Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wakai, Eiichi; Kondo, Hiroo; Kanemura, Takuji; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hoashi, Eiji*; Fukada, Satoshi*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Yagi, Juro*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of Plasma Conference 2014 (PLASMA 2014) (CD-ROM), 2 Pages, 2014/11
In the IFMIF/EVEDA (International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility/ Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activity), the validation tests of the EVEDA lithium test loop with the world's highest flow rate of 3000 L/min was succeeded in generating a 100 mm-wide and 25 mm-thick free-surface lithium flow steadily under the IFMIF operation condition of a high-speed of 15 m/s at 250 C in a vacuum of 10
C in a vacuum of 10  Pa. Some excellent results of the recent engineering validations including lithium purification, lithium safety, and remote handling technique were obtained, and the engineering design of lithium facility was also evaluated. These results will advance greatly the development of an accelerator-based neutron source to simulate the fusion reactor materials irradiation environment as an important key technology for the development of fusion reactor materials.
Pa. Some excellent results of the recent engineering validations including lithium purification, lithium safety, and remote handling technique were obtained, and the engineering design of lithium facility was also evaluated. These results will advance greatly the development of an accelerator-based neutron source to simulate the fusion reactor materials irradiation environment as an important key technology for the development of fusion reactor materials.
Kamiya, Kensaku; Honda, Mitsuru; Urano, Hajime; Yoshida, Maiko; Kamada, Yutaka
no journal, ,
In this study, we perform to identify the boundary condition for the toroidal plasma flow, which is known to play an important role for an improved plasma stability and/or confinement, to improve the prediction in the plasma core region by a code, experimentally. Boundary condition of toroidal plasma flow imposed at the separatrix in JT-60U ELMy H-mode plasmas has been identified, comparing between co- and counter-NBI discharges. Toroidal plasma flow at the separatrix can become non-zero value, varying with momentum input direction, but being unaffected by the ELM event. The results indicate that the viscosity damping due to SOL flow through ion-neutral collision may not affect strongly ion parallel momentum transfer.
Saito, Makiko; Maruyama, Takahito; Ueno, Kenichi; Takeda, Nobukazu; Kakudate, Satoshi
no journal, ,
In ITER, after plasma operation, The Blanket Remote Handling System (BRHS) will be installed in the vacuum vessel and it will remove and install the shield blanket module. BRHS will undergo hands-on maintenance in the maintenance area after the exchange of the shield blanket module. Since BRHS will be contaminated the radioactive dust in the vacuum vessel, the workers will be exposed by radioactive dust. In this study, potential contaminated areas and their respective dose rates from the BRHS using MCNP5 code to assess the exposure of maintenance workers. The assessment was performed using 3 types of equipment, vehicle manipulator, combination of cable handling and rail support, and sliding beam, which are installed in vacuum vessel or port. The dose calculations used the nuclides Ta-182 and W-181 and the dose was calculated from each of the 20 points spaced evenly around the equipment. As a result, there are some local points with high dose rates, which are exceed the target of acceptable dose limit for hands-on work in ITER (5  Sv/h) in vehicle manipulator and combination of cable handling and rail support. To decrease the dose rate, lead blocks were used for shielding and as a result, the dose rate decreased to around 2.5
Sv/h) in vehicle manipulator and combination of cable handling and rail support. To decrease the dose rate, lead blocks were used for shielding and as a result, the dose rate decreased to around 2.5  Sv/h using 5 mm and 10 mm lead shielding.
Sv/h using 5 mm and 10 mm lead shielding.
Shiraishi, Junya; Miyato, Naoaki; Matsunaga, Go
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Jeronimo, G.*; Honda, Mitsuru; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Hoshino, Kazuo; Ide, Shunsuke; Gerardo, G.*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Suzuki, Takahiro; Urano, Hajime
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Honda, Mitsuru; Satake, Shinsuke*; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Yoshida, Maiko; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Kamiya, Kensaku; Matsuyama, Akinobu; Shinohara, Koji; Matsunaga, Go; Nakata, Motoki; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Tsuyoshi; Hatae, Takaki; Yatsuka, Eiichi; Sugie, Tatsuo; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Takeuchi, Masaki; Kitazawa, Sin-iti; Ota, Kazuya*; Hashimoto, Yasunori*; Nakamura, Kitaru*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Masafumi; Hanada, Masaya; Kojima, Atsushi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Hiratsuka, Junichi; Akino, Noboru; Endo, Yasuei; Komata, Masao; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; et al.
no journal, ,
One of the key issues for producing high current beams in JT-60SA is a uniform production of the negative ions over the large ion extraction area. Non-uniformity of the negative ion beams in the JT-60 negative ion source was improved by modifying the magnetic filter in the source from the PG filter to a tent-shaped filter. In this work, in order to clarify the influence of the magnetic filter modification on arc efficiency and co-electron current is investigated by means of measurements of H ion, H atoms, co-electron current and beam intensity. As a result, the arc efficiency increase due to increase of H ions and H atoms by reduction of filter field. Although the higher electrons current was extracted than the original PG filter, the co-extracted electron could be suppressed by optimization of the bias voltage. This result contributes to extend the pulse duration time up to 100 s for JT-60SA.
