Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wakai, Eiichi; Kondo, Hiroo; Kanemura, Takuji; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Furukawa, Tomohiro; Hoashi, Eiji*; Fukada, Satoshi*; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Yagi, Juro*; Tsuji, Yoshiyuki*; et al.
Proceedings of Plasma Conference 2014 (PLASMA 2014) (CD-ROM), 2 Pages, 2014/11
In the IFMIF/EVEDA (International Fusion Materials Irradiation Facility/ Engineering Validation and Engineering Design Activity), the validation tests of the EVEDA lithium test loop with the world's highest flow rate of 3000 L/min was succeeded in generating a 100 mm-wide and 25 mm-thick free-surface lithium flow steadily under the IFMIF operation condition of a high-speed of 15 m/s at 250 C in a vacuum of 10
C in a vacuum of 10  Pa. Some excellent results of the recent engineering validations including lithium purification, lithium safety, and remote handling technique were obtained, and the engineering design of lithium facility was also evaluated. These results will advance greatly the development of an accelerator-based neutron source to simulate the fusion reactor materials irradiation environment as an important key technology for the development of fusion reactor materials.
Pa. Some excellent results of the recent engineering validations including lithium purification, lithium safety, and remote handling technique were obtained, and the engineering design of lithium facility was also evaluated. These results will advance greatly the development of an accelerator-based neutron source to simulate the fusion reactor materials irradiation environment as an important key technology for the development of fusion reactor materials.
Sugie, Tatsuo; Takeuchi, Masaki; Ishikawa, Masao; Shimada, Takahiko; Katsunuma, Atsushi*; Kitazawa, Daisuke*; Omori, Keisuke*; Itami, Kiyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Koji; Abe, Ganji; Isozaki, Masami; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Oda, Yasuhisa; Kajiwara, Ken; Sakamoto, Keishi; Kobayashi, Noriyuki*; Iida, Hiromasa*; Komatsuzaki, Manabu*; et al.
no journal, ,
It was analytically obtained that electron cyclotron current drive efficency at  =0.4
=0.4 0.6 can be doubled modifying the steering function of millimeter wave launching from the equatorial port from toroidally to poloidally. The design modification of the ITER equatorial launcher enhancing ECCD function is implemented. The millimeter wave design satisfying transmission efficiency more than 99% with the required ploidal beam steering capability is successfully obtained and reflected to the launcher structural design. The millimeter wave design optimization, BSM design modification to allow the required polidal beam steering capability and so on are reported in detail at the conference.
0.6 can be doubled modifying the steering function of millimeter wave launching from the equatorial port from toroidally to poloidally. The design modification of the ITER equatorial launcher enhancing ECCD function is implemented. The millimeter wave design satisfying transmission efficiency more than 99% with the required ploidal beam steering capability is successfully obtained and reflected to the launcher structural design. The millimeter wave design optimization, BSM design modification to allow the required polidal beam steering capability and so on are reported in detail at the conference.
Nakano, Tomohide; Shumack, A.*; Maggi, C. F.*; Reinke, M.*; Lawson, K.*; P tterich, T.*; Brezinsek, S.*; Lipschultz, B.*; Matthews, G. F.*; Chernyshova, M.*; et al.
tterich, T.*; Brezinsek, S.*; Lipschultz, B.*; Matthews, G. F.*; Chernyshova, M.*; et al.
no journal, ,
In an European tokamak device, JET, an existing high-resolution X-ray crystal spectrometer was upgraded together with installation of the W divertor for the purpose of monitoring the W density in the core plasma. We have identified W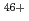 , W
, W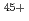 and Mo
and Mo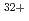 lines by comparing the spectrum observed by this spectrometer and that calculated by an atomic structure code. Further, from the intensities of these spectral lines, the W density and the Mo density over an electron density were determined to be
lines by comparing the spectrum observed by this spectrometer and that calculated by an atomic structure code. Further, from the intensities of these spectral lines, the W density and the Mo density over an electron density were determined to be 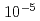 and
and 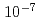 , respectively. The determined W density was in good agreement with that from another spectrometer. In addition, the plasma effective charge evaluated from the continuum intensity observed by the X-ray spectrometer was in agreement with that from a visible spectrometer within a factor of three. From these agreements, it is probable that the determined W and Mo density are valid. In contrast, the determined W density is only 15% compared with that from an soft X-ray array measurement. This inconsistency will be investigated in the near future.
