Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
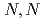 -dioctylthiodiglycolamic acid; Effect of S donor on metal extraction
-dioctylthiodiglycolamic acid; Effect of S donor on metal extractionShimojo, Kojiro; Fujiwara, Iori*; Saito, Takumi*; Oshima, Tatsuya*
Analytical Sciences, 40(8), p.1429 - 1436, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)Extraction ability of 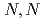 -dioctylthiodiglycolamic acid (T-DODGAA), a soft-base sulfur donor ligand with an amide group and a carboxylic acid connected by a thioether chain, for 56 metal ions have been comprehensively investigated and compared with that of N,N-dioctyldiglycolamic acid (DODGAA) with an etheric oxygen atom, a hard-base donor. The p
-dioctylthiodiglycolamic acid (T-DODGAA), a soft-base sulfur donor ligand with an amide group and a carboxylic acid connected by a thioether chain, for 56 metal ions have been comprehensively investigated and compared with that of N,N-dioctyldiglycolamic acid (DODGAA) with an etheric oxygen atom, a hard-base donor. The p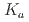 of the thiodiglycolamic acid framework was determined to be 3.71
of the thiodiglycolamic acid framework was determined to be 3.71  0.06 in water (0.1 M LiCl, 25
0.06 in water (0.1 M LiCl, 25 C ) by potentiometric titration, indicating that T-DODGAA is a slightly weaker acid than DODGAA (p
C ) by potentiometric titration, indicating that T-DODGAA is a slightly weaker acid than DODGAA (p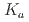 = 3.54
= 3.54  0.03). T-DODGAA can quantitatively extract various metal ions from the 56 metal ions through a proton-exchange reaction. T-DODGAA provided higher extraction performance than DODGAA for Hf(IV), Cr(III), Fe(III), Ni(II), Cu(II), Pd(II), Ag(I), Au(III), Hg(II), Al(III), and Ga(III), especially for soft metal ions. Furthermore, to demonstrate the practical feasibility of T-DODGAA for hydrometallurgy and metal recycling, we performed selective separation tests of rare metal ions such as Sc(III), Ni(II), Co(II), Pd(II), Au(III), In(III), and Ga(II) in metal-mixed extraction systems.
0.03). T-DODGAA can quantitatively extract various metal ions from the 56 metal ions through a proton-exchange reaction. T-DODGAA provided higher extraction performance than DODGAA for Hf(IV), Cr(III), Fe(III), Ni(II), Cu(II), Pd(II), Ag(I), Au(III), Hg(II), Al(III), and Ga(III), especially for soft metal ions. Furthermore, to demonstrate the practical feasibility of T-DODGAA for hydrometallurgy and metal recycling, we performed selective separation tests of rare metal ions such as Sc(III), Ni(II), Co(II), Pd(II), Au(III), In(III), and Ga(II) in metal-mixed extraction systems.
Miyagawa, Akihisa*; Hayashi, Naoki*; Iwamoto, Hibiki*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Nagatomo, Shigenori*; Miyazaki, Yasunori; Hasegawa, Kenta; Sano, Yuichi; Nakatani, Kiyoharu*
Analytical Sciences, 40(2), p.347 - 352, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:11.65(Chemistry, Analytical)The Eu(III) distribution mechanism in single extractant-impregnated polymer-layered silica particle in a complex solution containing multiple lanthanide ions was investigated using fluorescence microspectroscopy. The rate-determining step was the reaction of Eu(III) with the two extractant molecules. The obtained mechanism and rate constants agreed with those of the single-ion distribution system, in which Eu(III) was distributed to the particles in the Eu(III) solution.
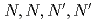 -tetraoctyldiglycolamide-impregnated polymer-coated silica particle using fluorescence microspectroscopy; Transfer mechanism and effect of polymer crosslinking degree
-tetraoctyldiglycolamide-impregnated polymer-coated silica particle using fluorescence microspectroscopy; Transfer mechanism and effect of polymer crosslinking degreeMiyagawa, Akihisa*; Takahashi, Takumi*; Kuzure, Yoshiaki*; Iwamoto, Hibiki*; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Nagatomo, Shigenori*; Watanabe, So; Sano, Yuichi; Nakatani, Kiyoharu*
Analytical Sciences, 39(11), p.1929 - 1936, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.65(Chemistry, Analytical)In this study, we revealed the Eu(III) distribution in a single diglycolamide-derivative extractant (TODGA)-impregnated polymer-coated silica particle. The reaction of Eu(III) with two TODGA molecules in the polymer layer was the rate-limiting process, as evidenced by the absence of any correlation between the rate constants (k and k
and k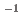 ) and concentrations of Eu(III) and HNO
) and concentrations of Eu(III) and HNO .
