Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ohashi, Tomonori*; Sakamaki, Tatsuya*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Steinle-Neumann, G.*; Hattori, Takanori; Yuan, L.*; Suzuki, Akio*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (Internet), 120(1), p.240926a_1 - 240926a_13, 2025/06
We explore the structures of dry and hydrated (H O and D
O and D O) Na
O) Na Si
Si O
O melt at 0-6 GPa and 1000-1300 K and glasses recovered from high pressure and temperatures by in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The structures of the melts at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K are also investigated by ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation. In-situ neutron experiments revealed that the D-O distance increases with compression due to the formation of -O-D-O- bridging species, which is reproduced by the molecular dynamics simulations. The pressure-induced -O-D-O- formation reflects a more rigid incorporation of hydrogen, which acts as a mechanism for the experimentally observed higher solubility of water in silicate melts. Together with shrinking modifier domains, this process dominates the compression behavior of hydrous Na
melt at 0-6 GPa and 1000-1300 K and glasses recovered from high pressure and temperatures by in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction. The structures of the melts at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K are also investigated by ab-initio molecular dynamics simulation. In-situ neutron experiments revealed that the D-O distance increases with compression due to the formation of -O-D-O- bridging species, which is reproduced by the molecular dynamics simulations. The pressure-induced -O-D-O- formation reflects a more rigid incorporation of hydrogen, which acts as a mechanism for the experimentally observed higher solubility of water in silicate melts. Together with shrinking modifier domains, this process dominates the compression behavior of hydrous Na Si
Si O
O melt, whereas the compression of dry Na
melt, whereas the compression of dry Na Si
Si O
O at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K is governed largely by bending of the Si-O-Si angle. The molecular dynamics simulations on hydrous Na
at 0-10 GPa and 3000 K is governed largely by bending of the Si-O-Si angle. The molecular dynamics simulations on hydrous Na Si
Si O
O melts further suggest that the sodium ions are scavenged from its network-modifying role via 2(
melts further suggest that the sodium ions are scavenged from its network-modifying role via 2(![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-O
Si-O + Na
+ Na )
) 
![$$^{[4]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZULV4SI.gif) Si-(O-
Si-(O-![$$^{[5]}$$](/search/images/ERPHWWZVLV4SI.gif) Si-O)
Si-O) + 2Na
+ 2Na and Si-O
and Si-O + Na
+ Na + Si-OH
+ Si-OH  Si-(O-H-O-Si)
Si-(O-H-O-Si) + Na
+ Na with increasing pressure.
with increasing pressure.
Suzuki, Satoshi*; Yuguchi, Takashi*; Ishiguro, Keito*; Endo, Kyoka*; Kato, Asuka*; Yokoyama, Kosuke*; Ogita, Yasuhiro; Yokoyama, Tatsunori; Sakata, Shuhei*; Ono, Takeshi*; et al.
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (Internet), 119(1), p.230807_1 - 230807_18, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.28(Mineralogy)Understanding the crustal evolutionary dynamics of island arc-trench systems requires a thorough evaluation of magma chamber processes, and especially of shallow crustal granitic magma intrusion and emplacement processes. To address this, we studied the petrography and geochronology of the Kuki granite, Kitakami Mountains, northeast Japan, as an example of a non-adakitic granite at the magmatic flare-up stage. Granitic borehole samples reflect vertical variation within a magma chamber. Whole-rock chemical composition and mode data reveal a vertical transition from felsic to mafic composition with increasing depth, potentially due to gravitational fractionation of crystals in the magma chamber. The pressure and temperature history of the Kuki granite indicates no change in the magma depth with cooling from 800 to 730 C, and geobarometric calculations indicate the emplacement of magma at a depth of approximately10 km. Simultaneous determination of the zircon U Pb age, Ti concentration, and Th/U yields 1) the time temperature history of granitic magma before its solidification, and 2) the correlation between temperature and Th/U in the magma. The magma chamber cooled from ca. 900 to 700
C, and geobarometric calculations indicate the emplacement of magma at a depth of approximately10 km. Simultaneous determination of the zircon U Pb age, Ti concentration, and Th/U yields 1) the time temperature history of granitic magma before its solidification, and 2) the correlation between temperature and Th/U in the magma. The magma chamber cooled from ca. 900 to 700 C at approximately 125 Ma. The change in Th/U with temperature indicates greater fractional crystallization in the magma chamber at temperatures above 800
C at approximately 125 Ma. The change in Th/U with temperature indicates greater fractional crystallization in the magma chamber at temperatures above 800 C than below 800
C than below 800 C. Samples from different depth exhibit common tendencies in terms of the relationship between Th/U and temperature, indicating the same system of fractional crystallization throughout the cooling magma chamber.
C. Samples from different depth exhibit common tendencies in terms of the relationship between Th/U and temperature, indicating the same system of fractional crystallization throughout the cooling magma chamber.