, respectively. The determined W density was in good agreement with that from another spectrometer. In addition, the plasma effective charge evaluated from the continuum intensity observed by the X-ray spectrometer was in agreement with that from a visible spectrometer within a factor of three. From these agreements, it is probable that the determined W and Mo density are valid. In contrast, the determined W density is only 15% compared with that from an soft X-ray array measurement. This inconsistency will be investigated in the near future.
Shiraishi, Junya; Miyato, Naoaki; Matsunaga, Go
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Jeronimo, G.*; Honda, Mitsuru; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Hoshino, Kazuo; Ide, Shunsuke; Gerardo, G.*; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Suzuki, Takahiro; Urano, Hajime
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Honda, Mitsuru; Satake, Shinsuke*; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Yoshida, Maiko; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Kamiya, Kensaku; Matsuyama, Akinobu; Shinohara, Koji; Matsunaga, Go; Nakata, Motoki; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yamamoto, Tsuyoshi; Hatae, Takaki; Yatsuka, Eiichi; Sugie, Tatsuo; Ogawa, Hiroaki; Takeuchi, Masaki; Kitazawa, Sin-iti; Ota, Kazuya*; Hashimoto, Yasunori*; Nakamura, Kitaru*; et al.
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Yoshida, Masafumi; Hanada, Masaya; Kojima, Atsushi; Kashiwagi, Mieko; Umeda, Naotaka; Hiratsuka, Junichi; Akino, Noboru; Endo, Yasuei; Komata, Masao; Mogaki, Kazuhiko; et al.
no journal, ,
One of the key issues for producing high current beams in JT-60SA is a uniform production of the negative ions over the large ion extraction area. Non-uniformity of the negative ion beams in the JT-60 negative ion source was improved by modifying the magnetic filter in the source from the PG filter to a tent-shaped filter. In this work, in order to clarify the influence of the magnetic filter modification on arc efficiency and co-electron current is investigated by means of measurements of H ion, H atoms, co-electron current and beam intensity. As a result, the arc efficiency increase due to increase of H ions and H atoms by reduction of filter field. Although the higher electrons current was extracted than the original PG filter, the co-extracted electron could be suppressed by optimization of the bias voltage. This result contributes to extend the pulse duration time up to 100 s for JT-60SA.
Miyata, Yoshiaki; Suzuki, Takahiro; Ide, Shunsuke; Urano, Hajime; Takechi, Manabu
no journal, ,
It is essential for a stable plasma equilibrium control to reconstruct an accurate plasma boundary in tokamak devices. Cauchy Condition Surface (CCS) method is a numerical approach to calculate the spatial distribution of the magnetic flux outside a hypothetical plasma surface and reconstruct the plasma boundary from the magnetic measurements located outside the plasma. It is found that the optimum number of unknown parameters and shape of the CCS for minimizing errors in the reconstructed plasma shape increase in proportion to the plasma size. It is shown that the accuracy of the plasma shape reconstruction greatly improves by using the optimum number of unknown parameters. The assessment of accuracy of plasma shape reconstruction by CCS method in JT-60SA is reported.
