Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Tanno, Takashi; Takeuchi, Masayuki; Otsuka, Satoshi; Kaito, Takeji
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 494, p.219 - 226, 2017/10
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:84.83(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) steel cladding tubes have been developed for fast reactors. 9 chromium ODS and 11Cr-ODS tempered martensitic steels are prioritized for the candidate material in research being carried out at JAEA. In this work, fundamental immersion tests and electro-chemical tests of 9 to 12Cr-ODS steels were systematically conducted in various nitric acid solutions at 95 C. The corrosion rate exponentially decreased with effective solute chromium concentration (Cr
C. The corrosion rate exponentially decreased with effective solute chromium concentration (Cr ) and nitric acid concentration. Addition of oxidizing ions also suppressed the corrosion rate. According to polarization curves and surface observations in this work, the combination of low Cr
) and nitric acid concentration. Addition of oxidizing ions also suppressed the corrosion rate. According to polarization curves and surface observations in this work, the combination of low Cr and dilute nitric acid could not prevent the active dissolution at the beginning of immersion, and the corrosion rate was high. In comparison, higher Cr
and dilute nitric acid could not prevent the active dissolution at the beginning of immersion, and the corrosion rate was high. In comparison, higher Cr , concentrated nitric acid and addition of oxidizing ions helped to prevent the active dissolution, and suppressed the corrosion rate.
, concentrated nitric acid and addition of oxidizing ions helped to prevent the active dissolution, and suppressed the corrosion rate.
Yano, Yasuhide; Tanno, Takashi; Oka, Hiroshi; Otsuka, Satoshi; Inoue, Toshihiko; Kato, Shoichi; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Kaito, Takeji; Ukai, Shigeharu*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 487, p.229 - 237, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:37 Percentile:96.77(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ultra-high temperature ring tensile tests were carried out to investigate the tensile behavior of oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) steel claddings and wrapper materials under severe accident conditions; temperatures ranged from room temperature to 1400 C which is near the melting point of core materials. The experimental results showed that tensile strength of 9Cr-ODS steel claddings was highest in the core materials at the ultra-high temperatures between 900 and 1200
C which is near the melting point of core materials. The experimental results showed that tensile strength of 9Cr-ODS steel claddings was highest in the core materials at the ultra-high temperatures between 900 and 1200 C, but that there was significant degradation in tensile strength of 9Cr-ODS steel claddings above 1200
C, but that there was significant degradation in tensile strength of 9Cr-ODS steel claddings above 1200 C. This degradation was attributed to grain boundary sliding deformation with
C. This degradation was attributed to grain boundary sliding deformation with  /
/ transformation, which was associated with reduced ductility. On the other hand, tensile strength of recrystallized 12Cr-ODS and FeCrAl-ODS steel claddings retained its high value above 1200
transformation, which was associated with reduced ductility. On the other hand, tensile strength of recrystallized 12Cr-ODS and FeCrAl-ODS steel claddings retained its high value above 1200  C unlike the other tested materials. Present study includes the result of "R&D of ODS ferritic steel fuel cladding for maintaining fuel integrity at the high temperature accident condition" entrusted to Hokkaido University by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (MEXT).
C unlike the other tested materials. Present study includes the result of "R&D of ODS ferritic steel fuel cladding for maintaining fuel integrity at the high temperature accident condition" entrusted to Hokkaido University by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (MEXT).
Akashi, Masatoshi; Morimoto, Kyoichi
no journal, ,

Watanabe, Masashi; Kato, Masato; Sunaoshi, Takeo*
no journal, ,
Diffusion phenomena of oxygen in mixed oxide fuel are especially important in understanding fuel behaviour. The reason is that sintering, evaporation, oxygen redistribution and behaviour of fission products are essentially involved in the oxygen diffusion process. Thus, the purpose of this work is to precisely measure the oxygen self and chemical diffusion coefficients in (U, Pu)O at high temperatures and to evaluate the relationship between both coefficients.
at high temperatures and to evaluate the relationship between both coefficients.