.
Sasaki, Yuji; Kaneko, Masashi; Ban, Yasutoshi; Kinoshita, Ryoma; Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Shinoku, Kota*; Shiroishi, Hidenobu*
Analytical Sciences, 39(9), p.1575 - 1583, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:38.46(Chemistry, Analytical)Extraction of Rh from HCl can be performed by NTAamide(C6) (hexahexyl-nitrilotriacetamide) and other related compounds into n-dodecane. We use ion-pair extraction of anionic species of Rh-chloride and protonated extractant. Rh behave as anion in hydrochloric acid and the tertiary nitrogen atom in extractant may be protonated to produce the quaternary amine in acidic condition. From the present work, the maximum distribution ratio of Rh(III) is 16. The D(Rh) values are changeable during preparation of the aqueous solutions because different Rh-Cl-H O complexes are formed in HCl media and show the slow exchange rate between Cl and H
O complexes are formed in HCl media and show the slow exchange rate between Cl and H O. Using the UV spectrum, Rh-chloride solution having the peak of spectrum at 504 nm can be extracted effectively, where RhCl
O. Using the UV spectrum, Rh-chloride solution having the peak of spectrum at 504 nm can be extracted effectively, where RhCl (H
(H O)
O) and RhCl
and RhCl (H
(H O)
O)
 exist mainly from DFT calculation. Stoichiometry of one-one complex of Rh and NTAamide is obtained from slope analysis, and 85 mM of concentrated Rh ion can be extracted.
exist mainly from DFT calculation. Stoichiometry of one-one complex of Rh and NTAamide is obtained from slope analysis, and 85 mM of concentrated Rh ion can be extracted.
Suzuki, Hideya*; Ban, Yasutoshi
Analytical Sciences, 39(8), p.1341 - 1348, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:49.52(Chemistry, Analytical)The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has proposed the Solvent Extraction from Liquid waste using Extractants of CHON-type for Transmutation (SELECT) process by solvent extraction as a new separation technology to recover minor actinides (MA) from high-level liquid waste (HLLW) produced by spent fuel reprocessing. The MA separation in the SELECT process comprises the batch recovery of MA and rare earths (RE) from HLLW, MA/RE separation, and Am/Cm separation. Three highly practical extractants are used in the MA separation. Furthermore, this flow configuration facilitates the preparation of nitric acid concentrations in the aqueous phase. However, the separation factor between Cm and Nd in the MA/RE separation is small (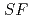
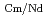 = 2.5), requiring many extraction stages for continuous extraction in a mixer-settler. Therefore, this study investigated the separation of only Am from an aqueous nitric acid solution containing MA (Am and Cm) and RE using an organic phase mixed with two extractants alkyl diamideamine with 2-ethylhexyl alkyl chains (ADAAM(EH)) and hexa-n-octylnitrilotriacetamide (HONTA) used in the SELECT process. Under high-concentration nitric acid conditions, Am and La, Ce, Pr, Nd (light lanthanides) were extracted in the ADAAM(EH) + HONTA mixed solvent, whereas Cm, medium, and heavy lanthanides, and Y were partitioned in the aqueous phase. Subsequently, only light lanthanides could be back extracted from the ADAAM(EH) + HONTA mixture solvent containing Am and light lanthanides in low nitric acid concentrations. Furthermore, Am could be easily stripped with 0.2 M or 5 M nitric acid. This method does not require the mutual separation of Cm and Nd, which have low separation factors. Am can be efficiently separated by one extraction and two back-extractions, reducing the number of steps in the SELECT process.
