Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsubara, Akihiro*; Kokubu, Yoko; Nishio, Kazuhisa*; Kimura, Kenji*; Kashimura, Keiichiro*; Shimada, Koji; Fujita, Natsuko
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 568, p.165863_1 - 165863_5, 2025/11
We propose a concept for a cesium-free negative ion source based on microwave heating of granular low work function materials, which allows for both safety and high efficiency. This negative ion source features a structure where the plasma region and the negative ion generation region are adjacent within a microwave cavity. In the negative ion generation region, granular low work function materials heated by microwaves are placed. The sample gas entering the plasma region is excited, then it enters the negative ion generation region. Subsequently, it comes into contact with the surface of the low work function material, changes into negative ions, and finally, is extracted by an electric field. One advantage of this negative ion source is that, by using low work function materials in granular form, the reactive area is more than ten times larger compared to conventional negative ion sources using low work function materials.
Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Labonnote, N.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 567, p.165791_1 - 165791_20, 2025/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00The general-purpose particle and heavy ion transport code system, PHITS, developed by the Japan Atomic Energy Agency, was validated against the SINBAD, an internationally recognized benchmark experiment archive for radiation shielding. Unlike the previous PHITS benchmark against SINBAD, which primarily focused on shielding experiments for proton accelerators, this study conducted benchmarking for double-differential neutron yields, activation, residual dose, and microdosimetric quantities induced by protons, electrons, ions, and pions. This allowed for the use of models and databases not previously employed in validation studies, leading to the discovery of previously overlooked issues. While PHITS calculations generally agreed with experimental data within a factor of two, a detailed comparison revealed the need for improvements in several areas. These include: the inability of the high-energy hadron cascade model to calculate the angular momentum of residual nuclei, the underestimation of neutrons below 100 MeV in pion-induced reactions by the same model, the underestimation of proton-rich nuclei by the evaporation model, and the underestimation of high-energy secondary neutrons by the heavy-ion reaction model. These findings will be used as guidelines for future improvements to PHITS.
Yamaguchi, Yuji; Niikura, Megumi*; Mizuno, Rurie*; Tampo, Motonobu*; Harada, Masahide; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Takeshita, Soshi*; Haga, Katsuhiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 567, p.165801_1 - 165801_11, 2025/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00As part of the development of a sample radioactivity calculation program, we have measured radionuclide production probabilities in negative muon nuclear capture to update experimental data and to validate a calculation dataset obtained by a Monte Carlo simulation code. The probabilities have been obtained by an activation experiment on  Al,
Al, 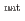 Si,
Si,  Co, and
Co, and 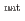 Ta targets. The obtained probabilities expand the validation scope to the radionuclide production processes outside of the existing data coverage. By comparing the resultant probabilities with the calculated dataset, it has been revealed that the dataset is generally on the safe side in radioactivity estimation and needs to be corrected in the following three cases: (i) isomer production; (ii) radionuclide production by the multiple neutron emission; (iii) radionuclide production by particle emissions involving a proton. The present probabilities and the new findings on the correction provide valuable clues to improvements of the simulation models.
Ta targets. The obtained probabilities expand the validation scope to the radionuclide production processes outside of the existing data coverage. By comparing the resultant probabilities with the calculated dataset, it has been revealed that the dataset is generally on the safe side in radioactivity estimation and needs to be corrected in the following three cases: (i) isomer production; (ii) radionuclide production by the multiple neutron emission; (iii) radionuclide production by particle emissions involving a proton. The present probabilities and the new findings on the correction provide valuable clues to improvements of the simulation models.
Morishita, Yuki; Miyamura, Hiroko; Sato, Yuki; Matsubara, Jun*; Sumali, B.*; Mitsukura, Yasue*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1076, p.170368_1 - 170368_7, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:76.46(Instruments & Instrumentation)Decommissioning nuclear reactor sites presents challenges due to the presence of various radionuclides, including alpha emitters (e.g., Pu, Am, Cm) and beta emitters (e.g.,  Cs,
Cs,  Sr-
Sr- Y), which pose significant internal exposure risks to workers. Traditional measurement methods require multiple instruments and are time-consuming, particularly in high gamma-ray environments. To address these issues, we developed a remote alpha and beta discrimination measurement system that integrates a stilbene scintillator detector with a silicon photomultiplier, enabling simultaneous detection of both alpha and beta particles. This study further incorporates machine learning techniques, specifically Support Vector Machines (SVM), for automatic discrimination, eliminating the need for user-defined thresholds and ensuring consistent operational conditions. The system was tested with known radiation sources, demonstrating over 96% classification accuracy for alpha and beta particles. Measurements conducted in motion effectively identified contamination sources, confirming the system's capability for real-time analysis. This innovative approach enhances radiation safety and efficiency in nuclear decommissioning operations, making it particularly beneficial in environments where human access is limited.
