Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Toigawa, Tomohiro; Hotoku, Shinobu; Kumagai, Yuta; Abe, Yuma*; Oyama, Kanichi*; Fukaya, Hiroyuki; Ban, Yasutoshi; Kida, Takashi; Hasegawa, Satoshi*; Nakano, Masanao*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 63(3), p.322 - 327, 2026/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The effect of temperature on hydrogen production generated from radiolysis was investigated to determine the associated implications for nuclear fuel reprocessing safety. The hydrogen yield from radiolysis of plutonium nitric acid solution was measured at temperatures up to the boiling temperature of the solution. The results showed no notable temperature dependence even under boiling conditions. The impact of solution agitation on hydrogen production was also assessed, which revealed minor differences in the hydrogen yield between static and agitated conditions at room temperature. These findings suggest that high temperatures or boiling the solution do not considerably enhance hydrogen generation, and provide crucial information for accurately modeling hydrogen risks under severe accidents.
Kondo, Ryoichi; Yamamoto, Akio*; Endo, Tomohiro*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 63(2), p.142 - 153, 2026/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The flux distribution tallies using proper orthogonal decomposition, called POD tallies, have been developed to address issues of high-fidelity Monte Carlo simulations. The POD tallies can reduce both dimensionality and statistical error. The present study verifies the applicability of the POD tallies to sub-pin level flux distribution in the two-dimensional C5G7 benchmark. Statistical error estimation is also proposed by applying the circular block bootstrap method to the POD tallies to estimate the statistical error of the flux distribution in a single Monte Carlo calculation. In the verification, the dimensionality of the finely discretized distribution is reduced by more than 90% compared with conventional cell tallies. The statistical error is reduced by more than half as the average value of all tally regions. The proposed approach is confirmed to properly estimate the statistical error of flux distribution considering both the inter-cycle correlation and the correlation between the expansion coefficients of different POD orders.
Watanabe, Tomoaki; Aizawa, Naoto*; Chiba, Go*; Tada, Kenichi; Fujita, Tatsuya*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 63(2), p.166 - 186, 2026/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)A fast burnup calculation method based on neutron spectrum reconstruction is proposed. The method employs a reduced-order model (ROM), constructed using proper orthogonal decomposition (POD) and regression models, to estimate neutron spectra experienced by fuel during burnup. The ROM is built from snapshot data generated through detailed burnup and neutron transport simulations under various conditions. During burnup calculations, the ROM is used to rapidly reconstruct neutron spectra at each burnup step. These reconstructed spectra are then used to compute one-group cross sections from multi-group effective cross sections derived using background cross sections. The proposed method significantly reduces computational time by avoiding repeated neutron transport simulations. Its performance is demonstrated using a PWR UO fuel pin model. Results show that, with the 6th-order POD, the method predicts nuclide inventories with an average error within
fuel pin model. Results show that, with the 6th-order POD, the method predicts nuclide inventories with an average error within  5% compared to reference Monte Carlo calculations. Error analysis indicates that prediction accuracy is primarily limited by the regression models, rather than by the POD truncation or the multi-group cross section calculations.
5% compared to reference Monte Carlo calculations. Error analysis indicates that prediction accuracy is primarily limited by the regression models, rather than by the POD truncation or the multi-group cross section calculations.
