Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Ta and
Ta and  Bi considering experimental double differential cross-section data
Bi considering experimental double differential cross-section dataNguyen, T. T. H.*; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Sanami, Toshiya*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 322, p.10004_1 - 10004_3, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0Miyazaki, Yasunori; Sano, Yuichi; Ishigami, Ryoya*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 317, p.01006_1 - 01006_7, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The gamma-ray and He ion beam (which is simulated for alpha-ray from
ion beam (which is simulated for alpha-ray from  Am, for example) were irradiated on the TEHDGA adsorbent to evaluate the hydrogen gas production, leaching amount of organics in the immersed 3 M HNO
Am, for example) were irradiated on the TEHDGA adsorbent to evaluate the hydrogen gas production, leaching amount of organics in the immersed 3 M HNO solution, thermal characteristics and speciation of the degradation products. These were combined to assess the safety of the 1st run of the MA separation process from the raffinate at a dose rate of 1 kGy/h.
solution, thermal characteristics and speciation of the degradation products. These were combined to assess the safety of the 1st run of the MA separation process from the raffinate at a dose rate of 1 kGy/h.
Kawamura, Takuma; Shimomura, Kazuya; Osaki, Tsukasa*; Idomura, Yasuhiro
EPJ Web of Conferences, 302, p.11002_1 - 11002_8, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)In the field of nuclear engineering, complex simulations on exa-scale supercomputers generate large-scale data. To facilitate efficient analysis of such simulation data, one needs to share them among scientists at remote locations. However, data I/O and data transfer for such large-scale data are quite costly. To resolve these issues, we developed a remote in-situ visualization system IS-PBVR based on the particle-based volume rendering (PBVR), which is suitable for parallel processing on modern supercomputers. In this study, we extend IS-PBVR for VR visualization on multiple client PCs, thus developing a multi-point remote VR visualization. We apply this technique to fluid simulations on GPU-based supercomputers and verify its utility by sharing in-situ VR visualization between multiple client PCs.
Yamada, Susumu; Machida, Masahiko; Tanimura, Naoki*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 302, p.16004_1 - 16004_10, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)When we decommission a reactor building, it is desirable to identify the radiation source distribution for safety. It has been reported that the source distribution can be estimated from the measured air dose rates at appropriate observation points by minimizing an evaluation function using the Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator (LASSO). However, it is difficult to decide on suitable points in advance. Therefore, we estimate the posterior distribution from the prior distribution of the source amounts, which are calculated by the standard LASSO, using the Bayesian LASSO, and evaluate the predictive distribution of the evaluated air dose rates at the candidate observation points from the posterior distribution. We select the additional observation point based on the variances of the predictive distributions. We confirmed that the method can estimate the source distribution with fewer additional observation points than when adding ones randomly in most cases.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Onodera, Naoyuki
EPJ Web of Conferences, 302, p.03005_1 - 03005_9, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)We implemented the ensemble data assimilation (DA) method, the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LETKF), into the mesh-refined lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) for turbulent flows. Both the LETKF and the mesh-refined LBM were fully implemented on GPUs, so that they are efficiently computed on modern GPU-based supercomputers. We examined the DA accuracy against the flow around a cylinder. The result showed that our method enabled accurate DA with spatially- and temporarily-sparse observation data; the error of the assimilated velocity field with the observation interval of 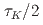 and the observation resolution
and the observation resolution 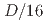 (1.56% of the total computational grids) was smaller than the amplitude of the observation noise, where
(1.56% of the total computational grids) was smaller than the amplitude of the observation noise, where 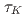 is the period of the K
is the period of the K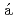 rm
rm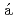 n vortex and
n vortex and  is diameter of the square cylinder.
is diameter of the square cylinder.
Sitompul, Y.; Sugihara, Kenta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro
EPJ Web of Conferences, 302, p.05004_1 - 05004_10, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)In fast reactor designs, it is of critical importance to avoid gas entrainment phenomena due to free-surface vortices. Numerical analysis is one of the key methods to understand these phenomena. However, the challenges in computational efficiency and accuracy of the previous numerical methods lead to exploring the Lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) as an alternative, known for its computational efficiency and capability in simulating complex flows. In this study, we implement free-surface LBM to accelerate gas entrainment analysis, significantly reducing computational costs while maintaining accuracy compared to traditional methods. Simulation results using LBM align well with experimental data, offering a promising avenue for faster analysis in future fast reactor designs.
Kondo, Ryoichi; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 302, p.04002_1 - 04002_10, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)In the recent study, we have developed an efficient flux distribution tallying method in the Monte Carlo calculation toward the high-fidelity, large scale multi-physics simulation. In this method, the proper orthogonal decomposition is applied to the flux distribution tallies. While the tallying method was implemented with the collision estimator in the previous study, the track length estimator is implemented in the present study to obtain the tally with lower statistical error. The implementation of the flux distribution tally with the track length estimator is compared with that of the collision estimator and the normal track length estimator in a one-dimensional problem. The numerical results reveal that the distribution tally using the POD with the track length estimator can obtain a more precise solution compared with that with the collision estimator. Therefore, in terms of the statistical error, the relationship between the distribution tally with track length and collision estimator is similar to that between the conventional track length and collision estimators.
