Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kodama, Katsuaki; Honda, Takashi*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Shamoto, Shinichi; Otomo, Toshiya*
no journal, ,
Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Aizawa, Kazuya
no journal, ,
Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Tsuchida, Noriyuki*; Morooka, Satoshi; Aizawa, Kazuya
no journal, ,
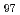 Zn
Zn Y
Y consisting of LPSO phase and
consisting of LPSO phase and  Mg phase
Mg phaseHarjo, S.; Aizawa, Kazuya; Gong, W.*; Kawasaki, Takuro
no journal, ,
Kawakita, Yukinobu; Matsuura, Masato*; Tominaga, Taiki*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Kobayashi, Makoto*; Nakagawa, Hiroshi
no journal, ,
The ToF back scattering spectrometer, DNA at BL02, MLF, J-PARC, is a tool for quasi-elastic and inelastic neutron scattering studies aiming at atomic and spin dynamics ranged from pico to nano sec in bio-molecules, softmatters and solid state materials such as ionic conductors including batteries and strongly-correlated electron system. High signal-to-noise ratio are achieved by Si analyzer mirrors back-coated with a Gd neutron absorber. DNA equips a pulse shaping chopper of max 300 Hz and Si111 analyzer mirrors which select the scattered neutrons only with 2.08 meV with the Bragg angle of 87.5 degree and cover a momentum transfer from 0.08 to 1.9 (1/A). Recently we start installation of Si311 analyzer mirrors too which select a scattered neutron with 7.64 meV and widen a momentum transfer range up to 3.79 (1/A). In this presentation, we introduce the spec of DNA including recent commissioning for Si311 analyzer mirrors and several applications to materials science.
 studied by neutron scattering and their relation with thermal conductivities
studied by neutron scattering and their relation with thermal conductivitiesKajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Murai, Naoki; Shamoto, Shinichi; Honda, Takashi*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Hata, Hiroto*; Eto, Takahiro*; Noda, Masaaki*; et al.
no journal, ,
 mimFeCl
mimFeCl
Kofu, Maiko; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Ueki, Takeshi*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Yamamuro, Osamu*
no journal, ,
Ionic liquids (ILs) have been in the spotlight due to their unique and interesting properties. It is remarkable that their physicochemical properties are controlled by varying cations and anions. Magnetic IL is an example. The first discovered magnetic IL C mimFeCl
mimFeCl is easily vitrified upon cooling and also crystallized by annealing. Interestingly, an antiferromagnetic transition occurs at 2.3 K in the crystalline state while spin-glass behavior is observed below 0.45 K (=
is easily vitrified upon cooling and also crystallized by annealing. Interestingly, an antiferromagnetic transition occurs at 2.3 K in the crystalline state while spin-glass behavior is observed below 0.45 K (= 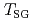 ) in the glassy state. Our inelastic neutron scattering experiments have demonstrated that the glassy C
) in the glassy state. Our inelastic neutron scattering experiments have demonstrated that the glassy C mimFeCl
mimFeCl exhibits a broad and non-dispersive excitation, while the crystal displays spin-wave excitations. The excitation spectrum in the glass state is scaled by the Bose population factor below
exhibits a broad and non-dispersive excitation, while the crystal displays spin-wave excitations. The excitation spectrum in the glass state is scaled by the Bose population factor below 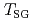 , which is highly reminiscent of "boson peak" commonly observed in structural glasses. We guess that, since there is no periodicity in structural glasses, magnons hardly propagate through magnetic medium and are localized. The localized magnetic excitations are suggestive of the formation of spin clusters.
, which is highly reminiscent of "boson peak" commonly observed in structural glasses. We guess that, since there is no periodicity in structural glasses, magnons hardly propagate through magnetic medium and are localized. The localized magnetic excitations are suggestive of the formation of spin clusters.
Higemoto, Wataru; Okazawa, Takeshi*; Oda, Yuto; Miyazaki, Itsuki*; Ito, Takashi; Yoshida, Yoshiyuki*
no journal, ,
Watanabe, Masao; Nojiri, Hiroyuki*; Kihara, Takumi*
no journal, ,
Superconducting DC magnet up to 17 Tesla has developed for neutron scattering experiments. Although the sample environment team in the MLF have several DC superconducting magnets up to 7 Tesla as a sample environment apparatus, some users have requested the preparation of higher field magnets. However, another magnet technology is needed to generate higher than 20 Tesla. However, it is difficult to construct such a large system in the MLF from the point of view of construction space. It is practical to employ a pulsed magnetic field as it enables operation of smaller energy as well as downsizing of the instruments. Therefore, we have been newly developed a compact and transportable pulsed magnet system up to 30 Tesla.
 K
K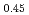 Li
Li )NbO
)NbO -based system with tetragonal structure
-based system with tetragonal structureYoneda, Yasuhiro; Takuwa, Chihaya*
no journal, ,
 O
O ceramic powder from high-energy X-ray diffraction
ceramic powder from high-energy X-ray diffractionYoneda, Yasuhiro; Fu, D.*
no journal, ,
 simulated with positively charged muons
simulated with positively charged muonsIto, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Koda, Akihiro*; Shimomura, Koichiro*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English