Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
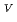 O
O
 /U
/U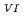 O
O
 redox equilibrium in [emim]Tf
redox equilibrium in [emim]Tf N-based liquid electrolytes towards uranium redox-flow battery
N-based liquid electrolytes towards uranium redox-flow batteryTakao, Koichiro*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Komatsu, Atsushi; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Watanabe, Masayuki
European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 27(14), p.e202300787_1 - e202300787_7, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Electrochemical behavior of U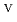 O
O
 /U
/U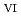 O
O
 in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethyl)sulfonylamide ([emim]Tf
in 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethyl)sulfonylamide ([emim]Tf N) ionic liquid was studied to clarify what are required to attain its redox reversibility for utilizing depleted U as an electrode active material in a redox flow battery. As a result, reversibility of the U
N) ionic liquid was studied to clarify what are required to attain its redox reversibility for utilizing depleted U as an electrode active material in a redox flow battery. As a result, reversibility of the U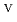 O
O
 /U
/U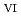 O
O
 redox reaction was successfully achieved in use of a glassy carbon working electrode under presence of Cl
redox reaction was successfully achieved in use of a glassy carbon working electrode under presence of Cl in [emim]Tf
in [emim]Tf N. To improve diffusivity of solutes, [emim]Tf
N. To improve diffusivity of solutes, [emim]Tf N diluted with an auxiliary molecular solvent, N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF). We have succeeded in demonstrating a reversible redox reaction of [U
N diluted with an auxiliary molecular solvent, N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF). We have succeeded in demonstrating a reversible redox reaction of [U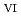 O
O Cl
Cl ]
] + e
+ e = [U
= [U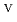 O
O Cl
Cl ]
] in the 50:50 v/v [emim]Tf
in the 50:50 v/v [emim]Tf N-DMF liquid electrolyte containing Cl
N-DMF liquid electrolyte containing Cl .
.
 O
O -75MoO
-75MoO binary glasses composed of isolated MoO
binary glasses composed of isolated MoO

Masuno, Atsunobu*; Munakata, Sae*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Yaji, Toyonari*; Kosugi, Yoshihisa*; Shimakawa, Yuichi*
Inorganic Chemistry, 63(12), p.5701 - 5708, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:65.79(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Transparent and brown La O
O -MoO
-MoO binary glasses were prepared in bulk form using a levitation technique. The glass-forming range was limited, with the primary composition being approximately 25 mol% La
binary glasses were prepared in bulk form using a levitation technique. The glass-forming range was limited, with the primary composition being approximately 25 mol% La O
O . This glass exhibited a clear crystallization at 546
. This glass exhibited a clear crystallization at 546  C, while determining its glass transition temperature was difficult. Notably, despite its amorphous nature, the glass possessed a density and packing density comparable to those of crystalline La
C, while determining its glass transition temperature was difficult. Notably, despite its amorphous nature, the glass possessed a density and packing density comparable to those of crystalline La Mo
Mo O
O . X-ray absorption fine structure and Raman scattering analyses revealed that the glass structure closely resembles La
. X-ray absorption fine structure and Raman scattering analyses revealed that the glass structure closely resembles La Mo
Mo O
O due to the presence of isolated MoO
due to the presence of isolated MoO
 units, whereas disordered atomic arrangement around La atoms was confirmed. The glass demonstrated transparency ranging from 378 to 5500 nm, and the refractive index at 1.0
units, whereas disordered atomic arrangement around La atoms was confirmed. The glass demonstrated transparency ranging from 378 to 5500 nm, and the refractive index at 1.0  m was estimated to be 2.0. The optical bandgap energy was 3.46 eV, which was slightly smaller than that of La
m was estimated to be 2.0. The optical bandgap energy was 3.46 eV, which was slightly smaller than that of La Mo
Mo O
O . Additionally, the glass displayed a transparent region ranging from 6.5 to 8.0
. Additionally, the glass displayed a transparent region ranging from 6.5 to 8.0  m. This occurrence results from the decreased diversity of MoO
m. This occurrence results from the decreased diversity of MoO units and connectivity of Mo-O-Mo, which resulted in the reduced overlap of multiphonon absorption. This glass formation, with its departure from conventional glass-forming rules, resulted in distinctive glasses with crystal-like atomic arrangements.
units and connectivity of Mo-O-Mo, which resulted in the reduced overlap of multiphonon absorption. This glass formation, with its departure from conventional glass-forming rules, resulted in distinctive glasses with crystal-like atomic arrangements.
