged Particle and Photon Interactions with Matter" held on November 6-9, 2007 at the Advanced Science Research Center (ASRC), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in Tokai.
Fu, H.*; Katsumura, Yosuke; Lin, M.; Muroya, Yusa*; Hata, Kuniki
no journal, ,
Yamashita, Shinichi*; Katsumura, Yosuke; Lin, M.; Muroya, Yusa*; Miyazaki, Toyoaki*; Murakami, Takeshi*; Meesungnoen, J.*; Jay-Gerin, J.-P.*
no journal, ,
Takahashi, Hiroyuki*; Katsumura, Yosuke; Lin, M.; Muroya, Yusa*; Kumagai, Yuta; Kudo, Hisaaki*
no journal, ,
Saito, Yuichi; Chiba, Atsuya; Adachi, Masahiro; Narumi, Kazumasa
no journal, ,

 , H
, H D
D , H
, H D
D
 , and H
, and H D
D
 produced in
produced in  -ray irradiated solid para-H
-ray irradiated solid para-H
Kumada, Takayuki; Kumagai, Jun*; Ushida, Takahiro*; Shimizu, Yuta*
no journal, ,
We carried out electron spin resonance (ESR) study of irradiated solid para-H . H
. H
 lines were observed. The H
lines were observed. The H
 ion is the ionic hydrogen radical whose spectrum is firstly observed in irradiated solid para-H
ion is the ionic hydrogen radical whose spectrum is firstly observed in irradiated solid para-H . The H
. The H
 ions diffuse in solid H
ions diffuse in solid H via the repetition of H
via the repetition of H
 + H
+ H
 H
H + H
+ H
 reaction, which terminate by the isotope-exchange reaction H
reaction, which terminate by the isotope-exchange reaction H
 + HD
+ HD  H
H D
D + H
+ H or H
or H
 + D
+ D
 H
H D
D
 + H
+ H . Unlike H
. Unlike H
 , the isotope substitutions H
, the isotope substitutions H D
D and H
and H D
D
 cannot diffuse in solid para-H
cannot diffuse in solid para-H . Rate-determining step of their decay is charge recombination with e
. Rate-determining step of their decay is charge recombination with e .
.
Nagaishi, Ryuji; Yamada, Reiji; Sato, Hideo; Kurosawa, Akira; Watahiki, Masaru; Hiyama, Toshiaki
no journal, ,
Radioactive glass wastes, which emit ionizing radiations and heats, are discharged at ca. 30 containers/yr for 1 GWe nuclear power reactor. The wastes are now kept air-cooling at the stage of interim storage, but are expected to be recycled as useful materials or energy resources in the future. We estimated the irradiation ability of wastes by conducting the dosimetry of analytical pieces of wastes from the wastes at Tokai Reprocessing Plant, JAEA. Non-toxic treatment of chromium(IV) as a useful reaction was confirmed by using the analytical pieces as a radiation source.