Y), which pose significant internal exposure risks to workers. Traditional measurement methods require multiple instruments and are time-consuming, particularly in high gamma-ray environments. To address these issues, we developed a remote alpha and beta discrimination measurement system that integrates a stilbene scintillator detector with a silicon photomultiplier, enabling simultaneous detection of both alpha and beta particles. This study further incorporates machine learning techniques, specifically Support Vector Machines (SVM), for automatic discrimination, eliminating the need for user-defined thresholds and ensuring consistent operational conditions. The system was tested with known radiation sources, demonstrating over 96% classification accuracy for alpha and beta particles. Measurements conducted in motion effectively identified contamination sources, confirming the system's capability for real-time analysis. This innovative approach enhances radiation safety and efficiency in nuclear decommissioning operations, making it particularly beneficial in environments where human access is limited.
 Sn using the GRIFFIN spectrometer at TRIUMF
Sn using the GRIFFIN spectrometer at TRIUMFSyeda, N. K.*; Smallcombe, J.; 44 of others*
Nuclear Physics A, 1059, p.123090_1 - 123090_5, 2025/07
Vu, TheDang*; Shishido, Hiroaki*; Aizawa, Kazuya; Oku, Takayuki; Oikawa, Kenichi; Harada, Masahide; Kojima, Kenji M*; Miyajima, Shigeyuki*; Soyama, Kazuhiko; Koyama, Tomio*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1075, p.170425_1 - 170425_9, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)
 He neutron spin filter at J-PARC
He neutron spin filter at J-PARCTakahashi, Shingo; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Okudaira, Takuya*; Takada, Shusuke*; Kobayashi, Ryuju; Okuizumi, Mao; Ino, Takashi*; Asai, Kanta*; Tsuchikawa, Yusuke; Oikawa, Kenichi; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1075, p.170410_1 - 170410_8, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Sasaki, Miyuki; Abe, Yuki*; Sanada, Yukihisa; Torii, Tatsuo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1072, p.170207_1 - 170207_12, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have developed an omnidirectional radiation imager with fractal geometry named the FRIE system. This paper presents the development and evaluation of the FRIE system, designed to accurately estimate radioactivity distribution within decommissioning environments, such as the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The FRIE system is a unit of tetrahedral radiation sensors; 16 sensors are arranged in a Sierpinski tetrahedron shape, and the space between the sensors is filled with tungsten-based alloy for radiation shielding. This study assessed the performance of the FRIE system in estimating radiation distribution through simulations and actual measurement tests. From the results of the simulations and experimental data, it was confirmed that by maintaining a measurement density of at least 2 points/m , limiting the positional error to within
, limiting the positional error to within  10 cm, and the angular error to within
10 cm, and the angular error to within  10 degrees, it is possible to estimate the source location with an angular resolution of approximately 30 degrees. Future improvements in the arrangement of the FRIE system's crystals and shielding should enhance the performance metrics. This research signifies a pioneering implementation of fractal-based radiation imaging technology, offering a new direction in radiation measurement.
10 degrees, it is possible to estimate the source location with an angular resolution of approximately 30 degrees. Future improvements in the arrangement of the FRIE system's crystals and shielding should enhance the performance metrics. This research signifies a pioneering implementation of fractal-based radiation imaging technology, offering a new direction in radiation measurement.