 -MoO
-MoO whiskers in
whiskers in  Mo/
Mo/ Tc radioisotope production and
Tc radioisotope production and  Mo/
Mo/ Tc extraction using hot atoms
Tc extraction using hot atomsNgo, M. C.*; Fujita, Yoshitaka; Suzuki, Tatsuya*; Do, T. M. D.*; Seki, Misaki; Nakayama, Tadachika*; Niihara, Koichi*; Suematsu, Hisayuki*
Inorganic Chemistry, 62(32), p.13140 - 13147, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:54.36(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Technetium-99m ( Tc) is one of the most important radioisotopes for diagnostic radio-imaging applications.
Tc) is one of the most important radioisotopes for diagnostic radio-imaging applications.  Tc is a daughter product of the
Tc is a daughter product of the  Mo isotope. There are two methods used to produce
Mo isotope. There are two methods used to produce  Mo/
Mo/ Tc: the nuclear fission (n,f) and the neutron capture (n,
Tc: the nuclear fission (n,f) and the neutron capture (n, ) methods. Between them, the (n,f) method is the main route, used for approximately 90% of the world's production. However, the (n,f) method faces numerous problems, including the use of highly enriched uranium, the release of highly radioactive waste, and nonproliferation problems. Therefore, the (n,
) methods. Between them, the (n,f) method is the main route, used for approximately 90% of the world's production. However, the (n,f) method faces numerous problems, including the use of highly enriched uranium, the release of highly radioactive waste, and nonproliferation problems. Therefore, the (n, ) method is being developed as a future replacement for the (n,f) method. In this work,
) method is being developed as a future replacement for the (n,f) method. In this work,  -MoO
-MoO whiskers prepared by the thermal evaporation method and
whiskers prepared by the thermal evaporation method and  -MoO
-MoO particles were irradiated in a nuclear reactor to produce
particles were irradiated in a nuclear reactor to produce  Mo/
Mo/ Tc via neutron capture. The irradiated targets were dispersed into water to extract the
Tc via neutron capture. The irradiated targets were dispersed into water to extract the  Mo/
Mo/ Tc. As a result,
Tc. As a result,  -MoO
-MoO whisker yielded higher
whisker yielded higher  Mo extraction rate than that from
Mo extraction rate than that from  -MoO
-MoO . In addition, by comparing the dissolved
. In addition, by comparing the dissolved  Mo concentrations in water, we clarified a prominent hot-atom of
Mo concentrations in water, we clarified a prominent hot-atom of  -MoO
-MoO whiskers. This research is the first demonstration of
whiskers. This research is the first demonstration of  -MoO
-MoO being used as an irradiation target in the neutron capture method. On the basis of the results,
being used as an irradiation target in the neutron capture method. On the basis of the results,  -MoO
-MoO is considered a promising irradiation target for producing
is considered a promising irradiation target for producing  Mo/
Mo/ Tc by neutron capture and using water for the radioisotope extraction process in the future.
Tc by neutron capture and using water for the radioisotope extraction process in the future.