= 2.5), requiring many extraction stages for continuous extraction in a mixer-settler. Therefore, this study investigated the separation of only Am from an aqueous nitric acid solution containing MA (Am and Cm) and RE using an organic phase mixed with two extractants alkyl diamideamine with 2-ethylhexyl alkyl chains (ADAAM(EH)) and hexa-n-octylnitrilotriacetamide (HONTA) used in the SELECT process. Under high-concentration nitric acid conditions, Am and La, Ce, Pr, Nd (light lanthanides) were extracted in the ADAAM(EH) + HONTA mixed solvent, whereas Cm, medium, and heavy lanthanides, and Y were partitioned in the aqueous phase. Subsequently, only light lanthanides could be back extracted from the ADAAM(EH) + HONTA mixture solvent containing Am and light lanthanides in low nitric acid concentrations. Furthermore, Am could be easily stripped with 0.2 M or 5 M nitric acid. This method does not require the mutual separation of Cm and Nd, which have low separation factors. Am can be efficiently separated by one extraction and two back-extractions, reducing the number of steps in the SELECT process.
Sasaki, Yuji; Nakase, Masahiko*; Kaneko, Masashi; Kobayashi, Toru; Takeshita, Kenji*; Matsumiya, Masahiko*
Analytical Sciences, 5 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)We conducted three field researches on Ru-extraction, XANES, and DFT-calculation. The order of the distribution ratio, D(Ru), from acid, HCl  H
H SO
SO
 HNO
HNO
 HClO
HClO , by MIDOA is studied by XANES spectra, which indicates the valency change of Ru in HCl media and supports the ion pairing extraction of anionic Ru ion and cationic MIDOA. The same extractant trend, NTAamide
, by MIDOA is studied by XANES spectra, which indicates the valency change of Ru in HCl media and supports the ion pairing extraction of anionic Ru ion and cationic MIDOA. The same extractant trend, NTAamide  MIDOA
MIDOA  IDOA, due to D values as the energy gap of HOMO and LUMO could be found by DFT calculation, which suggests that the reaction heat has a positive correlation with extractability for extractant.
IDOA, due to D values as the energy gap of HOMO and LUMO could be found by DFT calculation, which suggests that the reaction heat has a positive correlation with extractability for extractant.
 -CO
-CO mixed-gas reaction in inductively coupled plasma tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry
mixed-gas reaction in inductively coupled plasma tandem quadrupole mass spectrometryMatsueda, Makoto; Aoki, Jo; Koarai, Kazuma; Terashima, Motoki; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Analytical Sciences, 38(11), p.1371 - 1376, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:57.77(Chemistry, Analytical)The  I analysis using ICP-MS is challenging caused by xenon-129 (
I analysis using ICP-MS is challenging caused by xenon-129 ( Xe) and
Xe) and  IH
IH generated from excess stable isotope
generated from excess stable isotope  I. In this study, mass discrimination between iodine-129 (
I. In this study, mass discrimination between iodine-129 ( I) and interfering substances was achieved by inductively coupled plasma-tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS) with a dynamic reaction cell introduced a mixture gas of O
I) and interfering substances was achieved by inductively coupled plasma-tandem quadrupole mass spectrometry (ICP-MS/MS) with a dynamic reaction cell introduced a mixture gas of O and CO
and CO . As a result, the ratio of (background noise intensity at m/z 129)/
. As a result, the ratio of (background noise intensity at m/z 129)/ I was 3.8
I was 3.8  10
10 and 10 mBq/L of
and 10 mBq/L of  I was analyzed without chemical separation in the presence of 100 mg/L stable
I was analyzed without chemical separation in the presence of 100 mg/L stable  I. Spiked tests with actual rainwater were performed, and obtained values were agreed with the spiked amounts.
I. Spiked tests with actual rainwater were performed, and obtained values were agreed with the spiked amounts.
Yanagisawa, Kayo; Matsueda, Makoto; Furukawa, Makoto*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Analytical Sciences, 38(8), p.1105 - 1114, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.86(Chemistry, Analytical)We demonstrate the sensitivity enhancement in inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) by combining ultrasonic nebulization via the nitrogen mixed gas effect. We showed the effect of nitrogen gas concentration (0-5%) in the nebulizer gas on the signal sensitivity for 63 elements using commercially available (concentric and ultrasonic) nebulizers. In addition, the limit of detection was calculated in each case. Finally, we compared the sensitivity (i.e., the slope of the calibration curve), background noise intensity, and three-dimensional intensity distribution in the plasma to elucidate the effects of the concurrent use of mixed gas plasmas and nebulization methods.
