Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kimura, Atsushi; Kondo, Takafumi*; Yang, J.*; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Yoshida, Yoichi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Iwamatsu, Kazuhiro; Sugo, Yumi; Kurashima, Satoshi; Katsumura, Yosuke
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Rokita, B.*; Ulanski, P.*; Hiroki, Akihiro; Rosiak, J. M.*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 radiation on carbon steel corrosion in compacted bentonite
radiation on carbon steel corrosion in compacted bentoniteTaniguchi, Naoki; Yamaguchi, Makoto; Naito, Morimasa; Tateishi, Tsuyoshi*
no journal, ,
Corrosion tests of carbon steel were performed to estimaste possible effect of groundwater radiolysis by  radiation from vitrified waste on corrosion rate of carbon steel overpack in HLW repository. While average corrosion rates from weight loss increased by
radiation from vitrified waste on corrosion rate of carbon steel overpack in HLW repository. While average corrosion rates from weight loss increased by  radiation (dose rate : 30-50 Gy/h) in synthetic seawater, accompanying increased corrosion potential and cathodic current density possibly due to contribution of radiolytically generated oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide participated in cathodic reaction. On the other hand, no apparent effect of
radiation (dose rate : 30-50 Gy/h) in synthetic seawater, accompanying increased corrosion potential and cathodic current density possibly due to contribution of radiolytically generated oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide participated in cathodic reaction. On the other hand, no apparent effect of  radiation was observed for samples in compacted bentonite buffer. In addition, corrosion rates little affected by dry density of bentonite buffer. A plausible mechanism was considered to explain the absence of the
radiation was observed for samples in compacted bentonite buffer. In addition, corrosion rates little affected by dry density of bentonite buffer. A plausible mechanism was considered to explain the absence of the  radiation.
radiation.
Hiroki, Akihiro; Sato, Toshihiro*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Tamada, Masao
no journal, ,
Radiation modification of hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) hydrogels by blending polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) was investigated. The blend hydrogels constructed with HPC and PVA were prepared by electron beam irradiation to high concentrated aqueous solutions. Gel fraction of the blend hydrogels increased sharply up to 10 kGy, and leveled off at 50 kGy. It was found that PVA content caused a decrease in the gel fraction. Elongation at break of the blend hydrogels obtained at 50 kGy gradually increased with the PVA content beyond 0.4 wt%, and reached 125 % at 4 wt% of PVA, which was about 1.8 times larger than that of the pure HPC hydrogel. Therefore, the HPC hydrogels with desired mechanical properties were obtained by the combination of PVA blending with the radiation crosslinking technique.
 ion irradiation
ion irradiationIwamatsu, Kazuhiro; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Sugo, Yumi; Kurashima, Satoshi; Katsumura, Yosuke
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shimada, Akihiko; Seguchi, Tadao*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi; Oshima, Takeshi; Idesaki, Akira; Kudo, Hisaaki*
no journal, ,
Silicone rubber (SiR) is used widely in cable insulation in nuclear power plants. SiR sheets with different formulation were examined on the two points, specimen's thickness and thermal and radiation combined accelerated ageing. The 0.5 and 2 mm thick sheets were aged by thermal at up to 235 C and
C and  Co
Co  rays radiation with 1 kGy/h up to 800 kGy. The degradation was measured by tensile testing and gel fraction and swelling experiments. For check the distribution of degradation in depth of sheet, the 2 mm sheet sample was sliced by 0.3 mm thickness after ageing. The results indicated that the degradation progressed uniformly throughout the 2 mm thick sheet. For the ageing combination, the degradation by three different combinations was examined, that is, (a) simultaneous ageing, (b) thermal and radiation sequential ageing, and (c) radiation and thermal reversed sequential ageing. Elongation at break indicated that the order of degradation mild to severe was reverse sequential, sequential, simultaneous ageing. The study was supported by Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency (NISA), Japanese Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI).
rays radiation with 1 kGy/h up to 800 kGy. The degradation was measured by tensile testing and gel fraction and swelling experiments. For check the distribution of degradation in depth of sheet, the 2 mm sheet sample was sliced by 0.3 mm thickness after ageing. The results indicated that the degradation progressed uniformly throughout the 2 mm thick sheet. For the ageing combination, the degradation by three different combinations was examined, that is, (a) simultaneous ageing, (b) thermal and radiation sequential ageing, and (c) radiation and thermal reversed sequential ageing. Elongation at break indicated that the order of degradation mild to severe was reverse sequential, sequential, simultaneous ageing. The study was supported by Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency (NISA), Japanese Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI).
