Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sekikawa, Takuya; Takada, Kazuki*; Kai, Takeshi; Ono, Yoshiaki*
Journal of Applied Physics, 137(20), p.203901_1 - 203901_10, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0no abstracts in English
Kawasaki, Takuro; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Yamanaka, Satoru*; Murayama, Ichiro*; Kato, Takanori*; Baba, Masaaki*; Hashimoto, Hideki*; Harjo, S.; Aizawa, Kazuya; Tanaka, Hirohisa*; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 137(9), p.094101_1 - 094101_7, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Egashira, Naoya*; Matsuda, Tomoki*; Okuchi, Takuo*; Seto, Yusuke*; Ito, Yusuke*; Shobu, Takahisa; Nakanii, Nobuhiko*; Sano, Tomokazu*; 4 of others*
Journal of Applied Physics, 137(10), p.105903_1 - 105903_8, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied) , AgNbO
, AgNbO , and KNbO
, and KNbO
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Kobayashi, Toru; Tsuji, Takuya; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Yuji; Noguchi, Yuji*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 63(9), p.09SP12_1 - 09SP12_10, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)NaNbO , AgNbO
, AgNbO , and KNbO
, and KNbO with ABO
with ABO -type perovskite system is known to possess good ferroelectric properties. We directly determined the rattling space of each atom through local structure analysis. This analysis revealed the bonding sites with large fluctuations varied with varying ion size. Experimental evidence including soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy, indicates that the A-site ions are hybridized with oxygen.
-type perovskite system is known to possess good ferroelectric properties. We directly determined the rattling space of each atom through local structure analysis. This analysis revealed the bonding sites with large fluctuations varied with varying ion size. Experimental evidence including soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy, indicates that the A-site ions are hybridized with oxygen.
Ding, H.*; Ito, Keita*; Endo, Yasushi*; Takanashi, Koki; Seki, Takeshi*
Journal of Physics D; Applied Physics, 57(38), p.385002_1 - 385002_10, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:62.71(Physics, Applied)Takyu, Sodai*; Matsumoto, Kenichiro*; Hirade, Tetsuya; Nishikido, Fumihiko*; Akamatsu, Go*; Tashima, Hideaki*; Takahashi, Miwako*; Yamaya, Taiga*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 63(8), p.086003_1 - 086003_8, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:40.97(Physics, Applied)Positrons and electrons sometimes exist as a bound state, positronium (Ps), in living organisms. The triplet Ps (ortho-Ps) annihilation time represents the ortho-Ps pick-off annihilation lifetime, and it varies depending on the surrounding electron density. The ortho-Ps lifetime may add new biological information to PET scan information. In order to discuss the feasibility of quantifying (free) radicals in vivo by the ortho-Ps lifetime, we used a clinical PET system to make ortho-Ps lifetime measurements in aqueous solutions containing radicals. The results suggested that differences in radical concentrations in aqueous solutions of the order of a few mM could be quantified by the ortho-Ps lifetime if the counting statistic of the positron annihilation events was more than 10 events. This concentration was higher than the radical concentration generated in the physiological functions of living organisms.
events. This concentration was higher than the radical concentration generated in the physiological functions of living organisms.
 gamma-ray imager using detector response patterns
gamma-ray imager using detector response patternsKitayama, Yoshiharu; Nogami, Mitsuhiro*; Hitomi, Keitaro*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 63(7), p.076502_1 - 076502_8, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)We constructed a gamma-ray imager that estimates the distribution of gamma-ray sources based on the response patterns of multiple gamma-ray detectors randomly positioned in three-dimensional space. The Coded Cube Camera for Gamma-ray (C3G), comprising eight GAGG (Ce) scintillator and eighteen lead cubes is housed in a cubical casing with an 86 mm edge length and weighs approximately 600 g. Results of the 4 imaging experiment confirmed the feasibility of imaging a 10 MBq
imaging experiment confirmed the feasibility of imaging a 10 MBq  Cs source located 3 m away with an angular uncertainty of 5
Cs source located 3 m away with an angular uncertainty of 5 within a 10 min measurement. C3G operates with only eight channels, instead of the hundreds needed by a typical imager, offering a simplified circuit and reconstruction algorithm, thereby achieving a cost-effective and reliable system. With its compact and lightweight design, 4
within a 10 min measurement. C3G operates with only eight channels, instead of the hundreds needed by a typical imager, offering a simplified circuit and reconstruction algorithm, thereby achieving a cost-effective and reliable system. With its compact and lightweight design, 4 field of view, and high angular uncertainty, this technology is expected to find extensive applications in astronomy, medicine, nuclear security, and decommissioning projects.
field of view, and high angular uncertainty, this technology is expected to find extensive applications in astronomy, medicine, nuclear security, and decommissioning projects.