Shimojo, Kojiro; Fujiwara, Iori*; Oshima, Tatsuya*; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Analytical Sciences, 38(7), p.1003 - 1006, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:13.92(Chemistry, Analytical)Liquid-liquid extraction of lanthanide (Ln) ions was investigated using 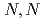 -dioctylthiodiglycolamic acid (DOTDGAA), which is a sulfur donor ligand with an amide group and a carboxyl group connected by a thioether chain. The extraction performance and selectivity of DOTDGAA for Ln ions were compared with those of
-dioctylthiodiglycolamic acid (DOTDGAA), which is a sulfur donor ligand with an amide group and a carboxyl group connected by a thioether chain. The extraction performance and selectivity of DOTDGAA for Ln ions were compared with those of 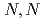 -dioctyldiglycolamic acid (DODGAA), which is also an oxygen donor ligand with a similar chemical structure, to assess the effect of the soft/hard donor atom on Ln separation. DOTDGAA quantitatively extracted all Ln ions while being selective toward light and middle Ln ions, in contrast to the selectivity of DODGAA for heavier Ln ions. Slope analysis demonstrated that the Ln
-dioctyldiglycolamic acid (DODGAA), which is also an oxygen donor ligand with a similar chemical structure, to assess the effect of the soft/hard donor atom on Ln separation. DOTDGAA quantitatively extracted all Ln ions while being selective toward light and middle Ln ions, in contrast to the selectivity of DODGAA for heavier Ln ions. Slope analysis demonstrated that the Ln transfer using DOTDGAA proceeded through a proton-exchange reaction, forming a 1:3 complex, Ln(DOTDGAA)
transfer using DOTDGAA proceeded through a proton-exchange reaction, forming a 1:3 complex, Ln(DOTDGAA) . The back-extraction of Ln ions from the extracting phase was successfully achieved under acidic conditions.
. The back-extraction of Ln ions from the extracting phase was successfully achieved under acidic conditions.
 aqueous solution system revealed by fluorescence microspectroscopy
aqueous solution system revealed by fluorescence microspectroscopyMiyagawa, Akihisa*; Kusano, Yuka*; Nagatomo, Shigenori*; Sano, Yuichi; Nakatani, Kiyoharu*
Analytical Sciences, 38(7), p.955 - 961, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.86(Chemistry, Analytical)In this study, we reveal an Eu(III) extraction mechanism at the interface between HNO and tributyl phosphate (TBP) solutions using fluorescence microspectroscopy. The mass transfer rate constant at the interface is obtained from the analysis of fluorescence intensity changes during the forward and backward extractions at various HNO
and tributyl phosphate (TBP) solutions using fluorescence microspectroscopy. The mass transfer rate constant at the interface is obtained from the analysis of fluorescence intensity changes during the forward and backward extractions at various HNO and TBP concentrations to investigate the reaction mechanism. This result indicates that one nitrate ion reacts with Eu(III) at the interface, whereas TBP molecules are not involved in the interfacial reaction, which is different from the results obtained using the NaNO
and TBP concentrations to investigate the reaction mechanism. This result indicates that one nitrate ion reacts with Eu(III) at the interface, whereas TBP molecules are not involved in the interfacial reaction, which is different from the results obtained using the NaNO solution in our previous study. We demonstrate that the chemical species of Eu(III) complex with nitrate ion and TBP in the aqueous solution play an important role for the extraction mechanism.
solution in our previous study. We demonstrate that the chemical species of Eu(III) complex with nitrate ion and TBP in the aqueous solution play an important role for the extraction mechanism.
Ito, Tatsuya; Osugi, Haruka*; Osawa, Naoki*; Takahashi, Tadayuki*; Kim, S.-Y.*; Nagaishi, Ryuji
Analytical Sciences, 38(1), p.91 - 97, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.50(Chemistry, Analytical)A novel ionic liquid (IL) functionalized with thiodiglycol amic acid containing a soft S donor was synthesized for the effective and efficient extraction of platinum group metals (Ru, Rh, and Pd) from aqueous nitric acid solutions, such as high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW). The IL allowed a rapid extraction of Pd(II) with an extraction ratio of approximately 100%. The extractions of Ru(III) and Rh(III) by the IL were slower than that of Pd(II), but the rates were accelerated by temperature elevation. The extractions of Ru(III) and Rh(III) at 50 C reached equilibrium within 4 and 8 h, respectively, with the extraction ratios of over 90% without assisting agents or other methods for the extraction system. Furthermore, the IL could extract more than 90% of Ru(III), Rh(III), and Pd(II) from the simulated HLLW within 2 h at 50
C reached equilibrium within 4 and 8 h, respectively, with the extraction ratios of over 90% without assisting agents or other methods for the extraction system. Furthermore, the IL could extract more than 90% of Ru(III), Rh(III), and Pd(II) from the simulated HLLW within 2 h at 50 C.