Mitsui, Seiichiro
no journal, ,
In order to develop robust performance assessment models on waste glass corrosion, JAEA has been conducting experimental studies and has been preparing an information basis regarding the near-field processes under disposal conditions. To determine silicon migration parameters such as distribution coefficient of Si in buffer material, we conducted percolation type migration experiments and batch sorption experiments using Si-32 as radioactive tracer for Kunigel-V1 as a joint project with SCKCEN. The values of the apparent diffusion coefficient and the distribution coefficient of dissolved silica in Kunigel-V1 are estimated to be 3.4  10
10
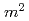 /s and 0.5
/s and 0.5 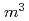 /kg on average, respectively. The preparation of the information basis has been conducted as a part of joint project with NUMO. Based on the information basis, we developed a preliminary model of the glass corrosion considering the near-field processes and conducted sensitivity analyses for selected processes.
/kg on average, respectively. The preparation of the information basis has been conducted as a part of joint project with NUMO. Based on the information basis, we developed a preliminary model of the glass corrosion considering the near-field processes and conducted sensitivity analyses for selected processes.
Mihara, Takeshi; Udagawa, Yutaka; Amaya, Masaki
no journal, ,
Kato, Shoichi; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Yano, Yasuhide; Tanno, Takashi; Otsuka, Satoshi; Oka, Hiroshi; Inoue, Toshihiko; Kaito, Takeji; Ukai, Shigeharu*; Kimura, Akihiko*; et al.
no journal, ,
Oxide dispersion strengthened (ODS) steel is a prime candidate for cladding tubes of Japan Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (JSFR) due to the high temperature and radiation resistances. One of the safety design of JSFR for Design Extension Condition (DEC) is the control of severe plant conditions, including prevention of severe accidents and mitigation of severe-accident consequences. Therefore, it is necessary to acquire the mechanical properties at ultra-high temperature conditions for core materials to evaluate safety design. There are, however, no data for ODS claddings at ultra-high temperature condition for the reflecting to the design criteria. In this study, creep rupture tests of 9Cr-ODS, 12Cr-ODS and FeCrAl-ODS steel claddings have been done at elevated temperatures, and the effect of minor elements such as Al, Zr and O on the mechanical strength and the creep rupture curve for the safety design were evaluated. The effect of minor elements was estimated based on the data at 700 C and 1000
C and 1000 C. As the results, it was confirmed that the addition of Zr had an effect on the improvement of creep strength at elevated temperature for the FeCrAl-ODS steel claddings.
C. As the results, it was confirmed that the addition of Zr had an effect on the improvement of creep strength at elevated temperature for the FeCrAl-ODS steel claddings.
Nakayoshi, Akira; Suzuki, Seiya; Okamura, Nobuo; Watanabe, Masayuki; Koizumi, Kenji
no journal, ,
Treatment policies for debris from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant is not decided, however, any policies may include medium and long term storages of debris. Dry storages may be desirable in terms of costs and handlings, but it is necessary to assess generating hydrogen during storages due to radiolysis of accompanied water with debris before debris storages. Al O
O , SiO
, SiO , ZrO
, ZrO , UO
, UO and cement paste pellets as simulated debris were prepared, which have some porosities and pore. Weight changes of wet samples were measured at various drying temperatures (200, 300, and 1000
and cement paste pellets as simulated debris were prepared, which have some porosities and pore. Weight changes of wet samples were measured at various drying temperatures (200, 300, and 1000  C) using a thermal gravity measurement, under helium gas flow (50 cc/min) or reduced pressure conditions (reducing pressure rate: 200 Pa in 30 min.). From the results, drying curves were evaluated.
C) using a thermal gravity measurement, under helium gas flow (50 cc/min) or reduced pressure conditions (reducing pressure rate: 200 Pa in 30 min.). From the results, drying curves were evaluated.
Ishikawa, Norito
no journal, ,
Radiation damage due to irradiation with swift heavy ions (SHI) with the energy above 1 MeV/u has many different features compared to that due to irradiation with electrons and neutrons. One of the well-known phenomena related to SHI irradiation is formation of ion tracks. An ion track is a cylindrical region where the material near ion-path is locally modified in nanometric scale. Ion tracks are of great interest in a wide variety of research fields including nuclear materials science, physics of ion-solid interaction, nanotechnology, archaeology and so on. Mechanism of ion track formation in inorganic materials has always been one of the central and intriguing subjects in the SHI research community. It is still challenging to untangle the related problems. In this plenary talk, I would like to concentrate on the vital part of the recent advancement so that the audience can understand the logical pathway of the latest research works.