 Th as a long-life
Th as a long-life  Ac generator using the experimental fast reactor Joyo
Ac generator using the experimental fast reactor JoyoSasaki, Yuto; Maeda, Shigetaka; Fukasawa, Tetsuo*; Takaki, Naoyuki*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 63(2), p.154 - 165, 2026/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)In recent years, targeted alpha therapy, which utilizes  Ac combined with antibodies or peptides that selectively accumulate in cancer cells, has garnered attention in the field of nuclear medicine. To meet the resulting increasing demand for
Ac combined with antibodies or peptides that selectively accumulate in cancer cells, has garnered attention in the field of nuclear medicine. To meet the resulting increasing demand for  Ac, exploring alternative production methods is essential. While several researchers, including the authors, have explored production methods using
Ac, exploring alternative production methods is essential. While several researchers, including the authors, have explored production methods using  Ra as a raw material, challenges remain, such as the limited availability of
Ra as a raw material, challenges remain, such as the limited availability of  Ra, difficulties in handling it, and the requirement for regular irradiation. To address these challenges, the authors focused on developing a production strategy for a long-life
Ra, difficulties in handling it, and the requirement for regular irradiation. To address these challenges, the authors focused on developing a production strategy for a long-life  Ac generator using
Ac generator using  Th as a raw material and the experimental fast reactor Joyo. A detailed investigation was conducted, encompassing chemical processing after irradiation, target availability, and production yields, including the most probable values and associated uncertainties. Results revealed that although enrichment of the raw material and long-term irradiation are required,
Th as a raw material and the experimental fast reactor Joyo. A detailed investigation was conducted, encompassing chemical processing after irradiation, target availability, and production yields, including the most probable values and associated uncertainties. Results revealed that although enrichment of the raw material and long-term irradiation are required,  Ac can be produced in quantities comparable to its current global supply. Furthermore, this research has shown that the THOREX method, which is already in practical use, be applied to effectively separate by-products such as fission products and radioactive materials from thorium during the chemical processing after irradiation, as revealed by a literature survey.
Ac can be produced in quantities comparable to its current global supply. Furthermore, this research has shown that the THOREX method, which is already in practical use, be applied to effectively separate by-products such as fission products and radioactive materials from thorium during the chemical processing after irradiation, as revealed by a literature survey.
Fukuda, Takanari; Yamashita, Susumu; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(12), p.1264 - 1278, 2025/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study compared three interface capturing schemes (ICSs) for multi-phase flow simulations based on the VOF method, focusing on bubble volume conservation. The THINC/WLIC scheme showed significant VOF diffusion and underestimated total bubble volume, while the original THINC and PLIC conserved bubble volumes. Moreover, an analysis of THINC/WLIC based on a new visualization approach revealed that VOF fragments were ripped off by shear forces around interface, making it unsuitable for accurate void fraction prediction in boiling water reactors. The original THINC may be a viable alternative to PLIC due to its simplicity.
Nakamura, Yuki*; Kojima, Yoshihiro*; Yamashita, Takuya; Shimomura, Kenta; Mizokami, Shinya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(12), p.1226 - 1230, 2025/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) Zr(n,
Zr(n,  )
) Zr and
Zr and 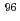 Zr(n,
Zr(n,  )
)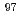 Zr reactions at JRR-3
Zr reactions at JRR-3Nakamura, Shoji; Kimura, Atsushi; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Shibahara, Yuji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 14 Pages, 2025/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)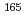 Ho(n,
Ho(n, )
)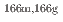 Ho reactions
Ho reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(11), p.1086 - 1099, 2025/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) , I
, I and HDO onto pre-Neogene sedimentary rocks
and HDO onto pre-Neogene sedimentary rocksHou, L.*; Fukatsu, Yuta; Okamoto, Shunichi*; Toda, Kanako*; Nakata, Kotaro*; Nohara, Shintaro*; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Saito, Takumi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(11), p.1121 - 1134, 2025/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)Takei, Hayanori
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(11), p.1051 - 1070, 2025/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Japan Atomic Energy Agency is working on the research and development of an accelerator-driven nuclear transmutation system (ADS) for transmuting minor actinides. This system combines a subcritical nuclear reactor with a high-power superconducting proton linear accelerator (JADS-linac). One of the factors limiting the advancement of the JADS-linac is beam trips, which often induce thermal cycle fatigue, thereby damaging the components in the subcritical core. The average beam current of the JADS-linac is 32 times higher than that of the linear accelerator (linac) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). Therefore, according to the development stage, comparing the beam trip frequency of the JADS-linac with the allowable beam trip frequency (ABTF) is necessary. Herein the beam trip frequency of the JADS-linac was estimated through a Monte Carlo program using the reliability functions based on the operational data of the J-PARC linac. The Monte Carlo program afforded the distribution of the beam trip duration, which cannot be obtained using traditional analytical methods. Results show that the frequency of the beam trips with a duration exceeding 5 min must be reduced to 27% of the current J-PARC linac level to be below the ABTF.