Hirata, Sakiko*; Kusaka, Ryoji; Meiji, Shogo*; Tamekuni, Seita*; Okudera, Kosuke*; Hamada, Shoken*; Sakamoto, Chihiro*; Honda, Takumi*; Matsushita, Kosuke*; Muramatsu, Satoru*; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 62(1), p.474 - 486, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.83(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Zheng, X.*; Kato, Masaru*; Uemura, Yohei*; Matsumura, Daiju; Yagi, Ichizo*; Takahashi, Kiyonori*; Noro, Shinichiro*; Nakamura, Takayoshi*
Inorganic Chemistry, 62(3), p.1257 - 1263, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:79.46(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Yamagata, Kazuhito*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Marumo, Kazuki*; Tasaki-Handa, Yuiko*; Haraga, Tomoko; Saito, Shingo*
Inorganic Chemistry, 62(2), p.730 - 738, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:42.77(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The inert NpO
 complex with a fluorescein-modified phenanthroline-2,9-dicarboxylic acid was found by kinetic selection using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) from a small chemical library. The small spontaneous dissociation rate constant of 8
complex with a fluorescein-modified phenanthroline-2,9-dicarboxylic acid was found by kinetic selection using polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) from a small chemical library. The small spontaneous dissociation rate constant of 8 10
10 s
s (the half-life of 23 hours) was determined. This is the singly-charged NpO
(the half-life of 23 hours) was determined. This is the singly-charged NpO
 complex exhibiting unusual kinetic inertness in aqueous solution, one million times slower than widely accepted fast kinetics of neptunyl complexes. Selective fluorescence detection of NpO
complex exhibiting unusual kinetic inertness in aqueous solution, one million times slower than widely accepted fast kinetics of neptunyl complexes. Selective fluorescence detection of NpO
 was achieved in PAGE with a detection limit of 68 pmol dm
was achieved in PAGE with a detection limit of 68 pmol dm (17 fg). This system was successfully applied to simulated spent nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive waste samples.
(17 fg). This system was successfully applied to simulated spent nuclear fuel and high-level radioactive waste samples.
 -edge to assess the U(V) electronic structure in FeUO
-edge to assess the U(V) electronic structure in FeUO
Yomogida, Takumi; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Ouchi, Kazuki; Kumagai, Yuta; Higashi, Kotaro*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro; Kirishima, Akira*; Kawamura, Naomi*; Takahashi, Yoshio*
Inorganic Chemistry, 61(50), p.20206 - 20210, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:59.79(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)FeUO was studied to clarify the electronic structure of U(V) in a metal monouranate compound. We obtained the peak splitting of HERFD-XANES spectra utilizing high-energy-resolution fluorescence detection-X-ray absorption near edge structure (HERFD-XANES) spectroscopy at the U L
was studied to clarify the electronic structure of U(V) in a metal monouranate compound. We obtained the peak splitting of HERFD-XANES spectra utilizing high-energy-resolution fluorescence detection-X-ray absorption near edge structure (HERFD-XANES) spectroscopy at the U L -edge, which is a novel technique in the U(V) compounds. Theoretical calculations revealed that the peak splitting was caused by splitting the 6d orbital of U(V). Such distinctive electronic states are of major interest to researchers and engineers working in various fields, from fundamental physics to the nuclear industry and environmental sciences for actinide elements.
-edge, which is a novel technique in the U(V) compounds. Theoretical calculations revealed that the peak splitting was caused by splitting the 6d orbital of U(V). Such distinctive electronic states are of major interest to researchers and engineers working in various fields, from fundamental physics to the nuclear industry and environmental sciences for actinide elements.
 O
O -pentadentate planar ligands designed for the strongest and selective capture of uranium from seawater
-pentadentate planar ligands designed for the strongest and selective capture of uranium from seawaterMizumachi, Takumi*; Sato, Minami*; Kaneko, Masashi; Takeyama, Tomoyuki*; Tsushima, Satoru*; Takao, Koichiro*
Inorganic Chemistry, 61(16), p.6175 - 6181, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:53.89(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Based on unique 5-fold equatorial coordination of UO
 , water-compatible pentadentate planar ligands, H
, water-compatible pentadentate planar ligands, H saldian and its derivatives, were designed as strong and selective capture of UO
saldian and its derivatives, were designed as strong and selective capture of UO
 in seawater. In the simulated seawater condition (0.5 M NaCl + 2.3 mM HCO
in seawater. In the simulated seawater condition (0.5 M NaCl + 2.3 mM HCO
 /CO
/CO
 , pH 8), saldian
, pH 8), saldian shows the strongest complexation with UO
shows the strongest complexation with UO
 to form UO
to form UO (saldian) (log
(saldian) (log
 = 28.05
= 28.05  0.07), which is more than 10 order of magnitude greater than amidoxime-based or -inspired ligand systems most commonly employed for U capture from seawater. Good selectivity for UO
0.07), which is more than 10 order of magnitude greater than amidoxime-based or -inspired ligand systems most commonly employed for U capture from seawater. Good selectivity for UO
 from other metal ions coexisting in seawater was also demonstrated.
from other metal ions coexisting in seawater was also demonstrated.