C.
Yomogida, Takumi; Saeki, Morihisa*; Morii, Shiori; Oba, Hironori*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Analytical Sciences, 37(12), p.1843 - 1846, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:3.83(Chemistry, Analytical)In this study, we developed a simple and one-step Pd separation technique based on photoreduction with Xe lamp irradiation for the determination of  Pd in highly radioactive samples. A simulated high-level radioactive liquid wastes (HLLW) solution, which consists of 14 major elements (Rb, Sr, Zr, Mo, Ru, Rh, Pd, Cs, Ba, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm) in a 3 mol L
Pd in highly radioactive samples. A simulated high-level radioactive liquid wastes (HLLW) solution, which consists of 14 major elements (Rb, Sr, Zr, Mo, Ru, Rh, Pd, Cs, Ba, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm) in a 3 mol L HNO
HNO solution, was used to evaluate the separation performance. The Pd precipitate were formed by Xe lamp irradiation and recovered by centrifugation. The results showed that the recovery of Pd from a simulated HLLW solution depend on the irradiation time and concentration of ethanol. By optimizing the conditions at photo irradiation, the Pd recovery from the simulated HLLW solution reached up to 50 %, while 99.5 % of the other 13 elements were separated. The Pd precipitate could be separated from the elements that are the main source of radioactivity (Sr, Cs, and Ba) and the source of spectral interference for the determination of
solution, was used to evaluate the separation performance. The Pd precipitate were formed by Xe lamp irradiation and recovered by centrifugation. The results showed that the recovery of Pd from a simulated HLLW solution depend on the irradiation time and concentration of ethanol. By optimizing the conditions at photo irradiation, the Pd recovery from the simulated HLLW solution reached up to 50 %, while 99.5 % of the other 13 elements were separated. The Pd precipitate could be separated from the elements that are the main source of radioactivity (Sr, Cs, and Ba) and the source of spectral interference for the determination of  Pd (Zr, and Ru). These results indicate that selective separation of Pd is achieved with the proposed method, showing the applicability of the proposed separation technique to HLLW samples.
Pd (Zr, and Ru). These results indicate that selective separation of Pd is achieved with the proposed method, showing the applicability of the proposed separation technique to HLLW samples.
Ouchi, Kazuki; Tsukahara, Takehiko*; Brandt, A.*; Muto, Yuki*; Nabatame, Nozomi*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Analytical Sciences, 37(12), p.1789 - 1794, 2021/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:3.83(Chemistry, Analytical)We attempted to scale down a separation process of uranium (U) using the microchip column loaded with anion exchange resin to develop safety and waste-reducing separation technique. The ideal separation performance of U was obtained by the properly design of a microchannel. The concentration of U in seawater as a real-world sample could be quantified with the prepared microchip column. It indicates that the microchip column is sufficiently practical. Compared to separation of U with a general column, the column size was successfully scaled down to  1/5000.
1/5000.
Matsutani, Takafumi; Sasaki, Yuji; Katsuta, Shoichi*
Analytical Sciences, 37(11), p.1603 - 1609, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:38.51(Chemistry, Analytical)We investigated the chemical behavior of lanthanides (Ln) using diglycolamide extractant with multistage extraction. We obtained the breakthrough curves for light and middle Ln. Our study reveals that the metal extraction limit depends on their  values and metal concentrations used in the experiments. From the multistage extractions of 15 aqueous phases and 15 organic phases, three curves (extraction curves, back-extraction curves, and separation curves) were obtained by changing the nitric acid concentration. As an example, under a condition of the separation curve experiment (aqueous phase: 0.5 M HNO
values and metal concentrations used in the experiments. From the multistage extractions of 15 aqueous phases and 15 organic phases, three curves (extraction curves, back-extraction curves, and separation curves) were obtained by changing the nitric acid concentration. As an example, under a condition of the separation curve experiment (aqueous phase: 0.5 M HNO , organic phase: 0.1 M TDDGA (
, organic phase: 0.1 M TDDGA (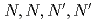 -tetradecyl-diglycolamide) in
-tetradecyl-diglycolamide) in  -dodecane), a recovery of more than 99% of Sm in the organic phase with less than 1% Nd can be obtained.
