Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Seki, Yohji; Hirose, Takanori; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Enoeda, Mikio
Proceedings of Plasma Conference 2011 (PLASMA 2011) (CD-ROM), 2 Pages, 2011/11
Development of test blanket module (TBM) with a water cooled solid breeder is being performed as the primary candidate of ITER-TBM of Japan. Prior to the installation of each TBM, it is necessary to develop the capability of the prediction analyses of all essential functions of the blanket to validate the analyses tools by the TBM. Especially the prediction tool of tritium concentration in the blanket system is one of the most important issues to control tritium recovery. From this view point, this paper discusses the flow phenomena and the tritium transport of the helium purge gas in the pebble bed. By prediction of purge gas flow using a numerical simulation, the result indicates tritium concentration depended on the position of the breeder layer. Namely, the large concentration still remains near the wall with approaching to an outlet.
Kondo, Hiroo; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Iuchi, Hiroshi; Kanemura, Takuji; Ida, Mizuho; Watanabe, Kazuyoshi; Horiike, Hiroshi*; Yamaoka, Nobuo*; Matsushita, Izuru*; et al.
Proceedings of Plasma Conference 2011 (PLASMA 2011) (CD-ROM), 2 Pages, 2011/11
The EVEDA Li test loop (ELTL) successfully completed its construction and commissioning in the frame work of the IFMIF/EVEDA as one of the ITER-BA. The construction was started on Nov. 2009 in the O-arai site of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency and completed on the middle of Nov. 2010. In the commissioning conducted subsequently, the following tests were performed: (1) Li ingots installation into the ELTL, (2) Li charging and draining operation, (3) Li circulation tests. In a final phase of the circulation test, stable liquid Li flow at a velocity of 5 m/s was successfully achieved.
Miyato, Naoaki; Scott, B. D.*; Yagi, Masatoshi
Proceedings of Plasma Conference 2011 (PLASMA 2011) (CD-ROM), 2 Pages, 2011/11
Tsujimoto, Kazufumi
Proceedings of Plasma Conference 2011 (PLASMA 2011) (CD-ROM), 2 Pages, 2011/11
Neutron beam is used for a wide variety of scientific and engineering research, such as materials and life science, and industrial applications. There are three kinds of neutron sources: (1) isotopic neutron source, (2) reactor sources, and (3) accelerator-based neutron sources. Recently, high intensity spallation neutron sources with high energy proton accelerator became to offer similar capabilities to research reactors, as well as a few extra features. In Japan, the JSNS (Japan Spallation Neutron Source) was constructed and operated at J-PARC (Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex). Moreover, as future utilization of spallation neutron, research and development for accelerator-driven subcritical system have been performed.
Nishitani, Takeo; Tobita, Kenji; Ishikawa, Masao; Shinohara, Koji
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ishii, Yasutomo
no journal, ,
The presentation titled as Outline of the IFERC-CSC activity will be given at the symposium of Prospect of Simulation Research for BA IFERC-CSC in Plasma Conference 2011. In this talk, the outline of the IFERC-CSC, which will start operation at January 2012, like as the purpose, organization, the way for applying to use the CSC HPC and evaluation processes for applied projects, will be introduced to the scientific communities of plasma physics and nuclear fusion technology. This presentation will accelerate the domestic researchers to use the CSC-HPC in a positive manner.
Tanimoto, Tsuyoshi; Nishiuchi, Mamiko; Mishima, Yosuke*; Kikuyama, Kenshiro*; Morioka, Tomoya*; Morita, Kiyoshi*; Kanasaki, Masato; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Yogo, Akifumi; Ogura, Koichi; et al.
no journal, ,
Shiraishi, Junya; Aiba, Nobuyuki; Yagi, Masatoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sasaki, Akira
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Nishikino, Masaharu; Yamamoto, Minoru*; Hasegawa, Noboru; Tomita, Takuro*; Terakawa, Kota*; Minami, Yasuo*; Takei, Ryota*; Onishi, Ryo*; Ishino, Masahiko; Kaihori, Takeshi; et al.
no journal, ,
The X-ray reflective imaging using a soft X-ray laser was used to observe the early stage of the femtosecond laser ablation process on the platinum. The fluence dependence of the soft X-ray reflectivity is classified into three regions: (1) strongly excited, (2) moderately excited, and (3) weakly excited regions. In strongly excited region, the rapid reduction of the reflectivity due to the explosive evaporation in the ablation process of the material surface was observed. In the moderately excited region, the reflectivity reduction is far slower than that in the strongly excited region. The reflectivity reduction is seemed to be caused by the growth of surface roughness on the ablation front because of the formation of nano-bubbles in the irradiated material.
Kotaki, Hideyuki; Kando, Masaki; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Kawase, Keigo*; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Fukuda, Yuji; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Okada, Hajime; Daito, Izuru; Kameshima, Takashi*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyata, Yoshiaki; Suzuki, Takahiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Ide, Shunsuke; Urano, Hajime
no journal, ,
The plasma position and shape control is important issue in JT-60SA, ITER and future fusion reactor which has a small number of coils. In order to study the plasma position and shape control, we are developing a simulator which consists of an equilibrium solver and an "isoflux" controller. The controller controls poloidal field (PF) coil currents so as to keep the poloidal flux is equal at all of specified locations. The equilibrium solver identifies an equilibrium under the specified PF coil current and implements the effect of eddy current. The position and shape control has been simulated in response to prescribed change in the poloidal beta and the internal inductance due to heating.
