Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 nanosheets for enhancing heat storage performance
nanosheets for enhancing heat storage performanceYoshisako, Hiroki*; Okamoto, Norihiko*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Ichitsubo, Tetsu
Communications Chemistry (Internet), 8, p.169_1 - 169_9, 2025/06
no abstracts in English
Kai, Takeshi; Toigawa, Tomohiro; Matsuya, Yusuke*; Hirata, Yuho; Tsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Yokoya, Akinari*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 162(15), p.154102_1 - 154102_11, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0Scientific knowledge of low-energy electrons resulting from water radiolysis is required to estimate radiation DNA damage. However, since the analysis of water radiolysis is very complex, this study focuses on the experimental values of low-energy electrons related to simple water photolysis and those generated by photoirradiation of electrodes in water. Both experimental analyses involve the presence or absence of a Coulomb field in the parent ion. In this study, we analyzed these experimental values using a calculation code that combines Monte Carlo and molecular dynamics methods. As a result, it was shown that the code reproduced the experimental values even under different experimental conditions, and the code was validated. The calculation code will be a powerful tool for analyzing the interaction between low-energy electrons and DNA, and is expected to be applied to elucidate the formation mechanism of radiation DNA damage.
Li, F.*; Tang, X.*; Fei, Y.*; Zhang, J.*; Liu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Che, G.*; Zhao, Z.*; Zheng, Y.*; Fang, Y.*; et al.
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 147(17), p.14054 - 14059, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)We synthesized a crystalline graphane nanoribbon (GANR) via pressure-induced polymerization of 2,2'-bipyrazine (BPZ). By performing Rietveld refinement of in situ neutron diffraction data, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, infrared spectra, and theoretical calculation, we found that BPZ experienced Diels-Alder polymerization between the 

 stacked aromatic rings, and formed extended boat-GANR structures with exceptional long-range order. The unreacted -C=N- groups bridge the two ends of the boat, and ready for further functionalization. The GANR has a bandgap of 2.25 eV, with booming photoelectric response (
stacked aromatic rings, and formed extended boat-GANR structures with exceptional long-range order. The unreacted -C=N- groups bridge the two ends of the boat, and ready for further functionalization. The GANR has a bandgap of 2.25 eV, with booming photoelectric response (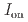 /
/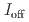 =18.8). Our work highlights that the high-pressure topochemical polymerization is a promising method for the precise synthesis of graphane with specific structure and desired properties.
=18.8). Our work highlights that the high-pressure topochemical polymerization is a promising method for the precise synthesis of graphane with specific structure and desired properties.
Matsuya, Yusuke; Yoshii, Yuji*; Kusumoto, Tamon*; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Onishi, Seiki*; Hirata, Yuho; Sato, Tatsuhiko; Kai, Takeshi
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 27(14), p.6887 - 6898, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Radicals by water radiolysis play an important role in evaluating radiation-induced biological effects, such as DNA damage induction, chromosomal aberrations, and carcinogenesis. In the Particle and Heavy Ion Transport code System (PHITS), a track-structure simulation mode enabling the estimation of each atomic interactions in water and a chemical simulation code (PHITS-Chem) dedicated to electron beams that can simulate radical dynamics have been developed in our previous study. Here, we developed the PHITS-Chem code applicable to any ion species, considering a space partitioning method to detect radical reactions more efficiently and the 4D visualization function. The updated PHITS-Chem code was verified by comparing the simulated G values of proton beams,  particle beams, and carbon ion beams to the corresponding values in the literature. We succeeded in intuitively evaluating the diffusion dynamics of radicals using the PHITS 3D drawing software, PHIG-3D. The time to calculate the G values was reduced (e.g., about 28 times faster) while maintaining its calculation accuracy. The developed PHITS-Chem code is expected to contribute to precise and intuitive understanding of the biological effects induced by radicals in ion-beam radiotherapy.
particle beams, and carbon ion beams to the corresponding values in the literature. We succeeded in intuitively evaluating the diffusion dynamics of radicals using the PHITS 3D drawing software, PHIG-3D. The time to calculate the G values was reduced (e.g., about 28 times faster) while maintaining its calculation accuracy. The developed PHITS-Chem code is expected to contribute to precise and intuitive understanding of the biological effects induced by radicals in ion-beam radiotherapy.
Kai, Takeshi; Toigawa, Tomohiro; Matsuya, Yusuke*; Hirata, Yuho; Tsuchida, Hidetsugu*; Ito, Yuma*; Yokoya, Akinari*
Communications Chemistry (Internet), 8, p.60_1 - 60_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Radiation DNA damage is formed from direct and indirect effects. The direct effect is the interaction between DNA and a radiation, while the indirect effect is the chemical reaction between DNA and radiolytic chemical species. We believed that when the direct effect is induced, multiple lesions are formed within 10 base pairs (about 3.4 nm) of DNA. The damage reduces repair efficiency and induces biological effects. In this study, DNA damage induced by only indirect effects was quantitatively evaluated. Our results indicated that the multiple damage is formed when only 10s of eV energy is deposited to water in the vicinity of DNA, although its formation probability is less than 1%. In other words, the possibility of late biological effects cannot be excluded simply by imparting energy to water in the extreme vicinity of DNA without direct interaction between radiation and DNA. Our results are one of the most important findings for understanding low-dose radiation risk.
