Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kunii, Katsuhiko; Itabashi, Keizo; Nagaya, Shun
International Journal of Nuclear Knowledge Management, 6(3), p.217 - 231, 2014/02
In regard to Fukushima Accident, it would be true that the concerned information has not been provided good enough for the affected people in and over Japan, for instance, as often being mixed, confused, too many to access or disappearing through the internet or websites. In this regard, necessary be to terminologically well line up ways to access such affected information, like a taxonomy, composed of semantically controlled terms on the related events forming lineage-like hierarchical structures. To come up with potential of the taxonomy to preserve and disseminate the affected information, described are preliminary view on its terminological aspects and availability of IAEA/INIS for the information implemented by JAEA Library. Remarks are that necessary be to make ever-new inexperienced aspects and terms derived from the affected information such as "beyond design basis" further detailed, scrutinised and involved in the both schemes, attributed to its taxonomical potential higher.
Makino, Hitoshi; Hioki, Kazumasa; Umeki, Hiroyuki; Takase, Hiroyasu*; McKinley, I. G.*
International Journal of Nuclear Knowledge Management, 5(1), p.93 - 110, 2011/00
The exponential growth in the knowledge base for radioactive waste management is a cause for concern in many national programmes. In Japan, this problem is exacerbated by a volunteering approach to siting of a deep geological repository, which requires particular flexibility in the tailoring of site characterisation plans, repository concepts and associated performance assessments. Recognition of this situation led, in 2005, to initiation by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) of an ambitious project to develop an advanced Knowledge Management System (KMS) aimed to facilitate its role as the supplier of background R&D support to both regulators and implementers of geological disposal. The paper will review progress to date in this work, with emphasis on tailoring of existing Knowledge Engineering tools and methods to radioactive waste management requirements, and outline future developments and challenges.
Yanagisawa, Kazuaki
International Journal of Nuclear Knowledge Management, 2(2), p.91 - 104, 2006/00
Taking into consideration of national funds invested to individual research divisions in JAERI during the course of safety project studies, one found that a total input was approximately corresponded to 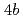 . Qualitatively, JAERI contributed to (1) the governmental policies, (2) the scientific technologies and scholarship, (3) the industries (technology transfer, patents, commissioned research etc.), (4) the local society in the lab location area, and (5) the international cooperation. Quantitatively, JAERI made the creation of added value (cost benefit), cost reduction and reduction of cost loss produced either in direct or indirect manner as research outputs. One found that a total output during the course of nuclear safety project study was approximately
. Qualitatively, JAERI contributed to (1) the governmental policies, (2) the scientific technologies and scholarship, (3) the industries (technology transfer, patents, commissioned research etc.), (4) the local society in the lab location area, and (5) the international cooperation. Quantitatively, JAERI made the creation of added value (cost benefit), cost reduction and reduction of cost loss produced either in direct or indirect manner as research outputs. One found that a total output during the course of nuclear safety project study was approximately 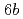 taking into consideration of nuclear market creation at electricity and facilities related to nuclear. This ex post evaluation tells that cost benefit made by nuclear safety project of JAERI is 1.5 (
taking into consideration of nuclear market creation at electricity and facilities related to nuclear. This ex post evaluation tells that cost benefit made by nuclear safety project of JAERI is 1.5 (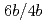 ) and such outcome contributes to the increase of general domestic products (GDP).
) and such outcome contributes to the increase of general domestic products (GDP).