Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakayama, Masashi; Sato, Haruo; Sugita, Yutaka; Ito, Seiji*; Minamide, Masashi*; Kitagawa, Yoshito*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.51 - 56, 2011/01
In Japan, any high level radioactive waste repository is to be constructed at over 300 m depth below surface. Tunnel support is used for safety during the construction and operation, and shotcrete and concrete lining are used as the tunnel support. Concrete is a composite material comprised of aggregate, cement and various additives. Low alkaline cement has been developed for the long term stability of the barrier systems whose performance could be negatively affected by highly alkaline conditions arising due to cement used in a repository. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has developed a low alkaline cement, named as HFSC (Highly fly-ash contained silicafume cement), containing over 60wt% of silica-fume (SF) and fly-ash (FA). HFSC was used experimentally as the shotcrete material in construction of part of the 140 m deep gallery in Horonobe URL. The objective of this experiment was to assess the performance of HFSC shotcrete in terms of mechanics, workability, durability, and so on. HFSC used in this experiment is composed of 40wt% OPC (Ordinary Portland Cement), 20wt% SF, and 40wt% FA. This composition was determined based on mechanical testing of various mixes of the above components. Because of the low OPC content, the strength of HFSC tends to be lower than that of OPC in normal concrete. The total length of tunnel using HFSC shotcrete is about 73 m and about 500 m of HFSC was used. The workability of HFSC shotcrete was confirmed in this experimental construction.
of HFSC was used. The workability of HFSC shotcrete was confirmed in this experimental construction.
Takeda, Seiji; Kimura, Hideo
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.131 - 140, 2011/01
Clearance levels for the solid materials contaminated with uranium were estimated based on deterministic dose calculation approach for metal reuse scenario. The activity concentrations for major radionuclides, U-234, U-235 and U-238, were calculated to be 1.5 Bq/g, 1.4 Bq/g and 1.8 Bq/g, respectively. In order to confirm the validity of the calculated concentrations, the authors estimated the uncertainties on scenario description after metal recycling and on parameter values used in the deterministic calculation. The validity of the calculated activity concentrations by the deterministic approach was confirmed from the results of both the analysis for an additional scenario on the landfill disposal of residue of slag after metal recycling and the Monte Carlo-based analysis for parameter uncertainties.
 with DTAB and F-pentanol for decontamination of radioactive wastes
with DTAB and F-pentanol for decontamination of radioactive wastesKurahashi, Kensuke; Tomioka, Osamu; Meguro, Yoshihiro
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.217 - 220, 2011/01
To develop a metal separation method using supercritical CO (scCO
(scCO ) solvent for the decontamination process of radioactive wastes, the reverse micelle formation in scCO
) solvent for the decontamination process of radioactive wastes, the reverse micelle formation in scCO was investigated. Dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide (DTAB) as a surfactant to form the reverse micelles and 2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5-octafluoro-1-pentanol (F-pentanol) as a modifier to increase the solubility of DTAB into scCO
was investigated. Dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide (DTAB) as a surfactant to form the reverse micelles and 2,2,3,3,4,4,5,5-octafluoro-1-pentanol (F-pentanol) as a modifier to increase the solubility of DTAB into scCO were used. The reverse micelles could be formed by using 0.02 mol/dm
were used. The reverse micelles could be formed by using 0.02 mol/dm DTAB and 0.45 mol/dm
DTAB and 0.45 mol/dm F-pentanol. A water concentration dissolved in scCO
F-pentanol. A water concentration dissolved in scCO was increased with an increase of pressure, and 0.42 mol/dm
was increased with an increase of pressure, and 0.42 mol/dm water, which was 3 times larger than that in the neat CO
water, which was 3 times larger than that in the neat CO , could be dissolved in scCO
, could be dissolved in scCO at 38 MPa. Moreover, 0.1 mol/dm
at 38 MPa. Moreover, 0.1 mol/dm HNO
HNO could dissolve at the same pressure as water. On the other hand, it was found that the solubility of water at outside of reverse micelles increased with F-pentanol. The ratio of water and F-pentanol affected the phase behavior of water in scCO
could dissolve at the same pressure as water. On the other hand, it was found that the solubility of water at outside of reverse micelles increased with F-pentanol. The ratio of water and F-pentanol affected the phase behavior of water in scCO .