Kubota, Masato; Kato, Seiichi*
Journal of Applied Physics, 136(2), p.025102_1 - 025102_5, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:40.97(Physics, Applied)Zhang, Z.*; Hattori, Takanori; Song, R.*; Yu, D.*; Mole, R.*; Chen, J.*; He, L.*; Zhang, Z.*; Li, B.*
Journal of Applied Physics, 136(3), p.035105_1 - 035105_8, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:40.97(Physics, Applied)Solid-state refrigeration using barocaloric materials is environmentally friendly and highly efficient, making it a subject of global interest over the past decade. Here, we report giant barocaloric effects in sodium hexafluorophosphate (NaPF ) and sodium hexafluoroarsenate (NaAsF
) and sodium hexafluoroarsenate (NaAsF ) that both undergo a cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transition near room temperature. We have determined that the low-temperature phase structure of NaPF
) that both undergo a cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transition near room temperature. We have determined that the low-temperature phase structure of NaPF is a rhombohedral structure with space group R
is a rhombohedral structure with space group R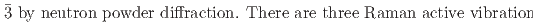 and NaAsF
and NaAsF , i.e., F
, i.e., F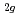 , E
, E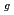 , and A
, and A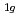 . The phase transition temperature varies with pressure at a rate of dT
. The phase transition temperature varies with pressure at a rate of dT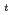 /dP = 250 and 310 K/GPa for NaPF
/dP = 250 and 310 K/GPa for NaPF and NaAsF
and NaAsF . The pressure-induced entropy changes of NaPF
. The pressure-induced entropy changes of NaPF and NaAsF
and NaAsF are determined to be around 45.2 and 35.6J kg
are determined to be around 45.2 and 35.6J kg K
K , respectively. The saturation driving pressure is about 40 MPa. The pressure-dependent neutron powder diffraction suggests that the barocaloric effects are related to the pressure-induced cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transitions.
, respectively. The saturation driving pressure is about 40 MPa. The pressure-dependent neutron powder diffraction suggests that the barocaloric effects are related to the pressure-induced cubic-to-rhombohedral phase transitions.
Jo, Sadaharu*; Suzuki, Seiya; Yoshimura, Masamichi*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 63(6), p.065503_1 - 065503_4, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Watanabe, Kenichi*; Oshima, Yuya*; Shigyo, Nobuhiro*; Hirata, Yuho
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 63(5), p.056001_1 - 056001_5, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Lithium-containing scintillators are used for neutron detection; Li-containing scintillators detect tritons and alpha rays produced by neutrons. Since these particles deposit higher energy than gamma rays, Li-containing scintillators can separate gamma rays and neutrons. However, the luminescence efficiency of scintillator decreases for ion beams due to a phenomenon called the quenching effect. Evaluation of the quenching effect is necessary to accurately separate neutrons and gamma rays. The Birks equation is used to predict the scintillation efficiency change due to the quenching effect, but it is necessary to determine the quenching coefficient in the Birks equation. In this study, we used PHITS to calculate the luminescence of Li-containing scintillators considering the quenching effect based on Birks' equation with the quenching coefficient as a free parameter. Then, by comparing the simulated results with the experimentally obtained luminescence, the extinction coefficients of Li glass, Ce:LiCaAlF , and Eu:LiCaAlF
, and Eu:LiCaAlF scintillators were determined.
scintillators were determined.
Omer, M.; Shizuma, Toshiyuki*; Hajima, Ryoichi*; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Journal of Applied Physics, 135(18), p.184903_1 - 184903_10, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Applied)Kitayama, Yoshiharu; Nogami, Mitsuhiro*; Hitomi, Keitaro*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 63(3), p.032005_1 - 032005_6, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:40.97(Physics, Applied)We introduce a novel gamma-ray imaging technique that uses detector response patterns. This method employs multiple shielding cubes randomly positioned in a three-dimensional configuration. Within the volume defined by these cubes, a unique gamma-ray flux pattern is formed based on the incidence direction of the gamma rays. This pattern can be measured using the responses of several scintillator cubes. By pre-measuring the detector response pattern and incidence direction of the gamma rays, the incidence direction can be estimated using an unfolding technique. Simulations were performed using a  Cs point source. Our results show that a 10 MBq
Cs point source. Our results show that a 10 MBq  Cs source, located 3 m away from the imager, can be imaged with an angular resolution close to 10
Cs source, located 3 m away from the imager, can be imaged with an angular resolution close to 10 . These findings suggest that our new method is comparable to existing gamma-ray imaging techniques. Potential applications of this imaging method include nuclear power plant decommissioning, nuclear medicine, security, and astronomy.