Suzuki, Eriko; Di Lemma, F. G.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Osaka, Masahiko
no journal, ,
In order to clarify the re-vaporization behavior of cesium (Cs) chemisorbed compounds which formed onto reactor structural materials during Severe Accident (SA), Cs chemisorbed samples were reheated at 1000 C and then microstructural analysis of the chemisorbed samples was conducted. In the case of stainless steel containing Mo, Cs-Mo-O compounds were formed on surface, together with major Cs-Fe-Si-O compounds, and re-vaporized easier than Cs-Fe-Si-O compounds at 1000
C and then microstructural analysis of the chemisorbed samples was conducted. In the case of stainless steel containing Mo, Cs-Mo-O compounds were formed on surface, together with major Cs-Fe-Si-O compounds, and re-vaporized easier than Cs-Fe-Si-O compounds at 1000 C.
C.
Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko
no journal, ,
Actinide dioxides, such as UO and PuO
and PuO , are the main components of nuclear fuel. However, the determination of their properties through experiments is not easy owing to limitations associated with their handling. In such cases, numerical simulations are effective for the evaluation of the properties of actinide dioxides. So far, we have evaluated thermal properties of actinide dioxides based on the ground-state calculation using first-principles density functional theory (DFT) and successfully reproduced the observed quantities such as heat capacity. In this paper, we apply this calculation method to thermal-conductivity estimation. The calculated thermal conductivities agree well with measurements between room temperature and 1800 K. In conclusion, our calculation method is available to evaluate thermal conductivity of actinide dioxides and can contribute the development of nuclear fuels.
, are the main components of nuclear fuel. However, the determination of their properties through experiments is not easy owing to limitations associated with their handling. In such cases, numerical simulations are effective for the evaluation of the properties of actinide dioxides. So far, we have evaluated thermal properties of actinide dioxides based on the ground-state calculation using first-principles density functional theory (DFT) and successfully reproduced the observed quantities such as heat capacity. In this paper, we apply this calculation method to thermal-conductivity estimation. The calculated thermal conductivities agree well with measurements between room temperature and 1800 K. In conclusion, our calculation method is available to evaluate thermal conductivity of actinide dioxides and can contribute the development of nuclear fuels.
Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Yano, Kimihiko; Ogino, Hideki; Matsunaga, Junji*
no journal, ,
Mechanical properties (micro-hardness, elastic modulus, and fracture toughness) of fuel debris are essential information for defueling work in the Fukushima Daiichi NPP. The Urania-Zirconia solid solution, (U,Zr)O , is expected to be separated into cubic phase with low Zr contents and tetragonal or monoclinic phase with high Zr contents during cooling process. In this study, the properties of tetragonal and monoclinic phase are investigated. The (U
, is expected to be separated into cubic phase with low Zr contents and tetragonal or monoclinic phase with high Zr contents during cooling process. In this study, the properties of tetragonal and monoclinic phase are investigated. The (U Zr
Zr )O
)O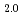 samples (x=0.85 for tetragonal phase and 0.95 for monoclinic phase) were prepared by sintering the compacted mixture of UO
samples (x=0.85 for tetragonal phase and 0.95 for monoclinic phase) were prepared by sintering the compacted mixture of UO and ZrO
and ZrO powders at maximum 2673 K. The micro-hardness of samples was lower than what has been expected from trend of cubic phase. The elastic modulus was comparable with cubic phase. The fracture toughness of the tetragonal phase was higher than the other two phases. The stress-induced martensitic transformation around the indent is expected to increase the fracture toughness.
powders at maximum 2673 K. The micro-hardness of samples was lower than what has been expected from trend of cubic phase. The elastic modulus was comparable with cubic phase. The fracture toughness of the tetragonal phase was higher than the other two phases. The stress-induced martensitic transformation around the indent is expected to increase the fracture toughness.
