Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suzuki, Takahiro; Kim, J. H.*; Na, Y. S.*; Ide, Shunsuke; Mueller, D.*; Miyata, Yoshiaki; Kim, H. S.*; Hahn, S. H.*; Yoon, S. W.*; Kim, W. C.*
no journal, ,
We have started advanced operation scenario development in KSTAR in this campaign, which opens up a new research area directly connecting to ITER and DEMO. The advanced scenario, which has higher performance than the standard H-mode, typically possesses lower internal inductance li (safety factor q above unity without sawtooth). In conventional KSTAR operation scenarios, divertor configuration with high elongation is realized after or near the end of Ip ramp-up, where sawtooth activity starts during the ramp-up before entering into the higher performance phase. Thus, we need a new KSTAR operation scenario without sawtooth during the Ip ramp-up and with lower li than unity. Our idea is to delay the inductive current penetration by simultaneous EC&NB heating application into the full-bore divertor plasma during the Ip ramp-up as early as possible. After the optimization, we have successfully established a start-up scenario without sawtooth throughout the Ip ramp-up. In a shot 7897, high 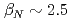 reaching an advanced scenario regime has been achieved in ELM-free H-mode (
reaching an advanced scenario regime has been achieved in ELM-free H-mode ( ) at
) at 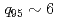 .
.
Na, Y. S.*; Suzuki, Takahiro; Ide, Shunsuke; Mueller, D.*; Kim, J. H.*; Miyata, Yoshiaki; Kim, S. H.*; Kim, H. S.*; Jeon, Y. M.*; Bae, Y. S.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Development of advanced scenarios, an important experimental goal for the KSTAR project, has just begun. Target plasmas were successfully produced using large bore plasma and early divertor formation which exhibit low internal inductance with low magnetic shear at the centre and no sawtooth instability. Auxilliary heating during the current rampup phase was employed to slow the inductive current diffusion to the centre of the plasma. With respect to hybrid scenario development, so-called "Ip-overshoot" method being used in JET is applied for tailoring magnetic shear at reduced plasma current for higher poloidal beta and bootstrap current fraction. The confinement characteristics of these scenarios are investigated. Transport modeling is performed self-consistently with an integrated simulation package incorporating plasma equilibrium, transport, heating and current drive. Firstly, the current rampup phase is simulated and its impact on the target q-profile is addressed. Secondly, energy confinement of flattop phases is discussed. In addition, the non-inductive current drive fraction including the bootstrap current fraction is calculated. Lastly, these scenarios are compared with advanced scenarios developed in other tokamak devices and future directions in achieving advanced regimes are discussed.
Miyata, Yoshiaki; Hahn, S.-H.*; Suzuki, Takahiro; Ide, Shunsuke
no journal, ,
The accurate plasma shape reconstruction is essential for plasma equilibrium control and analysis. Various methods to reconstruct a plasma shape have been developed for constructions of tokamak devices. A plasma shape has been reconstructed by the method of Cauchy condition surface (CCS) from the magnetic measurements in JT-60U. The CCS calculation can reconstruct the outermost magnetic surface, and calculate the quantities related to plasma shape such as the Shafranov lambda, the safety factor, and so on. It was found that the plasma shape reconstructed by CCS calculation agreed well with the measurements in KSTAR. CCS is robust at Ip ramp up/down even with small Ip. In this presentation, the result of first application of CCS to the KSTAR plasma is discussed.
Fukumoto, Masakatsu; Yoon, S. W.*; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Miyata, Yoshiaki; Kubo, Hirotaka
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English