Miyata, Yoshiaki; Suzuki, Takahiro; Ide, Shunsuke; Urano, Hajime; Takechi, Manabu
no journal, ,
It is essential for a stable plasma equilibrium control to reconstruct an accurate plasma boundary in tokamak devices. Cauchy Condition Surface (CCS) method is a numerical approach to calculate the spatial distribution of the magnetic flux outside a hypothetical plasma surface and reconstruct the plasma boundary from the magnetic measurements located outside the plasma. It is found that the optimum number of unknown parameters and shape of the CCS for minimizing errors in the reconstructed plasma shape increase in proportion to the plasma size. It is shown that the accuracy of the plasma shape reconstruction greatly improves by using the optimum number of unknown parameters. The assessment of accuracy of plasma shape reconstruction by CCS method in JT-60SA is reported.
Nakamura, Shigetoshi; Shibama, Yusuke; Masaki, Kei; Sakasai, Akira
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Hoshino, Kazuo; Kawashima, Hisato; Takizuka, Tomonori*
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tanigawa, Hisashi; Someya, Yoji; Nakamura, Makoto; Enoeda, Mikio
no journal, ,
Blanket is located on the vacuum vessel wall in the fusion reactor, and has functions of thermal energy transfer, tritium production and neutron shielding. In ITER, blanket does not have function of tritium production and coolant temperature is low because electric power generation is not planned. In the fusion reactor, the coolant temperature will be higher for the electric power generation and tritium breeding materials will be packed in the blanket. Therefore, safety-related characteristics of blanket are different for ITER and fusion reactor. In this study, thermal hydraulic behaviour in the blanket is analyzed to understand safety-related characteristic.
Toma, Mitsunori; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Honda, Mitsuru; Ide, Shunsuke
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Miyato, Naoaki; Yagi, Masatoshi; Scott, B. D.*
no journal, ,
Since the standard gyrokinetic model is constructed by the two-step phase space transformation, fluid moments can be represented in terms of a gyro-center distribution function and gyro-center coordinates in two ways. The representations of fluid moments are called push-forward representations. In the representation used in the standard gyrokinetic formulation, the gyro-center transformation part emerges as the pull-back transformation of the gyro-center distribution function and is separated from the guiding-center transformation part. In the alternative representation, the gyro-center part moves to the parts except the gyro-center distribution function and is combined with the guiding-center part. We compare the two representation by deriving explicit representations of particle flux.
Nakano, Tomohide; Shumack, A.*; Maggi, C. F.*; Reinke, M.*; Lawson, K.*; P tterich, T.*; Brezinsek, S.*; Lipschultz, B.*; Matthews, G. F.*; Chernyshova, M.*; et al.
tterich, T.*; Brezinsek, S.*; Lipschultz, B.*; Matthews, G. F.*; Chernyshova, M.*; et al.
no journal, ,
In an European tokamak device, JET, an existing high-resolution X-ray crystal spectrometer was upgraded together with installation of the W divertor for the purpose of monitoring the W density in the core plasma. We have identified W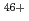 , W
, W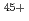 and Mo
and Mo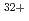 lines by comparing the spectrum observed by this spectrometer and that calculated by an atomic structure code. Further, from the intensities of these spectral lines, the W density and the Mo density over an electron density were determined to be
lines by comparing the spectrum observed by this spectrometer and that calculated by an atomic structure code. Further, from the intensities of these spectral lines, the W density and the Mo density over an electron density were determined to be 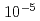 and
and 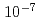 , respectively. The determined W density was in good agreement with that from another spectrometer. In addition, the plasma effective charge evaluated from the continuum intensity observed by the X-ray spectrometer was in agreement with that from a visible spectrometer within a factor of three. From these agreements, it is probable that the determined W and Mo density are valid. In contrast, the determined W density is only 15% compared with that from an soft X-ray array measurement. This inconsistency will be investigated in the near future.
, respectively. The determined W density was in good agreement with that from another spectrometer. In addition, the plasma effective charge evaluated from the continuum intensity observed by the X-ray spectrometer was in agreement with that from a visible spectrometer within a factor of three. From these agreements, it is probable that the determined W and Mo density are valid. In contrast, the determined W density is only 15% compared with that from an soft X-ray array measurement. This inconsistency will be investigated in the near future.
Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kitazawa, Sin-iti; Sugie, Tatsuo; Katsunuma, Atsushi*; Kitazawa, Daisuke*; Omori, Keisuke*; Itami, Kiyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sugie, Tatsuo; Takeuchi, Masaki; Ishikawa, Masao; Shimada, Takahiko; Katsunuma, Atsushi*; Kitazawa, Daisuke*; Omori, Keisuke*; Itami, Kiyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Sato, Satoshi; Iida, Hiromasa*; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Hirose, Takanori; Ochiai, Kentaro; Konno, Chikara; Enoeda, Mikio
no journal, ,
Shielding analyses have been performed on the ITER/TBM and its port by using Monte Carlo radiation transport calculation code MCNP and activation calculation code ACT-4. CAD data were automatically converted to MCNP data on the TBM, shield, pipes and bio-shield by the CAD/MCNP conversion code, and their MCNP data have been inserted to the ITER 40 degree model. We evaluated the effective dose rate in operation, nuclear heating, tritium production rate, effective dose rate after shutdown and induced activity.
Takechi, Manabu; Matsunaga, Go; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Nakamura, Yuji*; Bolzonella, T.*; Ide, Shunsuke; JT-60SA Team
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Imazawa, Ryota; Ono, Takehiro; Kawano, Yasunori; Itami, Kiyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English