 Ta
Ta O
O
Kimura, Kenta*; Yagi, Naoki*; Hasegawa, Shunsuke*; Hagihara, Masato; Miyake, Atsushi*; Tokunaga, Masashi*; Cao, H.*; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Kimura, Tsuyoshi*
Inorganic Chemistry, 60(20), p.15078 - 15084, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:22.10(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Simonnet, M.; Kobayashi, Toru; Shimojo, Kojiro; Yokoyama, Keiichi; Yaita, Tsuyoshi
Inorganic Chemistry, 60(17), p.13409 - 13418, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:25 Percentile:91.54(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)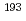 Ir M
Ir M ssbauer spectroscopic parameters of Vaska's complexes and their oxidative adducts
ssbauer spectroscopic parameters of Vaska's complexes and their oxidative adductsKaneko, Masashi; Nakashima, Satoru*
Inorganic Chemistry, 60(17), p.12740 - 12752, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:29.88(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)In the present study, density functional theory (DFT) calculation was applied to Vaska's complexes of formula 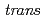 -[IrCl(CO)(PPh
-[IrCl(CO)(PPh )
) ], and their oxidative adducts with small molecules (YZ) including H
], and their oxidative adducts with small molecules (YZ) including H , i.e.,
, i.e., 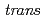 -[IrCl(YZ)(CO))(PPh
-[IrCl(YZ)(CO))(PPh )
) ], to successfully correlate the electronic states of the complexes with the corresponding
], to successfully correlate the electronic states of the complexes with the corresponding 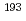 Ir M
Ir M ssbauer spectroscopic parameters. After confirming the reproducibility of the DFT methods for elucidating the equilibrium structures and
ssbauer spectroscopic parameters. After confirming the reproducibility of the DFT methods for elucidating the equilibrium structures and  Ir M
Ir M ssbauer isomer shifts of the octahedral Ir complexes, the isomer shifts and quadrupole splitting values of Vaska's complexes and their oxidative adducts were calculated. A bond critical point analysis revealed that the tendency in the isomer shifts was correlated with the strength of the covalent interaction in the coordination bonds. In an electric field gradient (EFG) analysis of the oxidative adducts, the sign of the principal axis was found to be positive for the complex with YZ = Cl
ssbauer isomer shifts of the octahedral Ir complexes, the isomer shifts and quadrupole splitting values of Vaska's complexes and their oxidative adducts were calculated. A bond critical point analysis revealed that the tendency in the isomer shifts was correlated with the strength of the covalent interaction in the coordination bonds. In an electric field gradient (EFG) analysis of the oxidative adducts, the sign of the principal axis was found to be positive for the complex with YZ = Cl and negative for the complex with YZ = H
and negative for the complex with YZ = H . This reversal of the sign of the EFG principal axis was caused by the difference in the electron density distribution for the coordination bonds between Ir and YZ, according to a density of states analysis.
. This reversal of the sign of the EFG principal axis was caused by the difference in the electron density distribution for the coordination bonds between Ir and YZ, according to a density of states analysis.
Kwon, H.*; Pietrasiak, E.*; Ohara, Takashi; Nakao, Akiko*; Chae, B.*; Hwang, C.-C.*; Jung, D.*; Hwang, I.-C.*; Ko, Y. H.*; Kim, K.*; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 60(9), p.6403 - 6409, 2021/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Nakano, Satoshi*; Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori; Machida, Shinichi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Fujihisa, Hiroshi*; Yamawaki, Hiroshi*; Goto, Yoshito*; Kikegawa, Takumi*
Inorganic Chemistry, 60(5), p.3065 - 3073, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:73.97(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)X-ray and neutron diffraction analyses of ammonia borane were conducted at ambient and high pressures. The H-H distance in dihydrogen bonds was shorter than twice the van der Waals radius (2.4  ). The half of the dihydrogen bonds were broken on phase transition from AP to the first high pressure phase (HP1) at approximately 1.2 GPa as revealed by an increase in the H-H distances. On further pressure increase, all of the H-H distances became shorter than 2.4
). The half of the dihydrogen bonds were broken on phase transition from AP to the first high pressure phase (HP1) at approximately 1.2 GPa as revealed by an increase in the H-H distances. On further pressure increase, all of the H-H distances became shorter than 2.4  again, implying the pressure-induced reformation of the dihydrogen bonds. Furthermore, the HP1 transformed to the second one with the structure of
again, implying the pressure-induced reformation of the dihydrogen bonds. Furthermore, the HP1 transformed to the second one with the structure of 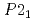 (Z = 2) at about 11 GPa. In this phase transition, the inclination of the molecule axis became larger and the number of types of dihydrogen bonds increased from 6 to 11. Just before the third transition at 18.9 GPa, the shortest dihydrogen bond decreased to 1.65
(Z = 2) at about 11 GPa. In this phase transition, the inclination of the molecule axis became larger and the number of types of dihydrogen bonds increased from 6 to 11. Just before the third transition at 18.9 GPa, the shortest dihydrogen bond decreased to 1.65  . The present study experimentally first confirmed the breakage and reformation of the dihydrogen bonds by the structural change under pressure.