Nguyen, T. H. T.; Iwamoto, Nobuyuki; Sanami, Toshiya*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(10), p.967 - 986, 2025/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tomita, Ryohei; Tomita, Jumpei; Suzuki, Daisuke; Miyamoto, Yutaka; Yasuda, Kenichiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(10), p.939 - 948, 2025/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)A new automated particle measurement (APM) combined with micromanipulation using large geometry secondary ion mass spectrometry instrument was proposed and demonstrated to remove the particle mixing effect, which indicated that the aggregation of uranium particles was detected as a single uranium particle, from APM results. The results showed that the new APM method was more effective than the traditional APM method in removing the particle mixing effect from the APM results and determining the existence of minor uranium isotopes in the samples.
Iwamoto, Nobuyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 13 Pages, 2025/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Tomita, Jumpei; Tomita, Ryohei; Suzuki, Daisuke; Yasuda, Kenichiro; Miyamoto, Yutaka
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 12 Pages, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sato, Takuto; Nakayama, Hiromasa; Satoh, Daiki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 17 Pages, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)We developed a framework for rapid monitoring of radioactive plumes in the vicinity of nuclear facilities based on a quick and practical high-resolution atmospheric dispersion simulation method that combines a large-eddy simulation (LES) model pre-simulation database (pre-sim DB) of wind conditions and onsite meteorological observation results, as proposed by the previous study. However, this framework was not quantitatively demonstrated using measurement data. In this study, we evaluated the performance of the wind condition reproduction and plume dispersion analysis methods. Air dose rates observed at monitoring posts around the stack were compared with the values reproduced by the method using the pre-sim DB, and the reproducibility of both air dose rate and flow field was discussed. The pre-sim DB-based method successfully captured the temporal variation of air dose rates at the monitoring posts, though it tended to overestimate the peak values. Particularly when the vertical wind shear was pronounced, the method using the pre-sim DB could cause significant errors. This is likely because the method relies on wind conditions from a single observation point, which inherently limits its ability to represent vertical wind shear within the pre-sim DB. Despite these limitations, particularly in reproducing complex wind fields, the method utilizing the pre-sim DB offers a valuable and practical tool for rapid dose rate simulation due to its lower computational cost compared to unsteady simulations using an LES model.
 Co inventory in the core of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant; Contribution of fuel deposits to the reactor core inventory
Co inventory in the core of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant; Contribution of fuel deposits to the reactor core inventoryUchida, Shunsuke*; Kino, Chiaki*; Karasawa, Hidetoshi; Takahatake, Yoko; Koma, Yoshikazu
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(9), p.863 - 879, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Evaluation of radioactive nuclide behavior on and after the accident is important for the estimating radioactive nuclide composition in the wastes. The reactor core inventories have been obtained from the ORIGEN2 analysis, but the inventory of activation products is determined by the amount of their parent nuclides which are impurities contained in the structural materials. The ORIGEN2 does not treat fuel deposits including the impurities. Estimation of the initial Co-60 inventory in accurate is needed on the evaluation of some kinds of radioactive nuclide amount, since it is possible Co-60 is standard in the scaling factor. In this study, contribution of fuel deposits to the reactor core inventory was estimated by comparing the amount of Co-60 and Ni-63 calculated by the amounts of deposition by the microlayer-evaporation and drying-out model (MEDO model) and the result of the ORIGEN2 analysis, and then the method of estimating the reactor core inventory was proposed.