.
Hanamuro, Takahiro; Yasue, Kenichi; Kokubu, Yoko; Asamori, Koichi; Ishimaru, Tsuneari; Umeda, Koji
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.25 - 30, 2011/01
Japanese islands are located in a tectonically active zone, where earthquakes and volcanic eruptions frequently occur. Therefore the understanding of the long-term stability of geological environment is important when assessing the long-term behaviour of the geological disposal system of high level radioactive waste (HLW) in Japan. The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) is promoting the establishment of investigation and assessment methods of the long-term stability of geological environment necessary for site selection and safety assessment of HLW geological disposal.
Matsuoka, Toshiyuki; Amano, Kenji; Osawa, Hideaki; Semba, Takeshi
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.169 - 173, 2010/10
It is important for site characterization project to manage decision-making process during site characterization project with transparency and traceability, and to accumulate and hand technical know-how on to the next generation. Evaluation of the impact of uncertainties in the geological environment model is important to identify and prioritize key issues for further investigations. The aim of the study is to support for the planning of initial surface-based site characterization based on the technical know-how accumulating from Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory Project and Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory project. In this study, the task-flow of the geological modeling, which is one of the geological environment models, and the related technical know-how using literature data have been summarized.
Ishimori, Kenichiro; Kameo, Yutaka; Nakashima, Mikio*; Takahashi, Kuniaki
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.117 - 123, 2010/10
Yokota, Hideharu; Yamamoto, Yoichi; Maekawa, Keisuke; Hara, Minoru*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.81 - 86, 2010/10
It is important for assessing the safety of geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste to understand groundwater flow as the driving force of mass transport. In the groundwater-flow simulation, hydraulic boundary conditions are required, including groundwater recharge rates. However, infiltration of water from the surface is difficult to clarify in detail because water near the surface is sensitive to external influence such as climatic variations. In the Horonobe area of northern Hokkaido, the Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been carrying out various hydrological observations to estimate the recharge rate. In the Horonobe area, subsurface temperature and soil moisture content have been observed at HGW-1 site and Hokushin Meteorological Station. These results have revealed the groundwater infiltration and recharge occurring throughout year, the shallow groundwater-infiltration velocity depending on the depth, and the position of Zero Flux Plane. In the future, it is necessary to quantitatively assess the shallow groundwater infiltration and recharge rate, the intermediate runoff, and the evapotranspiration based on the observed data of the weighing lysimeter, the tensiometer, and so on.
Kawamura, Makoto*; Tanikawa, Shinichi; Niizato, Tadafumi; Yasue, Kenichi
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.331 - 338, 2010/10
In order to assess the long-term safety of a geological disposal system for high-level radioactive waste (HLW), it is important to consider the impact of uplift and erosion, which cannot be precluded on a timescale in the order of several hundred thousand years for many locations in Japan. Geomorphic evolution, caused by uplift and erosion and coupled to climatic and sea-level changes, will impact the geological disposal system due to resulting spatial and temporal changes in the disposal environment. Degradation of HLW barrier performance will be particularly significant when the remnant repository structures near, and are eventually exposed at, the ground surface. In previous studies, fluvial erosion was identified as the key concern in most settings in Japan. Here, therefore, we present a methodology for development of a generic conceptual model for performance assessment based on best current understanding of fluvial erosion in Japan. Critical considerations that have to be taken into account when interpreting the geological record of past river-valley evolutions, as preserved in ancient fluvial deposits. Interpretation of the impact of such phenomena at relevant locations in Japan has led to development of a generic conceptual model which contains the features typical at middle reach of rivers. This paper presents the methodology to develop the conceptual model, which identifies the simplifications and uncertainties involved and assesses their consequences in the context of repository performance.