. These findings suggest that our new method is comparable to existing gamma-ray imaging techniques. Potential applications of this imaging method include nuclear power plant decommissioning, nuclear medicine, security, and astronomy.
 -Fe
-FeSuzudo, Tomoaki; Ebihara, Kenichi; Tsuru, Tomohito; Mori, Hideki*
Journal of Applied Physics, 135(7), p.075102_1 - 075102_7, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:62.71(Physics, Applied)Fracture of body centred cubic (bcc) metals and alloys below the ductile-to-brittle transition temperature is brittle. This is theoretically explained by the notion that the critical stress intensity factor of a given crack front for brittle fracture is smaller than that for plastic deformation; hence, brittle fracture is chosen over plastic deformation. Although this view is true from a macroscopic point of view, such brittle fracture is always accompanied by small-scale plastic deformation in the vicinity of the crack tip, i.e. crack tip plasticity. This short paper investigates the origin of this plasticity using atomistic modeling with a recently developed machine-learning interatomic potential of  -Fe. The computational results identified the precursor of crack tip plasticity, i.e. the group of activated atoms dynamically nucleated by fast crack propagation.
-Fe. The computational results identified the precursor of crack tip plasticity, i.e. the group of activated atoms dynamically nucleated by fast crack propagation.
 Na
Na TiO
TiO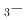 BaTiO
BaTiO solid solutions
solid solutionsYoneda, Yasuhiro; Kobayashi, Toru; Tsuji, Takuya; Matsumura, Daiju; Saito, Yuji; Noguchi, Yuji*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 62(SM), p.SM1006_1 - SM1006_8, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:50.15(Physics, Applied)Bi Na
Na TiO
TiO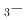 BaTiO
BaTiO (BNT
(BNT BT) solid solutions have been extensively studied because they exhibit good piezoelectric properties. In addition, a wide variety of phases are observed depending on the BT composition. Soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy and high-energy X-ray diffraction experiments of BNT
BT) solid solutions have been extensively studied because they exhibit good piezoelectric properties. In addition, a wide variety of phases are observed depending on the BT composition. Soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy and high-energy X-ray diffraction experiments of BNT BT solid solutions were performed using synchrotron radiation. From the electronic structure and local structure of BNT
BT solid solutions were performed using synchrotron radiation. From the electronic structure and local structure of BNT BT solid solution, the substitution effect of BT occurred mainly at the A site, which is the substitution site of Ba. The rhombohedral strain of the TiO
BT solid solution, the substitution effect of BT occurred mainly at the A site, which is the substitution site of Ba. The rhombohedral strain of the TiO octahedron did not change with the change in BT composition, suggesting that the change in the electronic structure at the O-
octahedron did not change with the change in BT composition, suggesting that the change in the electronic structure at the O- absorption edge is due to the change in the hybridization state.
absorption edge is due to the change in the hybridization state.
Hirata, Yuho; Kai, Takeshi; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Matsuya, Yusuke*; Sato, Tatsuhiko
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 62(10), p.106001_1 - 106001_6, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:50.15(Physics, Applied)Optimization of semiconductor detector design requires theoretical analysis of the process of radiation conversion to carriers (excited electrons) in semiconductor materials. We, therefore, developed an electron track-structure code that can trace an incident electron trajectory down to a few eV and simulate many excited electron productions in semiconductors, named ETSART, and implemented it into PHITS. The accuracy of ETSART was validated by comparing calculated electron ranges in semiconductor materials with the corresponding data recommended in ICRU Report 37 and obtained from another simulation code. The average energy required to produce a single excited electron (epsilon value) is an important value that describes the characteristics of semiconductor detectors. Using ETSART, we computed the epsilon values in various semiconductors and found that the calculated epsilon values cannot be fitted well with a linear model of the band-gap energy. ETSART is expected to be useful for initial and mechanistic evaluations of electron-hole generation in undiscovered materials.
Ogawa, Hiroki; Asamori, Koichi; Negi, Tateyuki*; Ueda, Takumi*
Journal of Applied Geophysics, 213, p.105012_1 - 105012_17, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:37.22(Geosciences, Multidisciplinary)A number of schemes for processing magnetotelluric (MT) data have been reported aiming at suppressing the strong effect of artificial electromagnetic noise, especially coherent noise that is correlated between electric and magnetic time series. Many of the recent denoising schemes are based on decomposing MT data into the responses of the natural signal and noise. Meanwhile, it is crucial to distinguish the natural signal from noise stably without depending on any empirical choice of parameter setting. In addition, improper subtraction of values from the separated signal can lead to the loss of useful values of the natural signal or missing noise-affected values, which may result in failure in deriving the true MT responses. We propose a novel data-processing method that applies frequency-domain independent component analysis (FDICA) to both the local MT data and the reference magnetic data. Among the separated signal, the proposed method can quantitatively distinguish the natural signal from the noise-affected components by calculating the ratio of cross-power spectrum with the reference data to the auto-power spectrum for each component. When determining which values to subtract from the separated signal, we introduce an evaluation index with respect to two characteristics of the MT response function: stationary in the time domain and smoothness in the frequency domain. We conduct the experiments both with MT time series severely contaminated by synthetic coherent noises and with MT field data interfered with DC (direct current) railways. Consequently, we confirm the superiority of the proposed method in the noise-suppression performance over the conventional methods of MT data processing.