 experiment using a
experiment using a  Cf calibration source
Cf calibration sourceLee, D. H.*; Dodo, Taku; Haga, Katsuhiro; Harada, Masahide; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Masuda, Shiho; Meigo, Shinichiro; Sakai, Kenji; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1072, p.170216_1 - 170216_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:91.88(Instruments & Instrumentation)Guembou Shouop, C. J.; Tsuchiya, Harufumi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1072, p.170189_1 - 170189_14, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:57.55(Instruments & Instrumentation)Sari, A.*; Meleshenkovskii, I.*; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Tran, K.-T.*; Jinaphanh, A.*; Jouanne, C.*; Zoia, A.*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1072, p.170168_1 - 170168_17, 2025/03
Electron accelerators cover a wide range of applications, from nuclear waste package assay and security-related tasks to radiation therapy. High-energy photons produced by electron Bremsstrahlung radiation might induce photonuclear reactions emitting secondary neutrons. In this paper, we perform a two-stage benchmark for Monte Carlo simulation of photoneutron fields from electron accelerators operating in the 4-20 MeV range. On the one hand, we benchmark three independently developed Monte Carlo codes, i.e., MCNP, TRIPOLI-4; and PHITS, using ENDF7u photonuclear data from the ENDF/B-VII.1 library. On the other hand, we benchmark two photonuclear data sub-libraries, i.e., ENDF7u and JENDL-5, as well as nuclear reaction models, using the PHITS code. Errors in ENDF7u for W-184 and Ta-181 cause unphysical shapes of the photoneutron energy spectra with the three codes. Questionable behaviors are also found with JENDL-5, which calls for further examinations in this recently released library. For the cases of heavy water and beryllium, the photoneutron energy spectra obtained with MCNP6 is invalidated. We identified that the problem stems from wrong treatment of the reference frame in using the ACE data files by MCNP and previous versions of PHITS. Results obtained for tungsten and tantalum show that photoneutrons are overall emitted in an isotropic manner. However, results obtained for heavy water and beryllium display different tendencies. This investigation should help Monte Carlo code users to refine the current validity domain of the latest releases of MCNP6, PHITS and TRIPOLI-4 for the simulation of photoneutrons.
 Sr/
Sr/ Y inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Unit 3 reactor building using a liquid light guide Cherenkov counter
Y inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Unit 3 reactor building using a liquid light guide Cherenkov counterTerasaka, Yuta; Sato, Yuki; Furuta, Yoshihiro*; Kubo, Shin*; Ichiba, Yuta*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1070, Part 2 , p.170021_1 - 170021_9, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:35.22(Instruments & Instrumentation)Costantini, J.-M.*; Guillaumet, M.*; Lelong, G.*; Ishikawa, Norito; Seo, P.*; Yasuda, Kazuhiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 558, p.165567_1 - 165567_6, 2025/01
Radiation damage is studied in ion-irradiated sintered CeO and (Ce, Gd)O
and (Ce, Gd)O samples. Near Infra-red (NIR) spectra measurements were carried out by using the diffuse reflectivity mode for all of these sintered samples. Samples were irradiated with 100-MeV Kr, 200-MeV Xe, and 36-MeV W ions. Four broad absorption bands centered at 3700, 4100, 6000, and 7600 cm
samples. Near Infra-red (NIR) spectra measurements were carried out by using the diffuse reflectivity mode for all of these sintered samples. Samples were irradiated with 100-MeV Kr, 200-MeV Xe, and 36-MeV W ions. Four broad absorption bands centered at 3700, 4100, 6000, and 7600 cm (i.e. 0.46, 0.51, 0.74, and 0.94 eV) are deduced from fits of the FTIR spectra for the ion-irradiated CeO
(i.e. 0.46, 0.51, 0.74, and 0.94 eV) are deduced from fits of the FTIR spectra for the ion-irradiated CeO and (Ce, Gd)O
and (Ce, Gd)O samples accompanied by a change in color from ivory to green. No such bands are recorded for the virgin (Ce, Gd)O
samples accompanied by a change in color from ivory to green. No such bands are recorded for the virgin (Ce, Gd)O samples with 5, 10, and 15 mol Gd
samples with 5, 10, and 15 mol Gd O
O with an increasing amount of oxygen vacancies. Absorption bands are tentatively assigned to electronic transitions involving cerium vacancy levels in the band gap, which has been also observed under high-energy electron irradiation.
with an increasing amount of oxygen vacancies. Absorption bands are tentatively assigned to electronic transitions involving cerium vacancy levels in the band gap, which has been also observed under high-energy electron irradiation.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Matsuda, Hiroki*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Yonehara, Katsuya*; Pellemoine, F.*; Liu, Z.*; Lynch, K.*; Yoshida, Makoto*; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Yoshiie, Toshimasa*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 557, p.165543_1 - 165543_8, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:35.22(Instruments & Instrumentation)The number of displacements per atom is widely used as an indicator of irradiation damage to materials in proton accelerator facilities. Experiments have been carried out on protons below 3 GeV to verify the dpa of metallic materials. However, the dpa for high-energy protons above 3 GeV has not been measured. In order to validate the displacement cross sections of metals in the high-energy region, the electrical resistivity changes of aluminium, copper and tungsten wires at a temperature of 8 K were measured using protons with energy of 120 GeV. The results show that the conventional irradiation damage model of PHITS overestimates the experimental data. On the other hand, the calculation results using the athermal recombination correction model were in agreement with the experimental data.