Sugihara, Kenta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Sitompul, Y.; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Yamashita, Susumu
EPJ Web of Conferences, 302, p.03002_1 - 03002_10, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Computer Science, Interdisciplinary Applications)In simulations of gas-liquid two-phase flows using conventional interface capture methods, we observed that when bubbles come close to each other, they tend to merge numerically, despite experimental evidence indicating that they would repel each other. Given the significant impact of sequential numerical coalescence on flow patterns, it is necessary to regulate the merging behavior of close bubbles. To address this issue, we introduced the Multi- Phase Field (MPF) method, which mitigates bubble coalescence by applying an independent fluid fraction function to each bubble. In this study, we employed the MPF based on the N-phase model to minimize numerical errors associated with surface interactions at triple junction points. Additionally, we implemented the Ordered Active Parameter Tracking (OAPT) method to efficiently store several hundreds of fluid fraction functions. To validate the MPF method, we conducted analysis of turbulent bubbly pipe flows and compared the results against experimental data from Colin et al. The validation results showed reasonable agreements with respect to the bubble distribution and the flow velocity profiles.
Khemchandani, K. P.*; Mart nez Torres, A.*; Kim, S.-H.*; Nam, S.-I.*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Nagahiro, Hideko*
nez Torres, A.*; Kim, S.-H.*; Nam, S.-I.*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Nagahiro, Hideko*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 301, p.03001_1 - 03001_10, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Kimura, Atsushi; Endo, Shunsuke; Nakamura, Shoji
EPJ Web of Conferences, 294, p.01002_1 - 01002_7, 2024/04
Nakayama, Shinsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Kimura, Atsushi
EPJ Web of Conferences, 294, p.07001_1 - 07001_6, 2024/04
Graphite is a candidate of moderator in innovative nuclear reactors such as molten salt reactors. Scattering of thermal neutrons by the moderator material has a significant impact on the reactor core design. To contribute to the development of innovative nuclear reactors, an evaluation method of thermal neutron scattering law for reactor grade graphite was studied. The inelastic scattering component due to lattice vibration was evaluated based on the phonon density of states computed with first-principles lattice dynamics simulations. The simulations were performed for ideal crystalline graphite. The coherent elastic scattering component due to crystal structure was evaluated based on neutron transmission and scattering experiments recently performed in the J-PARC/MLF facility. In comparison with the neutron transmission experiments, it was found that the quantification of small-angle neutron scattering due to structures larger than crystal, such as pores in graphite, is important. Based on the above methods, thermal neutron scattering law data for reactor-grade graphite at room temperature were evaluated.
 meson in nuclear matter from theory and experimental data
meson in nuclear matter from theory and experimental dataGubler, P.; Bratkovskaya, E.*; Ichikawa, Masaya; Song, T.*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 291, p.04003_1 - 04003_4, 2024/02
no abstracts in English
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Takeshita, Hayato; Maekawa, Fujio
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01033_1 - 01033_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:70.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 Pd using ANNRI at MLF/J-PARC
Pd using ANNRI at MLF/J-PARCNakano, Hideto*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Terada, Kazushi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kodama, Yu*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01032_1 - 01032_3, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Dimitriou, P.*; Chen, Z.*; deBoer, R. J.*; Hale, G.*; Kunieda, Satoshi; Leeb, H.*; Paris, M.*; Pigni, M. T.*; Srdinko, Th.*; Tamagno, P.*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.03002_1 - 03002_5, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Charged-particle-induced reactions at low energies in the resolved resonance region are important for applications such as ion beam analysis of materials and management of the nuclear fuels. However, the evaluated nuclear data libraries maintained by national or international coordinated efforts (ENDF, JEFF, JENDL, CENDL) are to date, incomplete as far as charged-particle- induced reactions in the resolved resonance region are concerned. The IAEA Nuclear Data Section is coordinating an international effort to (i) verify that the existing R-matrix codes are consistent, (ii) evaluate charged-particle cross sections in the resolved resonance region, (iii) produce evaluated nuclear data files for further processing and finally (iv) disseminate the evaluated data through general purpose evaluated nuclear data libraries. We present the results of the effort made thus far on (1) verification of the available R-matrix codes, minimization methods and calculation of covariances, (2) the evaluation of the compound system  Be*, and (3) improving
Be*, and (3) improving 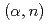 reaction data for the applications.
reaction data for the applications.