 /GaN interfaces with suppressed Ga-oxide interlayer via sputter deposition of SiO
/GaN interfaces with suppressed Ga-oxide interlayer via sputter deposition of SiO
Onishi, Kentaro*; Kobayashi, Takuma*; Mizobata, Hidetoshi*; Nozaki, Mikito*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Shimura, Takayoshi*; Watanabe, Heiji*
Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 62(5), p.050903_1 - 050903_4, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:50.15(Physics, Applied)While the formation of an GaO interlayer is key to achieving SiO
interlayer is key to achieving SiO /GaN interfaces with low defect density, it can affect the reliability and stability of metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) devices if the annealing conditions are not properly designed. In the present study, we aimed to minimize the growth of the GaO
/GaN interfaces with low defect density, it can affect the reliability and stability of metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) devices if the annealing conditions are not properly designed. In the present study, we aimed to minimize the growth of the GaO layer on the basis of the sputter deposition of SiO
layer on the basis of the sputter deposition of SiO on GaN. Synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectrometry measurements confirmed the suppressed growth of the GaO
on GaN. Synchrotron radiation X-ray photoelectron spectrometry measurements confirmed the suppressed growth of the GaO layer compared with a SiO
layer compared with a SiO /GaN structure formed by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Negligible GaO
/GaN structure formed by plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition. Negligible GaO growth was also observed when subsequent oxygen annealing up to 600
growth was also observed when subsequent oxygen annealing up to 600 C was performed. A MOS device with negligible capacitance-voltage hysteresis, nearly ideal flat-band voltage, and low leakage current was demonstrated by performing oxygen and forming gas annealing at temperatures of 600
C was performed. A MOS device with negligible capacitance-voltage hysteresis, nearly ideal flat-band voltage, and low leakage current was demonstrated by performing oxygen and forming gas annealing at temperatures of 600 C and 400
C and 400 C, respectively.
C, respectively.
Maekawa, Sadamichi; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Ieda, Junichi; Saito, Eiji
Journal of Applied Physics, 133(2), p.020902_1 - 020902_24, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:93.17(Physics, Applied) Np and
Np and  Am gamma ray regions
Am gamma ray regionsFukuda, Tatsuo; Kobata, Masaaki; Shobu, Takahisa; Yoshii, Kenji; Kamiya, Junichiro; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Makino, Takahiro*; Yamazaki, Yuichi*; Oshima, Takeshi*; Shirai, Yasuhiro*; et al.
Journal of Applied Physics, 132(24), p.245102_1 - 245102_8, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.32(Physics, Applied)Direct energy conversion has been investigated using Ni/SiC Schottky junctions with the irradiation of monochromatized synchrotron X-rays simulating the gamma rays of  Np (30 keV) and
Np (30 keV) and  Am (60 keV). From current-voltage measurements, electrical energies were obtained for both kinds of gamma rays. The energy conversion efficiencies were found to reach up to
Am (60 keV). From current-voltage measurements, electrical energies were obtained for both kinds of gamma rays. The energy conversion efficiencies were found to reach up to  1.6%, which is comparable to those of a few other semiconducting systems reported thus far. This result shows a possibility of energy recovery from nuclear wastes using the present system, judging from the radiation tolerant nature of SiC. Also, we found different conversion efficiencies between the two samples. This could be understandable from hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and secondary ion mass spectroscopy measurements, suggesting the formation of Ni-Si compounds at the interface in the sample with a poor performance. Hence, such combined measurements are useful to provide information that cannot be obtained by electrical measurements alone.
1.6%, which is comparable to those of a few other semiconducting systems reported thus far. This result shows a possibility of energy recovery from nuclear wastes using the present system, judging from the radiation tolerant nature of SiC. Also, we found different conversion efficiencies between the two samples. This could be understandable from hard X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and secondary ion mass spectroscopy measurements, suggesting the formation of Ni-Si compounds at the interface in the sample with a poor performance. Hence, such combined measurements are useful to provide information that cannot be obtained by electrical measurements alone.