-dodecane), a recovery of more than 99% of Sm in the organic phase with less than 1% Nd can be obtained.
Okamura, Hiroyuki; Hirayama, Naoki*
Analytical Sciences, 37(1), p.119 - 130, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:68.88(Chemistry, Analytical)This review summarizes recent progress in solvent extraction of rare earth elements (REEs) using an ionic liquid (IL) as the extraction solvent. These IL extraction systems are advantageous owing to the affinity of ILs for both charged and neutral hydrophobic species, in contrast to conventional organic solvent extraction systems. Herein, REE extraction studies using ILs are detailed and classified based on the type of extraction system. In IL extraction systems, the extracted complexes are often different from those in organic solvent systems, and the REE extraction and separation efficiencies are often significantly enhanced. Synergistic IL extraction is an effective approach to improving the extractability and separability of REEs. The development of novel task-specific ionic liquids (TSILs) suitable for IL extraction systems is also effective for REE separation.
Shimojo, Kojiro; Suzuki, Hideya; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Ikeda, Atsushi
Analytical Sciences, 36(12), p.1435 - 1437, 2020/12
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:68.40(Chemistry, Analytical)Liquid-liquid extraction for the removal of pertechnetate ( TcO
TcO
 ) and perrhenate (ReO
) and perrhenate (ReO
 ) is reported using tripodal extractant
) is reported using tripodal extractant 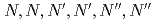 -hexa-
-hexa- -octylnitrilotriacetamide (HONTA) composed of three amide groups and a tertiary amine. The extraction behavior was compared with those using alkyldiamideamines (ADAAM(Oct) and ADAAM(EH)), and the commercial amine-type extractant, trioctylamine (TOA). HONTA quantitatively extracted
-octylnitrilotriacetamide (HONTA) composed of three amide groups and a tertiary amine. The extraction behavior was compared with those using alkyldiamideamines (ADAAM(Oct) and ADAAM(EH)), and the commercial amine-type extractant, trioctylamine (TOA). HONTA quantitatively extracted  TcO
TcO
 and ReO
and ReO
 in the pH range from 1.0 to 2.5 by co-extraction of protons. Extraction performance of extractants was improved in the order of HONTA
in the pH range from 1.0 to 2.5 by co-extraction of protons. Extraction performance of extractants was improved in the order of HONTA  ADAAM(Oct)
ADAAM(Oct)  ADAAM(EH)
ADAAM(EH)  TOA.
TOA.  TcO
TcO
 and ReO
and ReO
 in the extracting phase were successfully stripped using neutral aqueous solutions as the receiving phase, and the extraction ability of HONTA was maintained after five repeated uses.
in the extracting phase were successfully stripped using neutral aqueous solutions as the receiving phase, and the extraction ability of HONTA was maintained after five repeated uses.
Saeki, Morihisa*; Yomogida, Takumi; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Takumi*; Nakanishi, Ryuzo*; Tsuji, Takuya; Oba, Hironori*
Analytical Sciences, 36(11), p.1371 - 1378, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:21.11(Chemistry, Analytical)We measured X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) and Raman spectra of isopolymolybdates(VI) in HNO solution (0.15- 4.0 M), which change their geometries depending on acid concentration, and performed simultaneous resolution of the XAFS and Raman data using a multivariate curve resolution by alternating least-squares (MCR-ALS) analysis. In iterative ALS optimization, initial data matrices were prepared by two different methods. The MCR-ALS result of single XAFS data matrix shows large dependence on the preparation method of the initial data matrices. The MCR-ALS result of an augmented matrix of Raman and XAFS data has little dependence on the initial data matrices. It indicates that the augmentation method effectively improves the rotation ambiguities in the MCR-ALS analysis of the XAFS data. Based on the model fitting of the pure EXAFS oscillations, we revealed the change of [Mo
solution (0.15- 4.0 M), which change their geometries depending on acid concentration, and performed simultaneous resolution of the XAFS and Raman data using a multivariate curve resolution by alternating least-squares (MCR-ALS) analysis. In iterative ALS optimization, initial data matrices were prepared by two different methods. The MCR-ALS result of single XAFS data matrix shows large dependence on the preparation method of the initial data matrices. The MCR-ALS result of an augmented matrix of Raman and XAFS data has little dependence on the initial data matrices. It indicates that the augmentation method effectively improves the rotation ambiguities in the MCR-ALS analysis of the XAFS data. Based on the model fitting of the pure EXAFS oscillations, we revealed the change of [Mo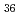 O
O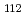 (H
(H O)
O) ]
]
 [Mo
[Mo O
O (H
(H O)
O) ]
]
 [HMoO
[HMoO (H
(H O)
O) ]
] in the highly concentrated HNO
in the highly concentrated HNO solution.
solution.