. The present study experimentally first confirmed the breakage and reformation of the dihydrogen bonds by the structural change under pressure.
 complexes of mixed N,O-donor ligands demonstrated on a 10-fold [Eu(TPAMEN)]
complexes of mixed N,O-donor ligands demonstrated on a 10-fold [Eu(TPAMEN)] chelate complex
chelate complexSchnaars, K.; Kaneko, Masashi; Fujisawa, Kiyoshi*
Inorganic Chemistry, 60(4), p.2477 - 2491, 2021/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:44.28(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)To reduce high-level radiotoxic waste generated by nuclear power plants, highly selective separation agents for minor actinides are mandatory. The mixed N,O-donor ligand 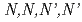 -tetrakis[(6-carboxypyridin-2-yl)methyl]ethylenediamine (H
-tetrakis[(6-carboxypyridin-2-yl)methyl]ethylenediamine (H TPAEN) has shown good performance as a masking agent in Am
TPAEN) has shown good performance as a masking agent in Am /Eu
/Eu separation studies. In this work, we examine whether a decrease in O-donor basicity can promote the M
separation studies. In this work, we examine whether a decrease in O-donor basicity can promote the M -N
-N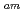 interactions. Therefore, we replace the deprotonated "charged" carboxylic acid groups of TPAEN
interactions. Therefore, we replace the deprotonated "charged" carboxylic acid groups of TPAEN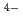 by neutral amide groups and introduce
by neutral amide groups and introduce 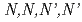 -tetrakis[(6-
-tetrakis[(6-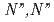 -diethylcarbamoylpyridin-2-yl)methyl]ethylenediamine (TPAMEN) as a new ligand. TPAMEN was crystallized with Eu(OTf)
-diethylcarbamoylpyridin-2-yl)methyl]ethylenediamine (TPAMEN) as a new ligand. TPAMEN was crystallized with Eu(OTf) and Eu(NO
and Eu(NO )
) 6H
6H O to form positively charged 1:1 [Eu(TPAMEN)]
O to form positively charged 1:1 [Eu(TPAMEN)] complexes in the solid state. Alterations in the M-O/N bond distances are compared to [Eu(TPAEN)]
complexes in the solid state. Alterations in the M-O/N bond distances are compared to [Eu(TPAEN)] and investigated by DFT calculations to expose the differences in charge/energy density distributions at europium(III) and the donor functionalities of the TPAEN
and investigated by DFT calculations to expose the differences in charge/energy density distributions at europium(III) and the donor functionalities of the TPAEN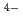 and TPAMEN. On the basis of estimations of the bond orders, atomic charges spin populations, and density of states in the Eu and potential Am and Cm complexes, the specific contributions of the donor-metal interaction are analyzed. The prediction of complex formation energy differences for the [M(TPAEN)]
and TPAMEN. On the basis of estimations of the bond orders, atomic charges spin populations, and density of states in the Eu and potential Am and Cm complexes, the specific contributions of the donor-metal interaction are analyzed. The prediction of complex formation energy differences for the [M(TPAEN)] and [M(TPAMEN)]
and [M(TPAMEN)] (M
(M = Eu
= Eu , Am
, Am ) complexes provide an outlook on the potential performance of TPAMEN in Am
) complexes provide an outlook on the potential performance of TPAMEN in Am /Eu
/Eu separation.
separation.