Nakamura, Shigetoshi; Shibama, Yusuke; Masaki, Kei; Sakasai, Akira
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tojo, Hiroshi; Hatae, Takaki; Sakuma, Takeshi; Hamano, Takashi; Itami, Kiyoshi; Suito, Satoshi*; Araki, Takashi*; Iwamoto, Kohei*; Takeda, Yuya*
no journal, ,
Imazawa, Ryota; Ono, Takehiro; Kawano, Yasunori; Itami, Kiyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Shibata, Yoshihide; Matsunaga, Go; Sakakibara, Satoru*; Kawano, Yasunori; Isayama, Akihiko; Watanabe, Kiyomasa
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Kamiya, Kensaku; Honda, Mitsuru; Urano, Hajime; Yoshida, Maiko; Kamada, Yutaka
no journal, ,
In this study, we perform to identify the boundary condition for the toroidal plasma flow, which is known to play an important role for an improved plasma stability and/or confinement, to improve the prediction in the plasma core region by a code, experimentally. Boundary condition of toroidal plasma flow imposed at the separatrix in JT-60U ELMy H-mode plasmas has been identified, comparing between co- and counter-NBI discharges. Toroidal plasma flow at the separatrix can become non-zero value, varying with momentum input direction, but being unaffected by the ELM event. The results indicate that the viscosity damping due to SOL flow through ion-neutral collision may not affect strongly ion parallel momentum transfer.
Miki, Kazuhiro; Idomura, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
Understanding of the energetic particles physics is of great interest in the future burning plasmas. We identify linear dynamics of energetic-particle-induced geodesic acoustic mode (EGAM). Representating bump-on-tail distributions as the energetic particles, we calculate real frequencies and linear growth rates, based on eigenmode analyses. Taking into account of finite-orbit-width (FOW) effects, we estimate the reduction of growth rates of the EGAM due to machine size. Results indicate that the reduction is small, within several percent, for experimentally relevant parameters. Next, applying more general distributions, i.e. slowing down, we examine linear evolution of the EGAM. Here the same q-profile is applied as the DIII-D experiments. Results on the gyrokinetic simulations are compared with the hybrid code ones. Obtained frequencies are similar to those obtained from the hybrid one. Linear growth rates are smaller than those obtained from the hybrid one.
Takechi, Manabu; Matsunaga, Go; Suzuki, Yasuhiro*; Nakamura, Yuji*; Bolzonella, T.*; Ide, Shunsuke; JT-60SA Team
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Ikeda, Ryosuke; Oda, Yasuhisa; Kajiwara, Ken; Takahashi, Koji; Kobayashi, Takayuki; Moriyama, Shinichi; Sakamoto, Keishi
no journal, ,
Long pulse gyrotrons for ITER are under development. At present, output power of 1.2 MW for 2 s pulse operation and long pulse operation of 1000 s at 0.5 MW were achieved in experiments of TE31,11 mode gyrotron. Moreover, a transmission efficiency of 91% was obtained in 40 m transmission experiment. Recently, development of TE31,9 mode gyrotron was started. 1 MW with oscillation efficiency of 33% was realized in 1 ms operation without depressed collector voltage. And, 0.61 MW with total electric efficiency 51 % was achieved in 10 s operation with depressed collector voltage.
Oshima, Katsumi; Oda, Yasuhisa; Hashimoto, Yasunori*; Hayashi, Kazuo*; Ikeda, Ryosuke; Kajiwara, Ken; Takahashi, Koji; Sakamoto, Keishi
no journal, ,
In the ITER gyrotron development activity, the local control system for ITER gyrotron has been carried out using the ITER CODAC Core system. This control system is composed of Fast controller and Slow controller. The former has a role to control the gyrotron oscillation, timing control, data acquisition, etc. The later has a role to manage the operation phase shift, machine protection and alarm management, etc. Using this prototype system, we succeeded the gyrotron oscillation and 5 kHz power modulation.
Ogawa, Hiroaki; Kitazawa, Sin-iti; Sugie, Tatsuo; Katsunuma, Atsushi*; Kitazawa, Daisuke*; Omori, Keisuke*; Itami, Kiyoshi
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English