Sasaki, Yuji; Matsumiya, Masahiko*; Tsuchida, Yusuke*
Analytical Sciences, 36(11), p.1303 - 1309, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:26.03(Chemistry, Analytical)The mutual separation of lanthanides is studied by multi-stage extraction using extractant, DGA (diglycolamide) compounds. Tetraoctyl-DGA (TODGA) has a high extractability to lanthanides and relatively high separation factor (SF) between Dy and Nd (SF: over 20). The complete separation with such SF value can be achieved by multi-stage extraction. Less information on multi-stage extraction compared to batch extraction is presented up to now, thus we conduct the basic study about that. Confirming the experimental data to be identical to the calculation, the sample solution including both metals is employed for the batchwise multi-stage extraction. Ninety-seven % of Dy with under detection limit of Nd can be recovered into the organic phase from Nd with ten times higher concentration than Dy using the condition, 0.1 M TODGA/n-dodecane and 0.3 M HNO by multi-stage extraction of 9
by multi-stage extraction of 9 9 for organic and aqueous phases.
9 for organic and aqueous phases.
 Sr using automatic solid-phase extraction inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry
Sr using automatic solid-phase extraction inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometryYanagisawa, Kayo*; Matsueda, Makoto; Furukawa, Makoto*; Takagai, Yoshitaka*
Analytical Sciences, 36(9), p.1131 - 1135, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:16.20(Chemistry, Analytical)In this paper, we propose an online water infusion system for rapid quantification of radioactive strontium-90 ( Sr) with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry coupled solid-phase extraction and O
Sr) with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry coupled solid-phase extraction and O dynamic reaction (cascade ICP-MS). The proposed system automatically provides a higher dilution ratio, which is at most 3.3 times the ratio obtained by the previous method, without increasing the analysis time (within 15 min). A detection limit of 2.7 Bq/kg wet (0.54 pg/kg wet) was achieved. The recovery test results were consistent with two different spiked values.
dynamic reaction (cascade ICP-MS). The proposed system automatically provides a higher dilution ratio, which is at most 3.3 times the ratio obtained by the previous method, without increasing the analysis time (within 15 min). A detection limit of 2.7 Bq/kg wet (0.54 pg/kg wet) was achieved. The recovery test results were consistent with two different spiked values.
Tsutsui, Nao; Ban, Yasutoshi; Suzuki, Hideya*; Nakase, Masahiko*; Ito, Sayumi*; Inaba, Yusuke*; Matsumura, Tatsuro; Takeshita, Kenji*
Analytical Sciences, 36(2), p.241 - 246, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:83.49(Chemistry, Analytical)To investigate the effective separation of actinides (Ans) from lanthanides (Lns), single-stage batch extraction experiments were performed with a novel extractant, tetradodecyl-1,10-phenanthroline-2,9-diamide (TDdPTDA) with various diluents such as 3-nitrobenzotrifluoride (F-3), nitrobenzene, and  -dodecane for Am, Cm, and Lns. The extraction kinetics with TDdPTDA was rapid enough to perform the actual extraction flow sheet. The slopes of the distribution ratio versus TDdPTDA concentration and the distribution ratio versus nitric acid concentration were similar for F-3 and nitrobenzene systems but different from
-dodecane for Am, Cm, and Lns. The extraction kinetics with TDdPTDA was rapid enough to perform the actual extraction flow sheet. The slopes of the distribution ratio versus TDdPTDA concentration and the distribution ratio versus nitric acid concentration were similar for F-3 and nitrobenzene systems but different from  -dodecane system. These differences were attributed to the characteristics of the diluents. This study reveals high distribution ratios of Am (
-dodecane system. These differences were attributed to the characteristics of the diluents. This study reveals high distribution ratios of Am (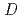
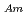 ) and Cm (
) and Cm (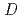
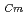 ) for TDdPTDA, with the high separation factors (
) for TDdPTDA, with the high separation factors ( s) of Am from Lns enough for their separation.
s) of Am from Lns enough for their separation.