Narita, Hirokazu*; Kasuya, Ryo*; Suzuki, Tomoya*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Tanaka, Mikiya*
Encyclopedia of Inorganic and Bioinorganic Chemistry (Internet), 28 Pages, 2020/12
Tamain, C.*; Bonato, L.*; Aupiais, J.*; Dumas, T.*; Guillaumont, D.*; Barkleit, A.*; Berthon, C.*; Solari, P. L.*; Ikeda, Atsushi; Guilbard, P.*; et al.
European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2020(14), p.1331 - 1344, 2020/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:24.09(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)The molecular characterization based on multi-technique approach has led to major highlights on revealing the coordination environment of americium (Am) surrounded by citric acid (H CitH). The structure of the different complexes at pH 1 and 3 are described. These characterizations are made possible by the comparison of the americium-citric acid system with the americium-tricarballylic acid (one analogue of the citric acid without the alpha-hydroxo group).
CitH). The structure of the different complexes at pH 1 and 3 are described. These characterizations are made possible by the comparison of the americium-citric acid system with the americium-tricarballylic acid (one analogue of the citric acid without the alpha-hydroxo group).
 Ru M
Ru M ssbauer parameters of ruthenium-nitrosyl complexes
ssbauer parameters of ruthenium-nitrosyl complexesKaneko, Masashi; Kato, Akane*; Nakashima, Satoru*; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Inorganic Chemistry, 58(20), p.14024 - 14033, 2019/10
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:56.50(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We applied density functional theory calculations to ruthenium-nitrosyl complexes, which are known to exist in high-level radioactive waste, to give a theoretical correlation between  Ru M
Ru M ssbauer spectroscopic parameters (
ssbauer spectroscopic parameters ( and
and 
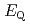 ) and ligand field strength (
) and ligand field strength (
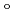 ) for the first time. The structures of the series of complexes, [Ru(NO)L
) for the first time. The structures of the series of complexes, [Ru(NO)L ] (L = Br
] (L = Br , Cl
, Cl , NH
, NH , CN
, CN ), were modeled based on the corresponding single-crystal X-ray coordinates. The comparisons of the geometries and total energies between the different spin states suggested that the singlet spin state of [Ru(II)(NO
), were modeled based on the corresponding single-crystal X-ray coordinates. The comparisons of the geometries and total energies between the different spin states suggested that the singlet spin state of [Ru(II)(NO )L
)L ] complexes were the most stable. The calculated results of both the
] complexes were the most stable. The calculated results of both the  and
and 
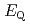 values reproduced the experimental results by reported previously and increased in the order of L = Br
values reproduced the experimental results by reported previously and increased in the order of L = Br , Cl
, Cl , NH
, NH , CN
, CN . Finally, we estimated the ligand field strength (
. Finally, we estimated the ligand field strength (
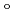 ) based on molecular orbitals, assuming C
) based on molecular orbitals, assuming C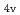 symmetry and showed the increase of
symmetry and showed the increase of 
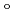 values in that order, being consistent with well-known spectrochemical series of ligands. The increase attributes to the strengthening of the abilities of
values in that order, being consistent with well-known spectrochemical series of ligands. The increase attributes to the strengthening of the abilities of  -donor and
-donor and  -acceptor of the L-ligands to the Ru atom, resulting in the increase of the
-acceptor of the L-ligands to the Ru atom, resulting in the increase of the  values.
values.
Narita, Hirokazu*; Nicolson, R. M.*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Ito, Fumiyuki*; Morisaku, Kazuko*; Goto, Midori*; Tanaka, Mikiya*; Heller, W. T.*; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; et al.
