Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...

Shibata, Goro; 9 of others*
Applied Physics Letters, 126(24), p.241902_1 - 241902_6, 2025/06
Sekikawa, Takuya; Takada, Kazuki*; Kai, Takeshi; Ono, Yoshiaki*
Journal of Applied Physics, 137(20), p.203901_1 - 203901_10, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0no abstracts in English
Huang, Y.-C.*; Kikkawa, Takashi; 5 of others*
Applied Physics Letters, 126(9), p.092403_1 - 092403_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Kawasaki, Takuro; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Yamanaka, Satoru*; Murayama, Ichiro*; Kato, Takanori*; Baba, Masaaki*; Hashimoto, Hideki*; Harjo, S.; Aizawa, Kazuya; Tanaka, Hirohisa*; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 137(9), p.094101_1 - 094101_7, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Egashira, Naoya*; Matsuda, Tomoki*; Okuchi, Takuo*; Seto, Yusuke*; Ito, Yusuke*; Shobu, Takahisa; Nakanii, Nobuhiko*; Sano, Tomokazu*; 4 of others*
Journal of Applied Physics, 137(10), p.105903_1 - 105903_8, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Iwata, Yoshihiro; Sekiya, Hiroyuki*; Ito, Chikara
Applied Physics A, 131, p.165_1 - 165_8, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Among various analytical methods for liquid samples, time-resolved laser-induced luminescence spectroscopy enables real-time measurements of Gd ion concentrations in aqueous solution without sample introduction into the spectrometer. In this work, we have developed a real-time monitoring method for Gd concentration in water. The detection limit was determined to be  60 ppb for Gd sulfate in ultrapure water. This value is about two orders of magnitude better than the reported value using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, and is close to that using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry which requires sample introduction into the spectrometer.
60 ppb for Gd sulfate in ultrapure water. This value is about two orders of magnitude better than the reported value using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy, and is close to that using inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry which requires sample introduction into the spectrometer.
 , AgNbO
, AgNbO , and KNbO
, and KNbO
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Kobayashi, Toru; Tsuji, Takuya; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Yuji; Noguchi, Yuji*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 63(9), p.09SP12_1 - 09SP12_10, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)NaNbO , AgNbO
, AgNbO , and KNbO
, and KNbO with ABO
with ABO -type perovskite system is known to possess good ferroelectric properties. We directly determined the rattling space of each atom through local structure analysis. This analysis revealed the bonding sites with large fluctuations varied with varying ion size. Experimental evidence including soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy, indicates that the A-site ions are hybridized with oxygen.
-type perovskite system is known to possess good ferroelectric properties. We directly determined the rattling space of each atom through local structure analysis. This analysis revealed the bonding sites with large fluctuations varied with varying ion size. Experimental evidence including soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy, indicates that the A-site ions are hybridized with oxygen.
Ding, H.*; Ito, Keita*; Endo, Yasushi*; Takanashi, Koki; Seki, Takeshi*
Journal of Physics D; Applied Physics, 57(38), p.385002_1 - 385002_10, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:62.71(Physics, Applied)Takyu, Sodai*; Matsumoto, Kenichiro*; Hirade, Tetsuya; Nishikido, Fumihiko*; Akamatsu, Go*; Tashima, Hideaki*; Takahashi, Miwako*; Yamaya, Taiga*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 63(8), p.086003_1 - 086003_8, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:40.97(Physics, Applied)Positrons and electrons sometimes exist as a bound state, positronium (Ps), in living organisms. The triplet Ps (ortho-Ps) annihilation time represents the ortho-Ps pick-off annihilation lifetime, and it varies depending on the surrounding electron density. The ortho-Ps lifetime may add new biological information to PET scan information. In order to discuss the feasibility of quantifying (free) radicals in vivo by the ortho-Ps lifetime, we used a clinical PET system to make ortho-Ps lifetime measurements in aqueous solutions containing radicals. The results suggested that differences in radical concentrations in aqueous solutions of the order of a few mM could be quantified by the ortho-Ps lifetime if the counting statistic of the positron annihilation events was more than 10 events. This concentration was higher than the radical concentration generated in the physiological functions of living organisms.
events. This concentration was higher than the radical concentration generated in the physiological functions of living organisms.
 gamma-ray imager using detector response patterns
gamma-ray imager using detector response patternsKitayama, Yoshiharu; Nogami, Mitsuhiro*; Hitomi, Keitaro*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 63(7), p.076502_1 - 076502_8, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)We constructed a gamma-ray imager that estimates the distribution of gamma-ray sources based on the response patterns of multiple gamma-ray detectors randomly positioned in three-dimensional space. The Coded Cube Camera for Gamma-ray (C3G), comprising eight GAGG (Ce) scintillator and eighteen lead cubes is housed in a cubical casing with an 86 mm edge length and weighs approximately 600 g. Results of the 4 imaging experiment confirmed the feasibility of imaging a 10 MBq
imaging experiment confirmed the feasibility of imaging a 10 MBq  Cs source located 3 m away with an angular uncertainty of 5
Cs source located 3 m away with an angular uncertainty of 5 within a 10 min measurement. C3G operates with only eight channels, instead of the hundreds needed by a typical imager, offering a simplified circuit and reconstruction algorithm, thereby achieving a cost-effective and reliable system. With its compact and lightweight design, 4
within a 10 min measurement. C3G operates with only eight channels, instead of the hundreds needed by a typical imager, offering a simplified circuit and reconstruction algorithm, thereby achieving a cost-effective and reliable system. With its compact and lightweight design, 4 field of view, and high angular uncertainty, this technology is expected to find extensive applications in astronomy, medicine, nuclear security, and decommissioning projects.
field of view, and high angular uncertainty, this technology is expected to find extensive applications in astronomy, medicine, nuclear security, and decommissioning projects.
