Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshiasa, Akira*; Murai, Keiichiro*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Katayama, Yoshinori
International Journal of Modern Physics B, 25(31), p.4159 - 4162, 2011/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Applied)Precise structure analyses of advanced materials under pressure were performed using each advantage of X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) and diffraction methods. Measurements were performed in-situ under pressure and temperature using a large-volume multi-anvil pressure apparatus and synchrotron radiation. XAFS spectra are useful for phase study under high temperature and high pressure. The XAFS Debye-Waller factor provides anharmonic effective pair potential with a pressure-dependent and temperature-independent shape. The phonon energies and anharmonicity are affected largely by the change in local structure and bonding character.
Noda, Akira*; Nakamura, Shu*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Shirai, Toshiyuki*; Tongu, Hiromu*; Soda, Hikaru*; Daido, Hiroyuki; Mori, Michiaki; Kado, Masataka; Sagisaka, Akito; et al.
International Journal of Modern Physics B, 21(3&4), p.319 - 330, 2007/02
Laser ion production has been studied for downsizing of the accelerator dedicated for cancer therapy. For optimization of various parameters such as pre-pulse condition, target position, laser spot size on target, laser pulse width and so on, time of flight (TOF) measurement utilizing the detected signal by a plastic scintillation counter played an essential role for real time measurement. Protons up to 900 keV and 600 keV are produced from the thin foil targets of Ti 3 micron and 5 micron in thickness, respectively. Modification of the energy distribution of the laser-produced ions with Maxwell distribution by utilizing an RF electric field synchronized to the pulse laser, which is the rotation of the ion beam in the longitudinal phase space (phase rotation), has been demonstrated for the first time.
Terranova, F.*; Bulanov, S. V.; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Kiriyama, Hiromitsu; Tajima, Toshiki; Collier, J. L.*; Migliozzi, P.*; Pegoraro, F.*
International Journal of Modern Physics B, 21(3&4), p.351 - 360, 2007/02
In the forthcoming decades, the physics of massive neutrinos will pose unprecedented challenges to traditional acceleration techniques. In this talk we revise the main motivations for pursuing neutrino oscillation studies with novel neutrino sources and, particularly, we consider the opportunities offered by laser-plasma accelerators. The existence of efficient ion acceleration regimes in collective laser-plasma interactions opens up the possibility to develop neutrino and, more generally, high-energy physics facilities in conjunction with projects for inertial confinement nuclear fusion (ICF) and neutron spallation sources. Moreover, parametric amplification techniques allow pulse compression implementations that do not fall in contradiction with current designs for ICF drivers. We discuss the conditions under which these efficient regimes can be put into operation and the perspectives for their empirical verification.
Mori, Michiaki; Kando, Masaki; Daito, Izuru; Kotaki, Hideyuki; Hayashi, Yukio; Ogura, Koichi; Sagisaka, Akito; Esirkepov, T. Z.; Nakajima, Kazuhisa; Daido, Hiroyuki; et al.
International Journal of Modern Physics B, 21(3&4), p.407 - 414, 2007/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Applied)The quasi-monoenergetic electron beam produced by intense laser-plasma interaction was observed at plasma densities from 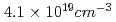 to
to 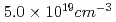 . The terawatt laser beam was focused by using an off-axis parabolic mirror with f=648 mm. We observed quasi-monoenergetic electron beams in the forward direction. The peak energy of quasi-monoenergetic component of the electron beam was increased from 9 MeV to
. The terawatt laser beam was focused by using an off-axis parabolic mirror with f=648 mm. We observed quasi-monoenergetic electron beams in the forward direction. The peak energy of quasi-monoenergetic component of the electron beam was increased from 9 MeV to  20 MeV with a energy spread of
20 MeV with a energy spread of  20
20 increasing the plasma density from
increasing the plasma density from 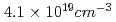 to
to 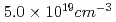 . However, the quasi-monoenergetic component of the electron beam disappeared at a plasma density of
. However, the quasi-monoenergetic component of the electron beam disappeared at a plasma density of 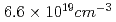 , and non-equilibrium (non Maxwellian) spectrum of the electron beam was observed. The table-top laser driven fs quasi-monoenergetic electron beam which is applicable to variety of fields has been demonstrated.
, and non-equilibrium (non Maxwellian) spectrum of the electron beam was observed. The table-top laser driven fs quasi-monoenergetic electron beam which is applicable to variety of fields has been demonstrated.
Ebihara, Kenichi; Watanabe, Tadashi
International Journal of Modern Physics B, 17(1-2), p.113 - 117, 2003/01
no abstracts in English
Yokota, Terufumi
International Journal of Modern Physics B, 15(26), p.3409 - 3417, 2001/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Physics, Applied)no abstracts in English