Takano, Masahiro*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Mori, Yuichiro*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Kakizawa, Sho*; Sano, Asami; Iizuka-Oku, Riko*; Tsuchiya, Taku*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (Internet), 119(1), p.240122_1 - 240122_9, 2024/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Mineralogy)Hydrogenation of iron sulfide (FeS) under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions has attracted attention because hydrogen and sulfur are promising candidates as light elements in the cores of the Earth and other terrestrial planets. In earlier reports describing the hydrogenation of FeS, the chemical compositions of starting materials were not fully clarified. This study reports in-situ neutron and X-ray diffraction measurements under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions of an Fe-S-H system using a stochiometric Fe1.000S (troilite) as a starting material. The occupancies determined were significantly lower than those reported from earlier studies, indicating that the hydrogenation of FeS can be affected strongly by the stoichiometry of iron sulfide.
Yamada, Raiki; Takahashi, Toshiro*; Ogita, Yasuhiro
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (Internet), 118(1), p.221219a_1 - 221219a_26, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:34.82(Mineralogy)Oligocene to Miocene volcanic rocks from the Toyama basin of the SW Japan arc, that were formed during back-arc spreading in the Japan Sea, were examined to reveal their petrogeneses and temporal change of arc volcanism during the Japan Sea opening. We reported whole-rock major and trace element and Sr-Nd isotopic compositions of andesites and rhyolites (23-16 Ma) and quantitatively discussed their petrogenesis, based on comparison with the results of model calculations, in this paper. Main concluding remarks are as follows: (1) Rhyolite magmas were generated by crustal assimilation of basaltic to andesitic magmas. (2) Andesites consist of high-Mg andesite, high-Sr, and tholeiitic andesite, generated by interaction among slab fluid, slab melt, and crustal material. (3) Upwelling of the asthenospheric mantle into the mantle wedge caused melting of the subducting Pacific plate, and andesitic magmatism induced rhyolitic magmatism.
Yuguchi, Takashi*; Izumino, Yuya*; Sasao, Eiji
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences (Internet), 117(1), p.220415_1 - 220415_12, 2022/00
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:7.69(Mineralogy)This study presents the use of petrographic plagioclase alteration indicators as a new method for quantitatively evaluating the extent of plagioclase alteration within granites, using the Toki granite, central Japan. Alteration indicators and areal fractions of microvoids in the plagioclases were obtained via BSE image analysis. The volume of the micropores in the altered plagioclase was characterized by the areal fraction of microvoids in the grains. The plagioclase alteration indicators were obtained as the ratio between the alteration product area and the original plagioclase area. In our previous study, we focused on biotite chloritization indicators. We found positive correlations between the plagioclase alteration and biotite chloritization indicators in the same sample, indicating that each alteration indicator can be used independently as a representative value for the sample. In the Toki granite, the plagioclase alteration was related to the biotite chloritization.

 3H(D)
3H(D) O by neutron diffraction and effect of pH on structural formulas of nesquehonite
O by neutron diffraction and effect of pH on structural formulas of nesquehoniteYamamoto, Genichiro*; Kyono, Atsushi*; Abe, Jun*; Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 116(2), p.96 - 103, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.55(Mineralogy)Neutron diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, and thermal analysis were performed to investigate the composition, structure, and formation conditions of the magnesium carbonate hydrate nesquehonite. The time-of-flight neutron diffraction revealed the crystal structure of the monoclinic space group  2
2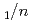 with lattice parameters of
with lattice parameters of  =7.72100(12)
=7.72100(12)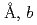 =5.37518(7)
=5.37518(7)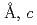 =12.1430(3)
=12.1430(3)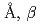 =90.165(4)
=90.165(4) , in which two deuterium atoms are coordinated to the O1, O2, and O6 atoms to form water molecules. The three water molecules in the structure suggests the structural formula of the nesquehonite should be MgCO
, in which two deuterium atoms are coordinated to the O1, O2, and O6 atoms to form water molecules. The three water molecules in the structure suggests the structural formula of the nesquehonite should be MgCO
 3H
3H O rather than Mg(HCO
O rather than Mg(HCO )(OH)
)(OH)  2H
2H O.
O.
Watanabe, Takahiro; Ishii, Chikako; Ishizaka, Chika; Niwa, Masakazu; Shimada, Koji; Sawai, Yuki*; Tsuchiya, Noriyoshi*; Matsunaka, Tetsuya*; Ochiai, Shinya*; Nara, Fumiko*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 116(3), p.140 - 158, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:33.36(Mineralogy)A portable energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (potable XRF) can be an effective tool for detecting chemical elements in various materials, such as geological, and environmental samples. In this study, working curves were confirmed using reference materials, such as igneous rocks and other geochemical standards, distributed by national and international organizations. Subsequently, quantification and semi-quantification analyses were performed by the portable XRF for inorganic elements in (A) fault rocks, (B) lake sediments from the middle Japan, and (C) soils with paleotsunami deposits from the Pacific coast of northeast Japan. Twenty-four elements (Mg-U) in these geological samples were measured by potable XRF using our working curves. Measured values by the portable XRF of the samples were good agreement with the reported values in almost cases.
 Si
Si at 14.7 GPa and 800 K
at 14.7 GPa and 800 KMori, Yuichiro*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Kakizawa, Sho*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Shito, Chikara*; Iizuka, Riko*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; et al.