Zhang, Z.*; Hattori, Takanori; Song, R.*; Yu, D.*; Mole, R.*; Chen, J.*; He, L.*; Zhang, Z.*; Li, B.*
Journal of Applied Physics, 136(3), p.035105_1 - 035105_8, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:40.97(Physics, Applied)Solid-state refrigeration using barocaloric materials is environmentally friendly and highly efficient, making it a subject of global interest over the past decade. Here, we report giant barocaloric effects in sodium hexafluorophosphate (NaPF ) and sodium hexafluoroarsenate (NaAsF
) and sodium hexafluoroarsenate (NaAsF ) that both undergo a cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transition near room temperature. We have determined that the low-temperature phase structure of NaPF
) that both undergo a cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transition near room temperature. We have determined that the low-temperature phase structure of NaPF is a rhombohedral structure with space group R
is a rhombohedral structure with space group R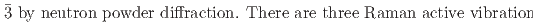 and NaAsF
and NaAsF , i.e., F
, i.e., F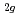 , E
, E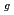 , and A
, and A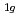 . The phase transition temperature varies with pressure at a rate of dT
. The phase transition temperature varies with pressure at a rate of dT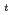 /dP = 250 and 310 K/GPa for NaPF
/dP = 250 and 310 K/GPa for NaPF and NaAsF
and NaAsF . The pressure-induced entropy changes of NaPF
. The pressure-induced entropy changes of NaPF and NaAsF
and NaAsF are determined to be around 45.2 and 35.6J kg
are determined to be around 45.2 and 35.6J kg K
K , respectively. The saturation driving pressure is about 40 MPa. The pressure-dependent neutron powder diffraction suggests that the barocaloric effects are related to the pressure-induced cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transitions.
, respectively. The saturation driving pressure is about 40 MPa. The pressure-dependent neutron powder diffraction suggests that the barocaloric effects are related to the pressure-induced cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transitions.
Kubota, Masato; Kato, Seiichi*
Journal of Applied Physics, 136(2), p.025102_1 - 025102_5, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:40.97(Physics, Applied)Jo, Sadaharu*; Suzuki, Seiya; Yoshimura, Masamichi*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 63(6), p.065503_1 - 065503_4, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Watanabe, Kenichi*; Oshima, Yuya*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Hirata, Yuho
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 63(5), p.056001_1 - 056001_5, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Lithium-containing scintillators are used for neutron detection; Li-containing scintillators detect tritons and alpha rays produced by neutrons. Since these particles deposit higher energy than gamma rays, Li-containing scintillators can separate gamma rays and neutrons. However, the luminescence efficiency of scintillator decreases for ion beams due to a phenomenon called the quenching effect. Evaluation of the quenching effect is necessary to accurately separate neutrons and gamma rays. The Birks equation is used to predict the scintillation efficiency change due to the quenching effect, but it is necessary to determine the quenching coefficient in the Birks equation. In this study, we used PHITS to calculate the luminescence of Li-containing scintillators considering the quenching effect based on Birks' equation with the quenching coefficient as a free parameter. Then, by comparing the simulated results with the experimentally obtained luminescence, the extinction coefficients of Li glass, Ce:LiCaAlF , and Eu:LiCaAlF
, and Eu:LiCaAlF scintillators were determined.
scintillators were determined.
Omer, M.; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Hajima, Ryoichi*; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Journal of Applied Physics, 135(18), p.184903_1 - 184903_10, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Yao, D.*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Yokoyama, Takehito*
Applied Physics Letters, 124(16), p.162603_1 - 162603_5, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:82.03(Physics, Applied)Shamoto, Shinichi; Akatsu, Mitsuhiro*; Chang, L.-J.*; Nemoto, Yuichi*; Ieda, Junichi
Applied Physics Letters, 124(11), p.112402_1 - 112402_5, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:40.97(Physics, Applied)The magnon excitation by ultrasound injection in Y Fe
Fe O
O is studied by inelastic neutron scattering. Both longitudinal and transverse ultrasound injections enhanced the inelastic neutron scattering intensity.
is studied by inelastic neutron scattering. Both longitudinal and transverse ultrasound injections enhanced the inelastic neutron scattering intensity.
 Fe
Fe O
O
Kawamoto, Yo*; Kikkawa, Takashi; Saito, Eiji; 9 of others*
Applied Physics Letters, 124(13), p.132406_1 - 132406_7, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:82.03(Physics, Applied) -Ga
-Ga O
O (001)
(001)Tsai, Y. H.*; Kobata, Masaaki; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Tanida, Hajime; Kobayashi, Toru; Yamashita, Yoshiyuki*
Applied Physics Letters, 124(11), p.112105_1 - 112105_5, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:62.71(Physics, Applied) -MgAgSb
-MgAgSbLi, J.*; Li, X.*; Zhang, Y.*; Zhu, J.*; Zhao, E.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Avdeev, M.*; Liu, P.-F.*; Sui, J.*; et al.
Applied Physics Reviews (Internet), 11(1), p.011406_1 - 011406_8, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:91.57(Physics, Applied)