Iwamoto, Hiroki; Nakano, Keita; Meigo, Shinichiro; Satoh, Daiki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Sugihara, Kenta*; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Ishi, Yoshihiro*; Uesugi, Tomonori*; Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01023_1 - 01023_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)For accurate prediction of neutronic characteristics for accelerator-driven systems (ADS) and a source term of spallation neutrons for reactor physics experiments for the ADS at Kyoto University Critical Assembly (KUCA), we have launched an experimental program to measure nuclear data on ADS using the Fixed Field Alternating Gradient (FFAG) accelerator at Kyoto University. As part of this program, the proton-induced double-differential thick-target neutron-yields (TTNYs) and cross-sections (DDXs) for iron, lead, and bismuth have been measured with the time-of-flight (TOF) method. For each measurement, the target was installed in a vacuum chamber on the beamline and bombarded with 107-MeV proton beams accelerated from the FFAG accelerator. Neutrons produced from the targets were detected with stacked, small-sized neutron detectors for several angles from the incident beam direction. The TOF spectra were obtained from the detected signals and the FFAG kicker magnet's logic signals, where gamma-ray events were eliminated by pulse shape discrimination. Finally, the TTNYs and DDXs were obtained from the TOF spectra by relativistic kinematics. The measured TTNYs and DDXs were compared with calculations by the Monte Carlo transport code PHITS with its default physics model of INCL version 4.6 combined with GEM and those with the JENDL-4.0/HE nuclear data library.
Konno, Chikara; Kwon, Saerom*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.15010_1 - 15010_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)For the JENDL development we analyzed the iron in-situ experiment at the DT neutron source facility FNS in JAEA with the two-dimensional Sn code DORT and the latest nuclear data libraries: JENDL-4.0, ENDF/B-VIII.0 and JEFF-3.3. As a result, we found that the result with ENDF/B-VIII.0 reproduced the measured data worse than those with JENDL-4.0 and JEFF-3.3 as follows: overestimation of neutron flux below a few keV, underestimation of the reaction rate of  In(n,n')
In(n,n')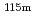 In sensitive to neutrons above 0.3 MeV and underestimation of neutron flux above 10 MeV. Our detailed study specified that the inelastic scattering cross section of Fe-56 in ENDF/B-VIII.0 mainly caused the overestimation of neutron flux below a few keV and underestimation of the reaction rate of
In sensitive to neutrons above 0.3 MeV and underestimation of neutron flux above 10 MeV. Our detailed study specified that the inelastic scattering cross section of Fe-56 in ENDF/B-VIII.0 mainly caused the overestimation of neutron flux below a few keV and underestimation of the reaction rate of  In(n,n')
In(n,n')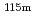 In and that the angular distribution data of the elastic scattering and the cross section of the (n,2n) reaction of
In and that the angular distribution data of the elastic scattering and the cross section of the (n,2n) reaction of  Fe in ENDF/B-VIII.0 were the reason of the underestimation of neutron flux above 10 MeV.
Fe in ENDF/B-VIII.0 were the reason of the underestimation of neutron flux above 10 MeV.
Kodama, Yu*; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Nakano, Hideto*; Sato, Yaoki*; Hori, Junichi*; Shibahara, Yuji*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.01024_1 - 01024_3, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Meigo, Shinichiro; Nakano, Keita*; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Yoshida, Makoto*
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.05001_1 - 05001_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:70.46(Nuclear Science & Technology)In high-intensity proton accelerator facilities such as Accelerator Driven System (ADS) and the spallation neutron source, it is crucial to evaluate the damage of beam-interception materials and accelerator components, such as a magnet coil. The displacement per atom (dpa) is used as a damage index, which is derived by integrating the particle flux and the displacement cross section based on the NRT model. Although the dpa is employed as the standard, the experimental data of displacement cross section are scarce for a proton in the energy region above 20 MeV. To obtain the data for superconducting materials for high-intensity accelerators and magnets, the displacement cross section of Nb for proton irradiation with a kinetic energy range between 0.4 and 3 GeV was measured. For sustaining damage in the sample, the Nb sample was cooled at a cryogenic temperature ( 8 K), where the recombination of Frenkel pairs due to thermal motion was well suppressed with maintaining the normal conductivity to maintain Matthiessen's rule. The displacement cross section of Nb was calculated using the PHITS code, and was compared with the present experimental results. It was found that the widely utilized NRT model overestimates the cross section by a factor of 2, as suggested by the previous works. It was also found that the calculation with a recently proposed athermal recombination corrected (arc) model based on Molecular Dynamics (MD) shows good agreement with the present data.
8 K), where the recombination of Frenkel pairs due to thermal motion was well suppressed with maintaining the normal conductivity to maintain Matthiessen's rule. The displacement cross section of Nb was calculated using the PHITS code, and was compared with the present experimental results. It was found that the widely utilized NRT model overestimates the cross section by a factor of 2, as suggested by the previous works. It was also found that the calculation with a recently proposed athermal recombination corrected (arc) model based on Molecular Dynamics (MD) shows good agreement with the present data.
Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi; Nakamura, Shoji; Endo, Shunsuke; Iwamoto, Osamu; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Katabuchi, Tatsuya*; Kodama, Yu*; Nakano, Hideto*; Hori, Junichi*; et al.
EPJ Web of Conferences, 284, p.06007_1 - 06007_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)