Sudo, Ayako; Takano, Masahide; Onozawa, Atsushi
no journal, ,
To characterize the reaction layers around core melt/concrete interface, MCCI experiments by using a light-concentrating technique was performed. As the main constituents of the core-melt, powder mixtures of ZrO , Zr, (U,Zr)O
, Zr, (U,Zr)O , stainless steel (SS), and B
, stainless steel (SS), and B C with various compositions were compacted into tablets. The tablet was placed on a concrete. Light from a lamp was concentrated on the tablet, and the vertical cross-section of the solidified sample was determined by XRD and SEM/EDX. The analyses identified 4 layers from top to bottom; (a) as-melted (U,Zr)O
C with various compositions were compacted into tablets. The tablet was placed on a concrete. Light from a lamp was concentrated on the tablet, and the vertical cross-section of the solidified sample was determined by XRD and SEM/EDX. The analyses identified 4 layers from top to bottom; (a) as-melted (U,Zr)O particles and silicate glass with U, (b) the silicate glass with U, (c) imperfectly melted concrete, and (d) dehydrated concrete. Unoxidized metal particles (Fe-Ni-Cr) also precipitated. Gd
particles and silicate glass with U, (b) the silicate glass with U, (c) imperfectly melted concrete, and (d) dehydrated concrete. Unoxidized metal particles (Fe-Ni-Cr) also precipitated. Gd O
O , Mo-Ru-Rh-Pd alloy, and sea salt were also added in the tablet. In this case Gd was included in both (U,Zr)O
, Mo-Ru-Rh-Pd alloy, and sea salt were also added in the tablet. In this case Gd was included in both (U,Zr)O and silicate glass, Mo and the platinum group elements formed alloys with Fe-Ni-Cr, and S originating from sea salt resulted in precipitation of FeS-type sulfide in the alloy.
and silicate glass, Mo and the platinum group elements formed alloys with Fe-Ni-Cr, and S originating from sea salt resulted in precipitation of FeS-type sulfide in the alloy.
Miwa, Shuhei; Shinada, Masanori; Osaka, Masahiko; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Maruyama, Yu
no journal, ,
In order to acquire the data on fission product chemical behavior during transport in a reactor for the improvement of source term evaluation method, we performed the chemical reaction tests of cesium (Cs) and iodine (I) deposits and boron oxide (B O
O ) vapor/aerosol using the apparatus which can simulate temperature conditions of reactor coolant system under a sever accident. The volatile I compounds were formed by the reaction of B
) vapor/aerosol using the apparatus which can simulate temperature conditions of reactor coolant system under a sever accident. The volatile I compounds were formed by the reaction of B O
O vapor/aerosol and deposit, and significant amount of I was revaporized from the deposit.
vapor/aerosol and deposit, and significant amount of I was revaporized from the deposit.
Nagase, Fumihisa
no journal, ,
JAEA conducts R&D to support the decommissioning at the Fukushima Daiichi NPS and to contribute improvement of the LWR safety in the frame of domestic and international collaborations as well as the own projects. The R&D mostly focuses on the phenomena in BWRs and covers various issues related to materials degradation in severe accidents. In parallel, JAEA has the research activity to establish technical basis for practical use of accident tolerant fuel (ATF) components in existing LWRs. The preliminary computer code analyses showed necessary material data and subjects to design the ATF components.
Takano, Masahide; Onozawa, Atsushi; Sudo, Ayako
no journal, ,
To understand the characteristics of MCCI products in Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, the simulated MCCI products in laboratory scale were prepared by arc melting of compacted powder mixtures of core materials and concrete. Stainless steel, boron carbide, metallic zirconium, (U,Zr)O , GdO
, GdO , and platinum group elements were selected as the core materials. Phases, morphology, and micro hardness were analyzed on cross-section of the solidified specimens. The specimens consisted of oxide part (MO
, and platinum group elements were selected as the core materials. Phases, morphology, and micro hardness were analyzed on cross-section of the solidified specimens. The specimens consisted of oxide part (MO corium and silicate glass or Al-Ca-O) and metallic part (alloys and borides). The phase relationships in the MCCI products were found to be dominated by the initial concrete/Zr mixing ratio, because the dehydration of concrete is the main oxidation factor and the metallic zirconium acts as a strong reductant. Micro hardness of main phases are 7 GPa for silicate glass, 13-15 GPa for (U,Zr,Gd,Ca)O
corium and silicate glass or Al-Ca-O) and metallic part (alloys and borides). The phase relationships in the MCCI products were found to be dominated by the initial concrete/Zr mixing ratio, because the dehydration of concrete is the main oxidation factor and the metallic zirconium acts as a strong reductant. Micro hardness of main phases are 7 GPa for silicate glass, 13-15 GPa for (U,Zr,Gd,Ca)O corium, and 25 GPa for ZrB
corium, and 25 GPa for ZrB and ferrous borides, respectively.