Ling, B.-K.*; Chang, M.*; Zhai, Y.-Q.*; Deng, J.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Guo, H.*; Zhao, J.*; Fu, Z.*; Zheng, Y.-Z.*
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 147(13), p.10935 - 10942, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Ito, Kengo*; Takahashi, Shin*; Kato, Chizu*; Fukutani, Satoshi*; Matsumura, Tatsuro; Fujii, Toshiyuki*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 334, p.2467 - 2475, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)In this study, the solvent extraction behavior of tin (Sn), specifically  Sn, from high-level radioactive waste was evaluated using six different extractants in a HNO
Sn, from high-level radioactive waste was evaluated using six different extractants in a HNO system. Among the tested extractants, N,N-Didodecyl-2-hydroxyacetoamide (HAA) exhibited higher efficiency, still not sufficient for industrial implementation. In systems where HCl was added to HNO
system. Among the tested extractants, N,N-Didodecyl-2-hydroxyacetoamide (HAA) exhibited higher efficiency, still not sufficient for industrial implementation. In systems where HCl was added to HNO , both tributyl phosphate (TBP) and N,N,N,N'-tetra-2-ethylhexyl diglycolamide (TEHDGA) achieved D
, both tributyl phosphate (TBP) and N,N,N,N'-tetra-2-ethylhexyl diglycolamide (TEHDGA) achieved D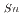 values greater than 1 at
values greater than 1 at  1 M HCl. However, due to practical challenges in industrial applications, HAA extraction in HNO
1 M HCl. However, due to practical challenges in industrial applications, HAA extraction in HNO systems, particularly at low Sn concentrations (0.0008 M), may provide a more effective solution for Sn recovery.
systems, particularly at low Sn concentrations (0.0008 M), may provide a more effective solution for Sn recovery.
Horiike, Yuki*; Aoki, Hiroyuki; Ouchi, Makoto*; Terashima, Takaya*
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 147(8), p.6727 - 6738, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Che, G.*; Fei, Y.*; Tang, X.*; Zhao, Z.*; Hattori, Takanori; Abe, Jun*; Wang, X.*; Ju, J.*; Dong, X.*; Wang, Y.*; et al.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 27(2), p.1112 - 1118, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:65.57(Chemistry, Physical)Pressure-induced polymerization (PIP) of aromatic molecules has emerged as an effective method for synthesizing various carbon-based materials. In this work, PIP of 1,4-difluorobenzene (1,4-DFB) was investigated.  high-pressure investigations of 1,4-DFB reveal a phase transition at approximately 12.0 GPa and an irreversible chemical reaction at 18.7 GPa. Structural analysis of the product and the kinetics of the reaction uncovered the formation of pseudohexagonal stacked fluoro-diamond nanothreads with linear growth. Compared to the crystal structures of benzene under high pressure, 1,4-DFB exhibits higher compression along the [001] axis. The anisotropic compression is attributed to the stronger H
high-pressure investigations of 1,4-DFB reveal a phase transition at approximately 12.0 GPa and an irreversible chemical reaction at 18.7 GPa. Structural analysis of the product and the kinetics of the reaction uncovered the formation of pseudohexagonal stacked fluoro-diamond nanothreads with linear growth. Compared to the crystal structures of benzene under high pressure, 1,4-DFB exhibits higher compression along the [001] axis. The anisotropic compression is attributed to the stronger H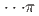 interaction along the [01
interaction along the [01 ] axis and the potential compression-inhibiting H
] axis and the potential compression-inhibiting H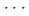 F interactions along the [100] and [010] axes, and it facilitates a possible reaction pathway along the [01
F interactions along the [100] and [010] axes, and it facilitates a possible reaction pathway along the [01 ] axis. This work emphasizes the crucial role of functionalization in modulating molecular stacking and influencing the reaction pathway.
] axis. This work emphasizes the crucial role of functionalization in modulating molecular stacking and influencing the reaction pathway.
