Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshida, Maiko; Kamada, Yutaka; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Urano, Hajime; Oyama, Naoyuki; Matsunaga, Go; JT-60 Team
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 3, p.S1007_1 - S1007_8, 2008/08
Toroidal rotation velocity profile plays essential roles in determining confinement and MHD stability at a high pressure in magnetic confined plasmas. Therefore, the critical importance of understanding the physical mechanisms determining the 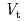 , and controlling
, and controlling 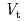 has recently been recognized. In JT-60U, the mechanisms of
has recently been recognized. In JT-60U, the mechanisms of 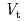 profile for L-mode, H-mode and ITB plasmas are investigated using the perturbative and non-perturbative experiments. The main conclusions are that the elements determining the
profile for L-mode, H-mode and ITB plasmas are investigated using the perturbative and non-perturbative experiments. The main conclusions are that the elements determining the 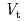 profile, i.e. the momentum transport, the external momentum input, and the intrinsic rotation (the rotation driven by plasma itself) have been identified, and the roles of these elements on
profile, i.e. the momentum transport, the external momentum input, and the intrinsic rotation (the rotation driven by plasma itself) have been identified, and the roles of these elements on 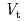 profile are also found.
profile are also found.
Tanaka, Kenji*; Michael, C.*; Vyacheslavov, L. N.*; Yokoyama, Masayuki*; Murakami, Sadayoshi*; Wakasa, Arimitsu*; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Muraoka, Katsunori*; Kawahata, Kazuo*; Tokuzawa, Tokihiko*; et al.
Plasma and Fusion Research (Internet), 3, p.S1069_1 - S1069_7, 2008/08
Density profiles in LHD were measured and particle transport coefficients were estimated from density modulation experiments in LHD. The dataset of different magnetic axis, toroidal magnetic filed and heating power provided data set of widely scanned neoclassical transport. At minimized neoclassical transport configuration (
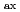 = 3.5 m,
= 3.5 m, 
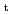 = 2.8 T) showed peaked density profile. Its peaking factor increased gradually with decrease of collisional frequency. This is a similar result observed in JT-60U. At other configuration, peaking factor reduced with decrease of collsional frequency. Data set showed that larger contribution of neoclassical transport produced hollowed density profile. Comparison between neoclassical and estimated particle diffusivity showed different minimum condition. Clear difference of spatial profile of turbulence was observed between hollowed and peaked density profiles. Major part of fluctuation existed in the unstable region of ion temperature gradient mode.
= 2.8 T) showed peaked density profile. Its peaking factor increased gradually with decrease of collisional frequency. This is a similar result observed in JT-60U. At other configuration, peaking factor reduced with decrease of collsional frequency. Data set showed that larger contribution of neoclassical transport produced hollowed density profile. Comparison between neoclassical and estimated particle diffusivity showed different minimum condition. Clear difference of spatial profile of turbulence was observed between hollowed and peaked density profiles. Major part of fluctuation existed in the unstable region of ion temperature gradient mode.
Asakura, Nobuyuki
no journal, ,
Fast (subsonic to sonic level) plasma flow along the magnetic field lines has been recently recognized in scrape-off layer (SOL) of many tokamaks. Understanding of the driving mechanisms was progressed by development of flow measurements and simulations. Fast plasma flow from low-field-side SOL to high-field-side divertor is produced by increase in plasma pressure at low-field-side SOL mainly due to asymmetrical diffusion and by plasma drift effects in a torus geometry. Plasma flow is accelerated to sonic level in the divertor, accompanied with the plasma detachment. At the same time, large radiation peak stays near lower X-point during the MARFE. This position change to the top of the main plasma for the reversed toroidal field, thus the plasma drifts also influences the MARFE.