Yano, Yasuhide; Miyazawa, Takeshi; Tanno, Takashi; Akasaka, Naoaki; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Kaito, Takeji; Otsuka, Satoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(8), p.748 - 755, 2025/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.76(Nuclear Science & Technology)The effects of strain rate on tensile properties of irradiated modified 316 stainless steel (PNC316) claddings were investigated. PNC316 claddings were irradiated at the experimental fast reactor Joyo using CRT402 control rod assembly at 400 C up to 25 dpa. Post-irradiation ring tensile tests were carried out at strain rates of 3.3
C up to 25 dpa. Post-irradiation ring tensile tests were carried out at strain rates of 3.3 10
10 , 3.3
, 3.3 10
10 and 3.3
and 3.3 10
10 s
s at a test temperature of 350
at a test temperature of 350 C. The results showed no obvious dependence of all strain rates on tensile properties, although a slight decrease in total elongation was observed at the slowest strain rate of 3.3
C. The results showed no obvious dependence of all strain rates on tensile properties, although a slight decrease in total elongation was observed at the slowest strain rate of 3.3 10
10 s
s . In addition, only a part of fracture surface at the slowest strain rate showed intergranular type region in the inner surface area, although the grain boundary separation occurred on inner surfaces near the fracture region at all strain rates. It is suggested that presence of a high content of helium near the inner surfaces would be related to the fracture behavior.
. In addition, only a part of fracture surface at the slowest strain rate showed intergranular type region in the inner surface area, although the grain boundary separation occurred on inner surfaces near the fracture region at all strain rates. It is suggested that presence of a high content of helium near the inner surfaces would be related to the fracture behavior.
 and -MOX lattice calculations
and -MOX lattice calculationsFujita, Tatsuya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(8), p.731 - 739, 2025/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study estimated the influence of implicit effect on the k-infinity uncertainty in the PWR-UO and -MOX fuel lattice geometries. Firstly, the preliminary investigation was performed, where the influence of implicit effect was roughly estimated based on the sandwich formula using the cross-section (XS) covariance matrix and the sensitivity coefficient. It was confirmed that the influence of implicit effect became large in the fission and (n,
and -MOX fuel lattice geometries. Firstly, the preliminary investigation was performed, where the influence of implicit effect was roughly estimated based on the sandwich formula using the cross-section (XS) covariance matrix and the sensitivity coefficient. It was confirmed that the influence of implicit effect became large in the fission and (n, ) reactions of heavy nuclides and the change of this dependence was small for the burnup of UO
) reactions of heavy nuclides and the change of this dependence was small for the burnup of UO and MOX fuel assemblies. Then, focussing on the heavy nuclides, the influence of implicit effect was compared under several energy group conditions of the XS covariance matrix and neutron transport calculation. For
and MOX fuel assemblies. Then, focussing on the heavy nuclides, the influence of implicit effect was compared under several energy group conditions of the XS covariance matrix and neutron transport calculation. For  Pu and
Pu and  Pu, the noticeable influence of implicit effect was observed in MOX fuel pin-cell geometry. However, increasing the number of energy groups for neutron transport calculations and that of the XS covariance matrix can reduce the influence of implicit effect. Consequently, by appropriately setting the number of energy groups for neutron transport calculations and that of the XS covariance matrix, it became practically possible not to explicitly consider the implicit effect during the random sampling.
Pu, the noticeable influence of implicit effect was observed in MOX fuel pin-cell geometry. However, increasing the number of energy groups for neutron transport calculations and that of the XS covariance matrix can reduce the influence of implicit effect. Consequently, by appropriately setting the number of energy groups for neutron transport calculations and that of the XS covariance matrix, it became practically possible not to explicitly consider the implicit effect during the random sampling.
Sakamoto, Masahiro; Okumura, Keisuke; Kanno, Ikuo; Matsumura, Taichi; Terashima, Kenichi; Riyana, E. S.; Kaneko, Junichi*; Mizokami, Masato*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(8), p.756 - 765, 2025/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) Er(n,
Er(n, )
)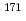 Er and
Er and  Hf(n,
Hf(n, )
) Hf reactions
Hf reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(7), p.617 - 630, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:86.98(Nuclear Science & Technology)