Ito, Tatsuya; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Kuwano, Ryo*; Godo, Masao*; Yoshida, Yoichi*
Radiation Physics and Chemistry, 226, p.112198_1 - 112198_5, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)In recent years, the use of radiation-resistant resins of polyimide and polyether ether ketone becomes increasing as vessels for irradiation and unsealed radioisotope experiments. However, in our radiolysis experiments, the possibility of interaction between radiolysis products of water and the resin was found, suggesting concerns that the resin may affect reactions in water in radiation fields. To clarify the interaction, dichromate (Cr O
O
 ) reduction and hydrogen peroxide (H
) reduction and hydrogen peroxide (H O
O ) formation in
) formation in  -radiolysis of water were compared with and without the resin. The Cr
-radiolysis of water were compared with and without the resin. The Cr O
O
 reduction amount in aqueous solution with the resin became larger than that without the resin at the same dose, indicating the promotion of Cr
reduction amount in aqueous solution with the resin became larger than that without the resin at the same dose, indicating the promotion of Cr O
O
 reduction by the resin. On the other hand, the H
reduction by the resin. On the other hand, the H O
O formation in pure water with and without an electron scavenger were almost independent of the presence of resin. These suggested the interaction between hydroxyl radical and the resin in contact with water in radiation fields.
formation in pure water with and without an electron scavenger were almost independent of the presence of resin. These suggested the interaction between hydroxyl radical and the resin in contact with water in radiation fields.
 capture and release at high pressures on a unique large-pore mesoporous carbon
capture and release at high pressures on a unique large-pore mesoporous carbonSzab , L.*; Inoue, Mizuki*; Sekine, Yurina; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Matsumoto, Yusuke*; Nge, T. T.*; Ismail, E.*; Ichinose, Izumi*; Yamada, Tatsuhiko*
, L.*; Inoue, Mizuki*; Sekine, Yurina; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Matsumoto, Yusuke*; Nge, T. T.*; Ismail, E.*; Ichinose, Izumi*; Yamada, Tatsuhiko*
ChemSusChem, p.e202402034_1 - e202402034_13, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Here, we developed a large-pore mesoporous carbon with pore sizes centered around 20-30 nm using a templated technical lignin. During the soft-templating process, unique cylindrical supramolecular assemblies form from the copolymer template, distinct from other systems reported thus far. This peculiar nanostructuring takes place due to the presence of polyethylene glycol (PEG) segments on both the Pluronic template and the PEG- grafted lignin derivative (glycol lignin). A large increase in CO uptake occurs on the resulting large-pore mesoporous carbon at 270 K close to the saturation pressure, owing to capillary condensation.
uptake occurs on the resulting large-pore mesoporous carbon at 270 K close to the saturation pressure, owing to capillary condensation.
 U/
U/ U isotope ratios in deep groundwater and its potential application as a groundwater mixing indicator
U isotope ratios in deep groundwater and its potential application as a groundwater mixing indicatorKuribayashi, Chika*; Miyakawa, Kazuya; Ito, Akane*; Tanimizu, Masaharu*
Geochemical Journal, 59(2), p.35 - 44, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geochemistry & Geophysics)no abstracts in English
Xu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Liang, S.*; Zhang, J.*; Fei, Y.*; Wang, Y.*; Gao, D.*; Hattori, Takanori; Abe, Jun*; Dong, X.*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), p.2445 - 2451, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)The Alder-ene reaction is a chemical reaction between an alkene with an allylic hydrogen, and it provides an efficient method to construct the C-C bond. Traditionally, this reaction requires catalysts, high temperatures, or photocatalysis. In this study, we reported a high-pressure-induced solid-state Alder-ene reaction of 1-hexene at room temperature without a catalyst. 1-Hexene crystallizes at 4.3 GPa and polymerizes at 18 GPa, forming olefins. By exploring gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, we discovered that 1-hexene generates dimeric products through the Alder-ene reaction under high pressures. The in situ neutron diffraction shows that the reaction process did not obey the topochemical rule. A six-membered ring transition state including one C-H  bond and two alkene
bond and two alkene  bonds was evidenced by the theoretical calculation, whose energy obviously decreased when compressed to 20 GPa. Our work offers a novel and promising method to realize the Alder-ene reaction at room temperature without a catalyst, expanding the application of this important reaction.
bonds was evidenced by the theoretical calculation, whose energy obviously decreased when compressed to 20 GPa. Our work offers a novel and promising method to realize the Alder-ene reaction at room temperature without a catalyst, expanding the application of this important reaction.
Takahashi, Yoshio*; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Yomogida, Takumi
Treatise on Geochemistry, 3rd edition, Vol.6, p.105 - 150, 2025/00
With the recent development of measurement techniques, new approaches to the environmental geochemistry of radionuclides have been applied for various research targets. In this review article, several topics within the last 10-15 years in the field of environmental geochemistry of radionuclides have been discussed. In particular, this article mainly focused on two topics, (i) studies on the migration of radionuclides emitted by the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (FDNPP) accident in 2011 and (ii) the development of X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) spectroscopy and its application to the geochemical processes of radionuclides.