and ferrous borides, respectively.
Okubo, Nariaki; Saito, Shigeru; Obayashi, Hironari; Sasa, Toshinobu
no journal, ,
In the ADS plant, the target window material will be heavily irradiated under the severe condition. Degradation of the mechanical properties, size change of the components and erosion/corrosion of the material surface after irradiation in the LBE flow should be suppressed within a range permissible for the ADS system design. Material irradiation experiments in the transmutation experimental facility (TEF-T), which is planned in JAEA, will realize the first ADS plant in near future. Overview of the material irradiation and PIE plan by using TEF-T including R&D of LBE corrosion test loop and elemental key technology toward TEF-T and ADS will be shown in this presentation. In order to select candidate materials prior to TEF-T irradiation, triple ion irradiations of Fe, He and H ions were conducted for ferritic/martensitic steels, T91 in TIARA. The swelling behavior of T91 irradiated at temperature from 350 to 550 C will be also discussed.
C will be also discussed.
Sato, Takumi; Hayashi, Hirokazu; Nakamura, Hitoshi*; Omori, Takashi*
no journal, ,
In pyrochemical reprocessing of spent nitride fuel for transmutation of MA using ADS, actinides are recovered in a liquid cadmium cathode and converted to nitrides again by heating in N gas stream. Nitridation of actinide-Cd alloys has been achieved on 1 to 10 g-Cd scale. However, experimental data of a larger scale test is required to design an industrial scale equipment. Furthermore, understanding the nitridation behaviour of Zr in Cd is necessary to determine the process condition because Zr is recovered in a liquid cadmium cathode with actinides at high current density in the electrorefining process. In the present study, the apparatus for 100 g-Cd scale tests is developed and the nitride formation reactions of Dy-Cd and Zr-Cd alloys have been studied in the temperature range of 973-1073 K in N
gas stream. Nitridation of actinide-Cd alloys has been achieved on 1 to 10 g-Cd scale. However, experimental data of a larger scale test is required to design an industrial scale equipment. Furthermore, understanding the nitridation behaviour of Zr in Cd is necessary to determine the process condition because Zr is recovered in a liquid cadmium cathode with actinides at high current density in the electrorefining process. In the present study, the apparatus for 100 g-Cd scale tests is developed and the nitride formation reactions of Dy-Cd and Zr-Cd alloys have been studied in the temperature range of 973-1073 K in N gas stream. Dy was used as a surrogate material of MAs and Pu. Most of Dy and Zr in Cd were converted to nitride at 1073 and 973 K, respectively.
gas stream. Dy was used as a surrogate material of MAs and Pu. Most of Dy and Zr in Cd were converted to nitride at 1073 and 973 K, respectively.
Inoue, Toshihiko; Sekio, Yoshihiro; Otsuka, Satoshi; Yano, Yasuhide; Tanno, Takashi; Oka, Hiroshi; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Kaito, Takeji; Torimaru, Tadahiko*; Hayashi, Shigenari*; et al.
no journal, ,
In order to evaluate the strength and deformation in severe accident, the transient burst tests were carried out with various heating rates (from 0.1 to 10 K/s) and hoop stresses (from 50 to 200 MPa) to provide more evaluation data. The test materials were core materials in fast reactors, 9-18Cr-ODS and accident tolerant fuel cladding tube in the light water reactors, FeCrAl-added ODS ferritic steels. Result, the rupture strength dropped with increasing hoop stress and decreasing heating rate. The burst strength of Al-added ODS steels was lower than other ODS steels, Al and Zr-added ODS steels show good transient burst strength.