Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sugie, Tatsuo; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kasai, Satoshi*; Kusama, Yoshinori
AIP Conference Proceedings 988, p.218 - 221, 2008/04
The detailed design of the Impurity Influx Monitor (divertor) has been carried out to provide the measurement capability in the harsh environment. The potential damaging effects for the first mirrors mounted close to the plasma are the formations of coatings of impurities and the deposition of the dust. Mitigating measures to minimize the degradation of their performance by these effects, such as changes in the reflectivity, are adopted: for example, the plasma is viewed through a small aperture, and baffle plates are inserted in front of the first mirrors. However, it will not be possible to prevent the degradation completely. It is important to know the change of the sensitivity of the optical systems. It is not feasible to install a light source in the vacuum chamber of ITER during operations and so an alternative method is needed. The in-situ calibration system using a micro retro-reflector array has been developed as a possible method.
Nishitani, Takeo; Ishikawa, Masao; Kondoh, Takashi; Kusama, Yoshinori; Asai, Keisuke*; Sasao, Mamiko*
AIP Conference Proceedings 988, p.267 - 274, 2008/04
no abstracts in English
Ishikawa, Masao; Itoga, Toshio*; Okuji, Toshio*; Nakohostin, M.*; Shinohara, Koji; Baba, Mamoru*; Nishitani, Takeo
AIP Conference Proceedings 988, p.295 - 298, 2008/03
A line-integrated neutron emission profile is routinely measured using Stilbene neutron detector in JT-60U tokamak. Although the SND has many advantages as a neutron detector, the maximum count rate is limited up to 10 cps due to the analog pulse shape discrimination (PSD) circuit. To overcome this issue, a digital signal processing (DSP) system using a flash ADC has been developed In this system anode signals from photomultiplier of the SND are directory stored and digitized. Then, the PSD between neutrons and
cps due to the analog pulse shape discrimination (PSD) circuit. To overcome this issue, a digital signal processing (DSP) system using a flash ADC has been developed In this system anode signals from photomultiplier of the SND are directory stored and digitized. Then, the PSD between neutrons and  rays is performed using software. The DSP system has been installed in the vertical neutron collimator system inJT-60U and applied to deuterium experiments. It is confirmed that the PSD is sufficiently performed and collimated neutron flux is successfully measured with count rate up to 10
rays is performed using software. The DSP system has been installed in the vertical neutron collimator system inJT-60U and applied to deuterium experiments. It is confirmed that the PSD is sufficiently performed and collimated neutron flux is successfully measured with count rate up to 10 cps without the effect of pileup of detected pulses.
cps without the effect of pileup of detected pulses.
Koide, Yoshihiko
AIP Conference Proceedings 988, p.413 - 419, 2008/03
An economically attractive DEMO requires a steady-state plasma with high bootstrap-current fraction fBS and high normalized beta. Development in diagnostic application to control of such advanced tokamak plasma is in progress worldwide, which will be discussed in this talk. For example, plasmas with a fraction of DEMO-relevant fBS of 70% have been sustained for 8s in JT-60 by real-time control of toroidal plasma flow based on the current profile measurement by which moderate relaxation of pressure gradient is induced, resulting into avoidance of collapse triggered at integer q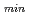 surfaces. In this experiment, change in the q value as a response to the pressure-gradient control was found to become big in the high fBS regime. Issues on (1) application of the present-day control methods to DEMO with self-heating, and (2) limitation of port space for the advanced control to keep a sufficient tritium-breeding ratio are also addressed.
surfaces. In this experiment, change in the q value as a response to the pressure-gradient control was found to become big in the high fBS regime. Issues on (1) application of the present-day control methods to DEMO with self-heating, and (2) limitation of port space for the advanced control to keep a sufficient tritium-breeding ratio are also addressed.
Kikuchi, Mitsuru
no journal, ,
This talk deals with so-called Broader Approach program between Japan and EURATOM, which includes IFMIF/EVEDA, IFERC and Satellite Tokamak Programs. This talk will summarize the overview of the Broader Approach program and will specifically address mission and scientific contents of JT-60SA program. The IFMIF/EVEDA program includes establishment of the engineering design of IFMIF. The IFERC (International Fusion Energy Research Center) program includes activities of DEMO Design Research and Development Coordination Center, Computer Simulation Center, and the ITER Remote Experimentation Center. The Satellite Tokamak Program includes participation in the upgrade of the JT-60U to the advanced superconducting tokamak, JT-60SA, and the participation in its exploitation, to support the exploitation of ITER and research towards DEMO by addressing key physics issues for ITER and DEMO. In this talk, details of diagnostics system will be given to fulfill the mission of the device.
Ishikawa, Masao; Kondoh, Takashi; Nishitani, Takeo; Kusama, Yoshinori
no journal, ,
The effects of the branch pipe and streaming neutrons to the responses of the MFCs are investigated by MCNP version 5. Results indicate the linear combination of total responses of MFCs at the lower and upper outboard positions is insensitive to the changes in the position of the plasma while the ratio of streaming neutrons at the upper outboard position is higher than that detected at the lower outboard position. It was found that the branch pipe reads to significant increase in the MFC response rate. The increase in the MFC response is caused by the slowing down of the neutrons due to the cooling water. One possible solution to reduce the effect is to cover the MFC with a material that absorbs thermal neutrons such as cadmium. The ways in which the absorbent material may affect MFC response is analyzed through neutron transport calculation. Results indicate that the increase in the MFC response can be reduced to 10 % through cadmium coating.