Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Osawa, Takahito; Nagasawa, Shunsaku*; Ninomiya, Kazuhiko*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; Nakamura, Tomoki*; Wada, Taiga*; Taniguchi, Akihiro*; Umegaki, Izumi*; Kubo, Kenya*; Terada, Kentaro*; et al.
ACS Earth and Space Chemistry (Internet), 7(4), p.699 - 711, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:72.47(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The concentrations of carbon and other major elements in asteroid samples provide very important information on the birth of life on the Earth and the solar-system evolution. Elemental analysis using muonic X-rays is one of the best analytical methods to determine the elemental composition of solid materials, and notably, is the only method to determine the concentration of light elements in bulk samples in a non-destructive manner. We developed a new analysis system using muonic X-rays to measure the concentrations of carbon and other major elements in precious and expectedly tiny samples recovered from the asteroid Ryugu by spacecraft Hayabusa2. Here we report the development process of the system in 4 stages and their system configurations, The analysis system is composed of a stainless-steel analysis chamber, an acrylic glove box for manipulating asteroid samples in a clean environment, and Ge semiconductor detectors arranged to surround the analysis chamber. The performance of the analysis system, including the background level, which is crucial for the measurement, was greatly improved from the first stage to the later ones. Our feasibility study showed that the latest model of our muonic X-ray analysis system is capable of determining the carbon concentration in Hayabusa2's sample model with an uncertainty of less than 10 percent in a 6-day measurement.
Francisco, P. C. M.; Tachi, Yukio
ACS Earth and Space Chemistry (Internet), 4(12), p.2366 - 2377, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.06(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) as a source of atmospheric I
as a source of atmospheric I
Watanabe, Kosuke*; Matsuda, Shohei; Cuevas, C. A.*; Saiz-Lopez, A.*; Yabushita, Akihiro*; Nakano, Yukio*
ACS Earth and Space Chemistry (Internet), 3(4), p.669 - 679, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:46.78(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)The photooxidation of aqueous iodide ions (I
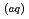 ) at sea surface results in the emission of gaseous iodine molecules (I
) at sea surface results in the emission of gaseous iodine molecules (I
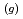 ) into the atmosphere. It plays a certain role in the transport of iodine from ocean to the atmosphere in the natural cycle of iodine. In this study, we determined the photooxidation parameters, the molar absorption coefficient (
) into the atmosphere. It plays a certain role in the transport of iodine from ocean to the atmosphere in the natural cycle of iodine. In this study, we determined the photooxidation parameters, the molar absorption coefficient (
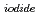 (
( )) and the photooxidative quantum yields (
)) and the photooxidative quantum yields (
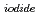 (
( )) of I
)) of I
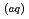 , in the range of 290-500 nm. Through the investigation of the influence of pH and dissolved oxygen (DO) on
, in the range of 290-500 nm. Through the investigation of the influence of pH and dissolved oxygen (DO) on 
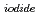 (
( ), the subsequent emission rates of I
), the subsequent emission rates of I
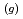 following the photooxidation of I
following the photooxidation of I
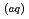 in deionized water solution (pH 5.6, DO 7.8 mg L
in deionized water solution (pH 5.6, DO 7.8 mg L ) and artificial seawater solution (pH 8.0, DO 7.0 mg L
) and artificial seawater solution (pH 8.0, DO 7.0 mg L ) were estimated. A global chemistry-climate model employed herein to assess the I
) were estimated. A global chemistry-climate model employed herein to assess the I
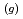 ocean emission on a global scale indicated that the photooxidation of I
ocean emission on a global scale indicated that the photooxidation of I
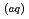 by solar light can enhance the atmospheric iodine budget by up to
by solar light can enhance the atmospheric iodine budget by up to  8% over some oceanic regions.
8% over some oceanic regions.
Yu, Q.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Kozai, Naofumi; Sakamoto, Fuminori; Tani, Yukinori*; Onuki, Toshihiko
ACS Earth and Space Chemistry (Internet), 2(8), p.797 - 810, 2018/08
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:54.42(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Most of Mn oxides are biogenic and known to adsorb cesium (Cs) on the surface. This study investigated structural transformation of biogenic birnessite by accommodating commonly occurring natural heavy metals (Zn, Ni) during the formation of Mn oxides and the influence of those metals on the adsorption behavior of Cs on Mn oxides. It was found that the presence of heavy metals during bio-oxidation of Mn(II), followed by exposure to a low pH aqueous solution, increased the number of available layer vacancies, which consequently increased the adsorption capacity of Cs in the final product birnessite.