Nagasawa, Makoto*; Shimizu, Yusuke*; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Tokunaga, Kohei; Mukai, Hiroki*; Aoyagi, Noboru; Mei, H.; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Chemical Geology, 670, p.122431_1 - 122431_25, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:47.42(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Sugiyama, Hitoshi*; Kato, Kenichi*; Sekine, Naoko*; Sekine, Yurina; Watanabe, Tomoaki*; Fukazawa, Tomoko*
Chemical Physics Letters, 856, p.141655_1 - 141655_8, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:42.16(Chemistry, Physical)To investigate the effects of polymer hydrophilicity on structures of water in hydrogels, differential scanning calorimetry and X-ray diffraction measurements were performed. The results show that the amount of intermediate water in polyacrylamide (PAA) hydrogel is about 12% smaller than that in poly-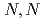 -dimethylacrylamide (PDMAA) hydrogel. Furthermore, it was found that the bound water in PAA hydrogel primarily exists around the surface of the polymer bundles, whereas that in PDMAA hydrogel acts as a crosslinker factor for dehydration and water absorption in hydrogels.
-dimethylacrylamide (PDMAA) hydrogel. Furthermore, it was found that the bound water in PAA hydrogel primarily exists around the surface of the polymer bundles, whereas that in PDMAA hydrogel acts as a crosslinker factor for dehydration and water absorption in hydrogels.
 CrN
CrN H
HFine, L.*; Lav n, R.*; Wei, Z.*; Tsumori, Tatsuya*; Kageyama, Hiroshi*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Jimen
n, R.*; Wei, Z.*; Tsumori, Tatsuya*; Kageyama, Hiroshi*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Jimen z-Ruiz, M.*; Koza, M. M.*; Karlsson, M.*
z-Ruiz, M.*; Koza, M. M.*; Karlsson, M.*
Chemistry of Materials, 37(1), p.489 - 496, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical) Cs/
Cs/ Cs isotope ratio
Cs isotope ratioShimada, Asako; Tsukahara, Takehiko*; Nomura, Masao*; Takeda, Seiji
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 333(12), p.6297 - 6310, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Analytical)Kato, Yuto*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Tonna, Ryutaro*; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro
Applied Geochemistry, 175, p.106196_1 - 106196_9, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Geochemistry & Geophysics) = 0.01-600
= 0.01-600 C,
C,  = 1-3000 bars,
= 1-3000 bars, 
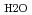 = 0.35-1.1 g cm
= 0.35-1.1 g cm , and
, and 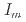 = 0
= 0
Walker, C. S.*; Arthur, R. C.*; Anraku, Sohtaro; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Mihara, Morihiro
Applied Geochemistry, 175, p.106086_1 - 106086_17, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Geochemistry & Geophysics)The thermodynamic properties and revised Helgeson-Kirkham-Flowers equation of state (r-H-K-F EoS) parameters of the hydrated (Si(OH) (aq), SiO(OH)
(aq), SiO(OH)
 and SiO
and SiO (OH)
(OH)
 ) and fictive dehydrated (SiO
) and fictive dehydrated (SiO (aq), HSiO
(aq), HSiO
 and SiO
and SiO
 ) monomeric silicon species are used extensively to describe the pH, composition, temperature, and pressure dependence of formation/breakdown reactions of all silicon-bearing compounds globally. Experimental log10 equilbrium constant, K values describing the formation reactions of the hydrated and dehydrated monomeric silicon species were therefore compiled from the literature, extrapolated to zero ionic strength by specific ion interaction theory as required and used to derive their thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters. Consideration of all formation reactions in the same study provides a collective, internally consistent update to the thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters of the monomeric silicon species that can provide a satisfactory match to the experimental log10 K values at
) monomeric silicon species are used extensively to describe the pH, composition, temperature, and pressure dependence of formation/breakdown reactions of all silicon-bearing compounds globally. Experimental log10 equilbrium constant, K values describing the formation reactions of the hydrated and dehydrated monomeric silicon species were therefore compiled from the literature, extrapolated to zero ionic strength by specific ion interaction theory as required and used to derive their thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters. Consideration of all formation reactions in the same study provides a collective, internally consistent update to the thermodynamic properties and r-H-K-F EoS parameters of the monomeric silicon species that can provide a satisfactory match to the experimental log10 K values at  = 0.01-600
= 0.01-600 C,
C,  = 1-3000 bars,
= 1-3000 bars, 
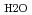 = 0.35-1.1 g cm
= 0.35-1.1 g cm , and zero ionic strength. These temperature and pressure limits comfortably bracket t=0.01-100
, and zero ionic strength. These temperature and pressure limits comfortably bracket t=0.01-100 C and P =1-270 bars relecant to the geological disposal of radioactive wastes at depths of up to 1 km.
C and P =1-270 bars relecant to the geological disposal of radioactive wastes at depths of up to 1 km.