Zaima, Naoki; Morimoto, Yasuyuki; Sugitsue, Noritake; Kado, Kazumi
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.311 - 320, 2010/10
Amamoto, Ippei; Mitamura, Naoki*; Tsuzuki, Tatsuya*; Takasaki, Yasushi*; Shibayama, Atsushi*; Yano, Tetsuji*; Nakada, Masami; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.503 - 508, 2010/10
The main objective of this development is to recycle the purified eutectic medium of the pyroreprocessing, delaying its disposal for as long as possible. We have introduced the simple filtration method to remove the rare earth element (REE) particles which were formed due to the conversion of REE chlorides to phosphates. Here, the iron phosphate glass is used as a filtration medium for the removal of FP particles. However, some soluble FP such as compounds of alkali-metals, alkaline-earth metals, etc. still remain in the eutectic medium. This time around, on an experimental basis, the iron phosphate glass has been used as a sorbent instead, to remove the soluble FP. We have obtained some positive results and have intention to incorporate it into the spent electrolyte recycle process as a part of the FP separation and immobilization system.
Sanada, Hiroyuki; Nakamura, Takahiro; Sugita, Yutaka
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.31 - 39, 2010/10
As part of the research and development program on the HLW geological disposal, JAEA has been implementing the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (URL) project investigating sedimentary rock formations distributed in Horonobe area, Hokkaido, Japan. The authors have been implementing the research and development program at Horonobe to clarify the in situ stress conditions in siliceous mudstones at the URL. The objective of this work is to establish a strategy for an in situ stress measurement program for geological disposal and to develop an understanding of the in situ stress conditions in the deep underground formed by the sedimentary rocks. The application of several stress measurement methods to the Horonobe siliceous mudstones carried out during the surface-based investigations and the investigations during construction of the underground facilities, as well as information on the initial stress state around the Horonobe URL are described in this paper.
Aosai, Daisuke; Yamamoto, Yuhei; Mizuno, Takashi
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.213 - 220, 2010/10
Size distribution of elements in groundwater is one of the most important information for understanding behavior of elements in deep underground environment. Size distribution is controlled mainly by groundwater physico-chemical parameters. Because the alteration of their physico-chemical states in groundwater cause changes of size distribution, systematic methodologies of ultrafiltration maintaining in-situ pressurized and anaerobic conditions is required. In this study, instrument for ultrafiltration maintaining in-situ pressurized/anaerobic conditions was developed and size distribution analysis was also conducted. The instrument developed in this study for consisted of passivated SUS materials is designed as to keep inner groundwater sample under a pressurized/anaerobic condition. Ultrafiltration was conducted at a borehole drilled from sub-stage at a depth of 200 m at the Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory site. The results obtained here indicate that ultrafiltration method is available for collection of filtered groundwater and passivation is an essential treatment before ultrafiltration.
Kunimaru, Takanori; Ota, Kunio; Amano, Kenji; Alexander, W. R.*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.159 - 168, 2010/10
Tokiwa, Tetsuya; Asamori, Koichi; Hiraga, Naoto*; Yamada, Osamu; Moriya, Hirokazu*; Hotta, Hikaru*; Kitamura, Itaru*; Yokota, Hideharu
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.117 - 122, 2010/10
In this paper, we discuss the relationship between the accurate hypocentral distribution and 3-D geological structure in and around the Horonobe area, Japan. We carried out multiplet-clustering analysis by using data of the 421 micro-earthquakes which occurred from 1st September, 2003 to 30th September, 2007. The 3-D geological structure model was mainly constructed from previous seismic reflection profiles and drilling data. As a result of this analysis, although there are some differences in depth between them, the hypocenters are distributed in NNW-SSE direction and become deeper from the west toward the east. The distributed pattern of the hypocenters is similar to the one of the geological structure. These results indicate that the hypocentral distribution may represent existence of active zone related to the geological structure, and provide effective information which can contribute to establishing methods for estimating the future evolution of the geological environment.
Tokiwa, Tetsuya; Asamori, Koichi; Niizato, Tadafumi; Nohara, Tsuyoshi; Matsuura, Yuki*; Kosaka, Hideki*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.407 - 413, 2010/10
In this study, we present the preliminary results for the estimation of a horizontal crustal movement by using geodetic and geological approach in the Horonobe area, northern Hokkaido, Japan. The estimations have been carried out by using a GPS data and a geological cross section obtained by applying balanced-section method. As results of this study, both of the shortening rates estimated by GPS data and balanced-section method indicate several millimeters per year. Namely, there is no contradiction between geodetic and geological data, and it is considered that Horonobe area is still situated similar tendency and magnitude of a crustal movement. Geodetic data is not usually used to evaluate the long-term crustal movement. However, the results of this study indicate that geodetic data provide valuable information for estimating the long-term crustal movement in the area.