Idesaki, Akira; Seguchi, Tadao*; Tamura, Kiyotoshi; Oshima, Takeshi; Shimada, Akihiko; Kudo, Hisaaki*
no journal, ,
The degradation of polyvinylchloride (PVC) used in cable insulation in nuclear power plant was investigated by accelerated thermal and radiation ageing. The sheets of PVC as same formulation as cables were subjected to thermal ageing at temperature range 100-135 C and/or to radiation ageing by
C and/or to radiation ageing by  Co
Co  -rays at a dose rate of 1 kGy/h in air. The degradation was evaluated by the tensile test and by the weight change. The relations between elongation at break and change of weight by loss of plasticizer were analyzed. At higher temperature, the plasticizer evaporates to cause the decrease of tensile properties. The study was supported by Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency (NISA), Japanese Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI).
-rays at a dose rate of 1 kGy/h in air. The degradation was evaluated by the tensile test and by the weight change. The relations between elongation at break and change of weight by loss of plasticizer were analyzed. At higher temperature, the plasticizer evaporates to cause the decrease of tensile properties. The study was supported by Nuclear and Industrial Safety Agency (NISA), Japanese Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI).
Oka, Toshitaka; Yokoya, Akinari; Fujii, Kentaro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tago, Takanori; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Kudo, Hisaaki*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Katsumura, Yosuke*
no journal, ,
Poly (L-lactic acid)(PLA) is a hard and transparent bioplastic and now widespread with a potential to replace the conventional petroleum-derived plastics. The PLA crosslinked to improve the thermal property by irradiating with triallyl isocyanurate (TAIC). The impact resistance, however, is nearly un-improved. To improve the above-mentioned two properties of PLA, we investigated a new combination method of blending of PLA with polyamide11 (PA11) having high impact resistance, which is produced from castor oil, and then crosslinking with TAIC by radiation. The crosslinking structures were formed in irradiated PLA/PA11 blends with TAIC. The gel content of PLA/PA11 blends increased with increasing the mixing ratio of PA11 and absorbed dose. At the dose of 100 kGy and more, the network was formed about 80% in the PLA / PA11 blends. The thermal properties of the blends were evaluated from the deformation at the melting-temperature (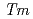 ) by the thermo-mechanical analysis. The blends with high gel contents (
) by the thermo-mechanical analysis. The blends with high gel contents ( 80%) demonstrated very little deformation above the
80%) demonstrated very little deformation above the 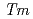 of PA11 around 185
of PA11 around 185 C. The improvement of the impact property was indicated by the Charpy impact testing. The blends (50/50wt%) irradiated with 100 kGy showed the higher impact resistance about 2.5 times of original PLA. Therefore, the applications of bioplastic will be expanded by the combination method of blending and radiation-induced crosslinking.
C. The improvement of the impact property was indicated by the Charpy impact testing. The blends (50/50wt%) irradiated with 100 kGy showed the higher impact resistance about 2.5 times of original PLA. Therefore, the applications of bioplastic will be expanded by the combination method of blending and radiation-induced crosslinking.