Inorganic Chemistry, 58(13), p.8720 - 8734, 2019/07
Times Cited Count:20 Percentile:75.87(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Yamaguchi, Toshio*; Nishino, Masaaki*; Yoshida, Koji*; Takumi, Masaharu*; Nagata, Kiyofumi*; Hattori, Takanori
European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2019(8), p.1170 - 1177, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:67.90(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Neutron diffraction measurements of an aqueous 2 mol dm CaCl
CaCl solutions in D
solutions in D O have been made at 1 GPa, 298 K as well as 0.1 MPa, 298 K. The experimental structure factors are subjected to Empirical Potential Structure Refinement (EPSR) modeling to reveal the ion hydration and association and solvent water at the atomic level. About seven water molecules surround Ca
O have been made at 1 GPa, 298 K as well as 0.1 MPa, 298 K. The experimental structure factors are subjected to Empirical Potential Structure Refinement (EPSR) modeling to reveal the ion hydration and association and solvent water at the atomic level. About seven water molecules surround Ca at the Ca-O and Ca-D distances of 2.44
at the Ca-O and Ca-D distances of 2.44  and 3.70
and 3.70  , respectively, at both pressures, suggesting no significant pressure effect on the cation hydration. On the other hand, the Cl
, respectively, at both pressures, suggesting no significant pressure effect on the cation hydration. On the other hand, the Cl ion shows a drastic change in water oxygen coordination from 7 at 0.1 MPa to 14 at 1 GPa, accompanied by shortening of Cl-O distance from 3.18
ion shows a drastic change in water oxygen coordination from 7 at 0.1 MPa to 14 at 1 GPa, accompanied by shortening of Cl-O distance from 3.18  to 3.15
to 3.15  . However, the number of water hydrogen atoms around Cl
. However, the number of water hydrogen atoms around Cl does not change significantly as 6.0
does not change significantly as 6.0  6.7 with shortening Cl-D distance from 2.22 to 2.18
6.7 with shortening Cl-D distance from 2.22 to 2.18  on compression. The pressure effect on the solvent water structure is also drastic as an increase in water oxygen atoms of 4.7 at the O-O distance of 2.79
on compression. The pressure effect on the solvent water structure is also drastic as an increase in water oxygen atoms of 4.7 at the O-O distance of 2.79  at 0.1 MPa to 10.3 at 2.85
at 0.1 MPa to 10.3 at 2.85  at 1 GPa. The number of water hydrogen atoms, however, does not change as 1.2 at the O-D distance of 1.74
at 1 GPa. The number of water hydrogen atoms, however, does not change as 1.2 at the O-D distance of 1.74  for both pressures, demonstrating the presence of the O
for both pressures, demonstrating the presence of the O D hydrogen bonds which are significantly bent at 1 GPa at 298 K. This change of hydrogen bonds in water with pressure probably causes the drastic increase in water oxygen atoms around Cl
D hydrogen bonds which are significantly bent at 1 GPa at 298 K. This change of hydrogen bonds in water with pressure probably causes the drastic increase in water oxygen atoms around Cl .
.
Kaneko, Masashi; Suzuki, Hideya; Matsumura, Tatsuro
Inorganic Chemistry, 57(23), p.14513 - 14523, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:79.73(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)We elucidated the separation mechanism between Am(III) and Cm(III) ions by using two different types of diamide ligands, diglycolamide (DGA) and alkylated diamide amine (ADAAM), by means of the density functional theory technique and electron density analysis. The molecular geometries and formation reactions of the metal-ligand complexes were modeled by using [M(DGA) ]
] and [M(ADAAM)(NO
and [M(ADAAM)(NO )
) (H
(H O)]. We successfully reproduced Cm(III) selectivity over Am(III) with DGA and Am(III) selectivity over Cm(III) with ADAAM. Furthermore, we analyzed the bonding properties between the metal ion and the diamide-type ligands by using model complexes, [M(DGA)
O)]. We successfully reproduced Cm(III) selectivity over Am(III) with DGA and Am(III) selectivity over Cm(III) with ADAAM. Furthermore, we analyzed the bonding properties between the metal ion and the diamide-type ligands by using model complexes, [M(DGA) ]
] and [M(ADAAM)(NO
and [M(ADAAM)(NO )
) (H
(H O)], and revealed the differences in terms of the bond dissociation energy and the metal 5f-orbital participation in the covalency between the Am(III) and the Cm(III) complexes. It was suggested that the differences were key factors to understand the Am(III)/Cm(III) selectivity.
O)], and revealed the differences in terms of the bond dissociation energy and the metal 5f-orbital participation in the covalency between the Am(III) and the Cm(III) complexes. It was suggested that the differences were key factors to understand the Am(III)/Cm(III) selectivity.