Maekawa, Keisuke; Makino, Hitoshi; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Niizato, Tadafumi; Inagaki, Manabu; Kawamura, Makoto*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.71 - 80, 2010/10
It is important for establishing safety assessment techniques of HLW geological disposal to understand groundwater flow and solute transport. We have carried out groundwater flow and solute transport analysis using geological and hydrological information from surface-based investigations in the Horonobe area. From this study, a methodology to integrate activities from site investigations and evaluation to solute transport analysis was tested. We have been also carrying out a simulation of groundwater flow and salinity concentration distribution using information on geological evolution considering the impacts of natural events and processes. From the result, we could outline the impacts of natural events and processes on geological environments. We plan to apply a methodology of groundwater flow and solute transport analysis to the shallow part, the Horonobe coastal area. It must be important techniques in support of generic safety assessment for future geologic disposal in Japan.
Sasao, Eiji
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.57 - 64, 2010/10
Long-term stability of the geological environment is one of the important keys for geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste in the Japanese Islands due to their location in a tectonically active island-arc. Uranium occurrences in Japan have been subjected to many geological processes inherent to the island-arc setting. Mode of occurrence of the uranium mineralization can be instructive as these could provide useful information on the long-term stability of the geological environment. Uranium mineralization is mainly in Tertiary sedimentary rocks and granitic rocks and less commonly in Cretaceous and Paleo/Mesozoic sedimentary sequences or metamorphic rocks. A variety of rocks host the Japanese uranium mineralization suggesting that geological environments suitable for geological isolation are widely distributed in the Japanese Islands, despite their location in a geologically active area. This effort will support building confidence in deep geological disposal.
Ota, Kunio; Amano, Kenji; Niizato, Tadafumi; Alexander, W. R.*; Yamanaka, Yoshiaki*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.123 - 132, 2010/10
The assurance of the long-term stability of the geological environment is 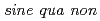 for deep geological disposal. In Japan, since uplift/subsidence and climatic and sea-level changes would result in a significant change to hydraulic and hydrochemical conditions at coastal sites, it is of importance to establish comprehensive techniques for characterising the overall evolution of coastal sites over geological time. To this end, palaeohydrogeological study is ongoing in the coastal area around Horonobe in northern Hokkaido. A "Geosynthesis Data Flow Diagram" defining a methodology for characterising the palaeohydrogeological evolution of the site has been formulated and, based on the geosynthesis methodology, a basic strategy has been established for stepwise investigations from initial survey of existing information to the final borehole programme at any coastal site. This technique has now been tested and optimised with the progress of the investigations.
for deep geological disposal. In Japan, since uplift/subsidence and climatic and sea-level changes would result in a significant change to hydraulic and hydrochemical conditions at coastal sites, it is of importance to establish comprehensive techniques for characterising the overall evolution of coastal sites over geological time. To this end, palaeohydrogeological study is ongoing in the coastal area around Horonobe in northern Hokkaido. A "Geosynthesis Data Flow Diagram" defining a methodology for characterising the palaeohydrogeological evolution of the site has been formulated and, based on the geosynthesis methodology, a basic strategy has been established for stepwise investigations from initial survey of existing information to the final borehole programme at any coastal site. This technique has now been tested and optimised with the progress of the investigations.
Kamei, Gento; Alexander, W. R.*; Clark, I. D.*; Degnan, P.*; Elie, M.*; Khoury, H.*; Milodowski, A. E.*; Pitty, A. F.*; Salameh, E.*; Smellie, J. A. T.*
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.141 - 147, 2010/10
Iyatomi, Yosuke; Hoshina, Hiroyuki; Seko, Noriaki; Kasai, Noboru; Ueki, Yuji; Tamada, Masao
Proceedings of 13th International Conference on Environmental Remediation and Radioactive Waste Management (ICEM 2010) (CD-ROM), p.485 - 490, 2010/10