Mori, Masahiro
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shinto, Katsuhiro; Wada, Motoi*; Nishida, Tomoaki*; Kisaki, Masashi*; Tsumori, Katsuyoshi*; Nishiura, Masaki*; Kaneko, Osamu*; Sasao, Mamiko*
no journal, ,
We have proposed a negative ion beam probe system as a new scheme to diagnose beam profiles of high power positive ion beams. We show the present status of the proof-of-principle experiment for the negative ion beam probe system performed at NIFS NBI test stand. A negative hydrogen ion source which produces a rectangular shape beam was installed at the diagnostic chamber in the NBI test stand and the total current of H beam extracted from the ion source was measured. We obtained the total H
beam extracted from the ion source was measured. We obtained the total H beam current of 10
beam current of 10  A with the beam energy of 3 kV.
A with the beam energy of 3 kV.
Nakamura, Tatsufumi; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Koga, J. K.; Pirozhkov, A. S.; Bulanov, S. V.; Kando, Masaki
no journal, ,
The concept of flying mirror is proposed to increase the laser irradiance, and generating the tunable compact X-ray source. The amplification factor is expressed by using Lorentz factor corresponding to the phase velocity of plasma wave 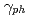 , as
, as 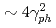 . Although the phase velocity of plasma wave is approximated as the laser group velocity in the one-dimensional model, it becomes lower at near the wave-breaking. In this study, we elucidate the plasma phase velocity including multi-dimensional effect and its nonlinear evolution towards wave-breaking by using two-dimensional PIC simulations. Its dependence on laser intensity, spot size, pulse duration, and plasma density is explored.
. Although the phase velocity of plasma wave is approximated as the laser group velocity in the one-dimensional model, it becomes lower at near the wave-breaking. In this study, we elucidate the plasma phase velocity including multi-dimensional effect and its nonlinear evolution towards wave-breaking by using two-dimensional PIC simulations. Its dependence on laser intensity, spot size, pulse duration, and plasma density is explored.
Kamiya, Kensaku; Honda, Mitsuru; Urano, Hajime; Yoshida, Maiko; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Matsunaga, Go; Oyama, Naoyuki; Koide, Yoshihiko; Kamada, Yutaka
no journal, ,
Depending on the direction of the external tangential momentum input, substantial changes in not only toroidal but also poloidal flows for the carbon impurity ions are observed at around the Er-well region. The shear in the edge Er becomes wider in the co-NBI case, while the edge Er-well becomes deeper in the counter-NBI case.
Atsumi, Kohei*; Sugawara, Shuhei*; Yamaguchi, Tomoki*; Saigusa, Mikio*; Oda, Yasuhisa; Takahashi, Koji; Kajiwara, Ken; Sakamoto, Keishi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shibama, Yusuke; Masaki, Kei; Nakamura, Shigetoshi; Kaminaga, Atsushi; Miyo, Yasuhiko; Sakurai, Shinji; Shibanuma, Kiyoshi; Sakasai, Akira
no journal, ,
JT-60SA is a fully superconducting coil tokamak upgraded from the JT-60U. This paper focuses on the vacuum vessel (VV, 150 tons) and cryostat (610 tons), whose structural concepts are developed from the ASME BPVC Section VIII Division 2. The VV is a stainless steel torus double-walled, which achieves high electrical resistivity in the toroidal and high stiffness in the light structure. The cryostat is large size vacuum thermal insulation vessel. The present status of both vessels is reported.
Kawashima, Hisato; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Hoshino, Kazuo; Takizuka, Tomonori*; Sakurai, Shinji
no journal, ,
For SONIC simulation on JT-60SA divertor, the heat flux limiter is introduced in the ion parallel heat transport besides electron one. Changing the limit factor from 
 = 0.5 to 10, density decrement and temperature increment in the edge-plasma are remarkable at
= 0.5 to 10, density decrement and temperature increment in the edge-plasma are remarkable at 
 = 0.5 in comparison with a case without limiter. Sensitivity on the radial particle or thermal diffusivity is surveyed with range of D = 0.1
= 0.5 in comparison with a case without limiter. Sensitivity on the radial particle or thermal diffusivity is surveyed with range of D = 0.1 1 m
1 m /s and
/s and  = 0.1
= 0.1 2 m
2 m /s. Divertor heat flux increases from 7.5 to 10.5 MW/m
/s. Divertor heat flux increases from 7.5 to 10.5 MW/m with decrease of D. This sensitivity is stronger than that for
with decrease of D. This sensitivity is stronger than that for  .
.
Yamaguchi, Toshikazu*; Takeichi, Tensei*; Komatsu, Reiji*; Fukunari, Masafumi*; Komurasaki, Kimiya*; Oda, Yasuhisa; Kajiwara, Ken; Takahashi, Koji; Sakamoto, Keishi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English