Kimura, Atsushi; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
 ray irradiation on deoxidation in aqueous solution by hydrazine
ray irradiation on deoxidation in aqueous solution by hydrazineMotooka, Takafumi; Sato, Tomonori; Yamamoto, Masahiro
no journal, ,
The effect of  ray irradiation on deoxidation in aqueous solution by hydrazine was investigated using pure water and artificial sea water at room temperature. We placed the solutions with small amount of hydrazine at
ray irradiation on deoxidation in aqueous solution by hydrazine was investigated using pure water and artificial sea water at room temperature. We placed the solutions with small amount of hydrazine at  ray irradiation field at dose rates of 0.3-7.5 kGy/h. The concentration of dissolved oxygen in the solutions was measured before and after
ray irradiation field at dose rates of 0.3-7.5 kGy/h. The concentration of dissolved oxygen in the solutions was measured before and after  ray irradiation. Concentration of dissolved oxygen was not decreased without
ray irradiation. Concentration of dissolved oxygen was not decreased without  ray irradiation, while concentration of dissolved oxygen was markedly decreased for one hour
ray irradiation, while concentration of dissolved oxygen was markedly decreased for one hour  ray irradiation, which is under detection limit at higher dose rate over 2 kGy/h. It is believed that the hydrazine addition to spent nuclear fuel pool water is effective as a method for decreasing concentration of dissolved oxygen.
ray irradiation, which is under detection limit at higher dose rate over 2 kGy/h. It is believed that the hydrazine addition to spent nuclear fuel pool water is effective as a method for decreasing concentration of dissolved oxygen.
Hanawa, Satoshi; Hata, Kuniki; Chimi, Yasuhiro; Nishiyama, Yutaka; Nakamura, Takehiko
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Kimura, Atsushi; Hiroki, Akihiro; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hirade, Tetsuya; Oka, Toshitaka
no journal, ,
Positronium(Ps) formation in insulating materials can be explained by spur reactions at the terminal spur of the positron track, so-called positron spur. Ps formation time is probably about 1ps and the yields of Ps formation give information of the reactions of the reactive species in the terminal spur, such as the free excess electrons. Ortho-Ps annihilation lifetime is about 1-5ns by the pick-off annihilation in condensed materials. Hence the o-Ps reactions with reactive species are quite possible. The most important reactions are, probably, ortho-Ps oxidation and spin conversion by reactive species, such as OH radical. We are introducing what we can study for water radiolysis by use of positron annihilation methods.
Katsumura, Yosuke*; Matsuura, Chihiro*; Yamashita, Shinichi; Hirade, Tetsuya; Iwamatsu, Kazuhiro; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
Relevant to the nuclear accident at Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Station, a radiolysis study of boiling water irradiated with Co-60  rays has been conducted. The evolution of hydrogen gas was clearly detected under boiling condition, while an extremely small amount of gas formation was found under the stable condition without boiling even at 97
rays has been conducted. The evolution of hydrogen gas was clearly detected under boiling condition, while an extremely small amount of gas formation was found under the stable condition without boiling even at 97 C. The G(H
C. The G(H ) of 0.37 was obtained under boiling condition. It was found that solution of 3.5% NaCl, similar to seawater, enhances the evolution, and the value of 0.7 was obtained. On the contrary, the O
) of 0.37 was obtained under boiling condition. It was found that solution of 3.5% NaCl, similar to seawater, enhances the evolution, and the value of 0.7 was obtained. On the contrary, the O gas formation was much lower than that of H
gas formation was much lower than that of H , suggesting the formed H
, suggesting the formed H O
O is not decomposed and remained in liquid. In addition, it was found that the evolved hydrogen is distributed selectively at the inner surface of the container under boiling condition. Gas injection experiments were also done without irradiation to clarify the behavior of hydrogen in the container.
is not decomposed and remained in liquid. In addition, it was found that the evolved hydrogen is distributed selectively at the inner surface of the container under boiling condition. Gas injection experiments were also done without irradiation to clarify the behavior of hydrogen in the container.