Jinno, Satoshi; Matsubara, Akihiro*; Fujita, Natsuko; Kimura, Kenji
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 557, p.165545_1 - 165545_4, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:35.22(Instruments & Instrumentation)This study introduces the development of a downsized Accelerator Mass Spectrometry (AMS) system aiming to enhance accessibility and cost-effectiveness in radiocarbon analysis. The "crystal surface stripper method" is introduced as a solution to challenges in AMS downsizing, demonstrating effective ion detection with a smaller angular spread compared to conventional gas stripper methods. The experimental results provide insights into charge conversion capabilities, scattering angle broadening, and energy loss associated with surface scattering.
Teshigawara, Makoto; Lee, Y.*; Tatsumoto, Hideki*; Hartl, M.*; Aso, Tomokazu; Iverson, E. B.*; Ariyoshi, Gen; Ikeda, Yujiro*; Hasegawa, Takumi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 557, p.165534_1 - 165534_10, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:35.22(Instruments & Instrumentation)At Japanese Spallation Neutron Source in J-PARC, the para-hydrogen fraction was measured by using Raman spectroscopy in-situ for an integrated beam power of 9.4 MW h at 1 MW operation, to evaluate the functionality of the ferric oxyhydroxide catalyst. This result showed that full functionality of the catalyst was retained up to the 1 MW operation. We attempted to study the effect of neutron scattering driven para to ortho-hydrogen back-conversion rate in the absence of the catalyst effect with a bypass line without catalyst. The measured increase of ortho-hydrogen fraction was 0.44% for an integrated beam power of 2.4 MW
h at 1 MW operation, to evaluate the functionality of the ferric oxyhydroxide catalyst. This result showed that full functionality of the catalyst was retained up to the 1 MW operation. We attempted to study the effect of neutron scattering driven para to ortho-hydrogen back-conversion rate in the absence of the catalyst effect with a bypass line without catalyst. The measured increase of ortho-hydrogen fraction was 0.44% for an integrated beam power of 2.4 MW h at 500 kW operation, however, which was considered to be due to not only to neutron collisions in cold moderators but also to the high ortho-hydrogen fraction of initially static liquid hydrogen in the bypass line and passive exudation of quasi-static hydrogen in the catalyst vessel to the main loop.
h at 500 kW operation, however, which was considered to be due to not only to neutron collisions in cold moderators but also to the high ortho-hydrogen fraction of initially static liquid hydrogen in the bypass line and passive exudation of quasi-static hydrogen in the catalyst vessel to the main loop.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Hashimoto, Shintaro; M rquez Dami
rquez Dami n, J. I.*; Niita, Koji*
n, J. I.*; Niita, Koji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 557, p.165535_1 - 165535_8, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)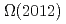 from QCD sum rules
from QCD sum rulesSu, N.*; Chen, H.-X.*; Gubler, P.; Hosaka, Atsushi
Nuclear and Particle Physics Proceedings, 347, p.2 - 5, 2024/12
Oguri, Kaori; Hagura, Naoto*; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Okumura, Masahiko; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Tsunashima, Yasumichi; Aoki, Katsumi; Arai, Yoichi; Watanabe, So
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 556, p.165516_1 - 165516_8, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ningyo-toge is the uranium mine that has been operated in Japan. Various radioactive elements such as Uranium (U), and Radium (Ra) are still present in the mine ground water with very small amount, and behavior of those elements is not fully understood. In this study, we investigated the composition of metal oxides and clay minerals in a soil of slag deposit at the mine, and systematics of adsorption structure of various ions were examined. Identifying the composition and chemical forms of minerals present in the soil of slag can provide useful information for the safety assessment and evaluation of influence on the surrounding environment.
Minowa, Kazuki*; Watanabe, So; Nakase, Masahiko*; Takahatake, Yoko; Miyazaki, Yasunori; Ban, Yasutoshi; Matsuura, Haruaki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 556, p.165496_1 - 165496_6, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)In this study, X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) spectral analysis and column experiments were used to verify the selectivity of rare earth (RE) ions by alkyl diamide amine (ADAAM) adsorbent. In addition, the interactions between the N atoms of ADAAM and RE ions were evaluated to determine whether any of the RE ions are a valid simulant for developing a mutual separation process for minor actinides (MAs) in highly radioactive liquid waste. It was confirmed that La and Ce interacted with the amine N atom of ADAAM and they showed a peak shift of the N-K edge XANES spectrum; this finding suggested that a soft interaction is an essential factor influencing ion selectivity. Therefore, the selection factor of RE ions by ADAAM adsorbent was similar to that of MAs. It was concluded that RE ions are reasonable species to simulate MAs.