Yamashita, Shinichi; Hiroki, Akihiro; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Murakami, Takeshi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
no journal, ,
A new polymer gel dosimeter was developed to overcome weakness of earlier polymer gel dosimeters. Hydroxyethyl 2-methacrylate (HEMA) and polyethylene glycol ester dimethacrylate (9G) were less toxic constituents, which polymerize with irradiations. One of cellulose derivatives, hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC), was crosslinked by irradiations of electron beam and used as a gel matrix, which doesn't soften with increasing temperature. Hydrogel of HPC is very transparent, so light scattering and absorption of products of radiation-induced polymerization are easily observable. As a result of irradiation, white turbidity was observed inside the gel at around 1-2 Gy. Increasing behavior of white turbidity with irradiation depended on composition of constituent monomers. White turbidity appears at rather lower dose and its increase saturates at around 10 Gy of 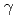 -irradiation when 9G is predominant. On the other hand, it becomes stronger even beyond 10 Gy when HEMA is predominant. In order to quantify the degree of white turbidity, haze measurement and UV-vis absorption spectrometry were conducted. In addition, white turbidity evolution was also confirmed after irradiations of therapeutic C ion beam although degree of white turbidity was less clear than that observed after
-irradiation when 9G is predominant. On the other hand, it becomes stronger even beyond 10 Gy when HEMA is predominant. In order to quantify the degree of white turbidity, haze measurement and UV-vis absorption spectrometry were conducted. In addition, white turbidity evolution was also confirmed after irradiations of therapeutic C ion beam although degree of white turbidity was less clear than that observed after  Co
Co 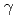 -irradiation.
-irradiation.
 produced in water radiolysis with
produced in water radiolysis with  Co
Co 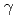 -rays and C ion beams
-rays and C ion beamsYamashita, Shinichi; Katsumura, Yosuke; Murakami, Takeshi*
no journal, ,
Main initial products of water radiolysis are e
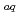 and
and  OH, which go through intraspur/track reactions in the time regime from ps to
OH, which go through intraspur/track reactions in the time regime from ps to 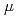 s, leading to production of H
s, leading to production of H O
O and H
and H . Among the main products, only H
. Among the main products, only H is not soluble in water and difficult to be accurately quantified. H
is not soluble in water and difficult to be accurately quantified. H also tends to leak even from a very small crevice where other gases do not leak. It is necessary to pay attentions to leakage and equilibrium between liquid-gas phases when ones want to accurately quantify H
also tends to leak even from a very small crevice where other gases do not leak. It is necessary to pay attentions to leakage and equilibrium between liquid-gas phases when ones want to accurately quantify H . Therefore, an online analysis apparatus of gaseous products arising from liquid samples has been developed to measure H
. Therefore, an online analysis apparatus of gaseous products arising from liquid samples has been developed to measure H production from water. In this work, at first accuracy and sensitivity of the apparatus were improved, and then, H
production from water. In this work, at first accuracy and sensitivity of the apparatus were improved, and then, H yields were measured as a function of concentration of the nitrate anion, which is a scavenger not only for e
yields were measured as a function of concentration of the nitrate anion, which is a scavenger not only for e
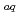 but also for the pre-solvated electron (e
but also for the pre-solvated electron (e
 ). Figure shows G(H
). Figure shows G(H ) measured in this work in comparison with reported values. Well-established primary G value for
) measured in this work in comparison with reported values. Well-established primary G value for  Co
Co 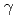 -irradiation, 0.46 (100 eV)
-irradiation, 0.46 (100 eV) , is obtained at low NO
, is obtained at low NO
 concentrations. Our data with
concentrations. Our data with  Co
Co 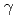 -irradiation were in good agreement with the reported values. In the cases of C ion irradiations G(H
-irradiation were in good agreement with the reported values. In the cases of C ion irradiations G(H ) values increased with increasing LET due to increasing significance of intratrack reactions. Further discussion on H
) values increased with increasing LET due to increasing significance of intratrack reactions. Further discussion on H production in fast process before 1 ps necessitate measurements of G(H
production in fast process before 1 ps necessitate measurements of G(H ) at other NO
) at other NO
 concentrations and with the usage of other scavengers of e
concentrations and with the usage of other scavengers of e
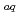 and e
and e
 .
.
Hiroki, Akihiro; Sato, Toshihiro*; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Tamada, Masao
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English