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 116(6), p.309 - 313, 2021/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:10.84(Mineralogy)The Earth's core is believed to contain some light elements because it is 10% less dense than pure Fe under the corresponding pressure and temperature conditions. Hydrogen, a promising candidate among light elements, has phase relations and physical properties that have been investigated mainly for the Fe-H system. This study specifically examined an Fe-Si-H system using in-situ neutron diffraction experiments to investigate the site occupancy of deuterium of hcp-Fez Si
Si hydride at 14.7 GPa and 800 K. Results of Rietveld refinement indicate hcp-Fe
hydride at 14.7 GPa and 800 K. Results of Rietveld refinement indicate hcp-Fe Si
Si hydride as having deuterium (D) occupancy of 0.24(2) exclusively at the interstitial octahedral site in the hcp lattice. The effect on the site occupancy of D by addition of 2.6 wt% Si into Fe (Fe
hydride as having deuterium (D) occupancy of 0.24(2) exclusively at the interstitial octahedral site in the hcp lattice. The effect on the site occupancy of D by addition of 2.6 wt% Si into Fe (Fe Si
Si ) was negligible compared to results obtained from an earlier study of an Fe-D system (Machida et al., 2019).
) was negligible compared to results obtained from an earlier study of an Fe-D system (Machida et al., 2019).
Nagashima, Mariko*; Sano, Yuko*; Kochi, Takako*; Akasaka, Masahide*; Sano, Asami
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 115(5), p.391 - 406, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Mineralogy)The crystal chemistry of Sr-rich piemontite from a layered manganese ore deposit of the Tone mine, Nishisonogi Peninsula, Japan, was studied using methods of electron microprobe analysis, single crystal X-ray structural refinement,  Fe M
Fe M ssbauer spectroscopy, and X-ray and Time-of-Flight neutron Rietveld analyses to elucidate the intracrystalline distributions of Sr, Mn and Fe and the general and individual features on the structural changes with Sr contents in piemontite and epidotes.
ssbauer spectroscopy, and X-ray and Time-of-Flight neutron Rietveld analyses to elucidate the intracrystalline distributions of Sr, Mn and Fe and the general and individual features on the structural changes with Sr contents in piemontite and epidotes.
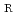 =100 mm spectrometer and correction of interferences between Th, U, and Pb with natural monazite
=100 mm spectrometer and correction of interferences between Th, U, and Pb with natural monaziteShimizu, Mayuko; Shibata, Kenji*; Suzuki, Kazuhiro; Sueoka, Shigeru; Niwa, Masakazu
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 112(2), p.88 - 96, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:8.30(Mineralogy)This paper outlines an advanced procedure involving the chemical Th-U-total Pb isochron method (CHIME) dating of monazite using a field-emission electron probe microanalyzer (FE-EPMA) equipped with spectrometers of 100 mm Rowland circle (R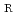 ) radius. The higher count rate of R
) radius. The higher count rate of R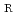 = 100 mm wavelength dispersive spectrometer (WDS) compared to R
= 100 mm wavelength dispersive spectrometer (WDS) compared to R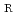 = 140 mm WDS enables measurements to be taken in a shorter time. CHIME dating using R
= 140 mm WDS enables measurements to be taken in a shorter time. CHIME dating using R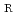 = 100 mm WDS had previously been difficult because of lower resolution compared to that of R
= 100 mm WDS had previously been difficult because of lower resolution compared to that of R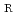 = 140 mm WDS. This problem has been overcome by a new interference correction method using natural monazites.
= 140 mm WDS. This problem has been overcome by a new interference correction method using natural monazites.
 -XRD with synchrotron radiation
-XRD with synchrotron radiationMotai, Satoko*; Mukai, Hiroki*; Watanuki, Tetsu; Owada, Kenji; Fukuda, Tatsuo; Machida, Akihiko; Kuramata, Chisaki*; Kikuchi, Ryosuke*; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Kogure, Toshihiro*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 111(5), p.305 - 312, 2016/10
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:48.36(Mineralogy)no abstracts in English
Yuguchi, Takashi*; Iwano, Hideki*; Kato, Takenori*; Sakata, Shuhei*; Hattori, Kentaro*; Hirata, Takafumi*; Sueoka, Shigeru; Danhara, Toru*; Ishibashi, Masayuki; Sasao, Eiji; et al.
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 111(1), p.9 - 34, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:53.36(Mineralogy)Zircon growth collected from a granitic pluton shows four (1st - 4th) events with specific mechanisms, crystallization temperatures and U-Pb ages, revealing the sequential formation process from intrusion through emplacement to crystallization / solidification. The events are recognized by: (1) internal structure of zircon based on the cathodoluminescence observation, (2) crystallization temperatures by the Ti-in-zircon thermometer in the internal structure and (3) U-Pb ages in the internal structure.
 Sr/
Sr/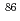 Sr ratios in the Toki granite, Central Japan; Implications for the intrusion and cooling processes of a granitic pluton
Sr ratios in the Toki granite, Central Japan; Implications for the intrusion and cooling processes of a granitic plutonYuguchi, Takashi; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Hama, Katsuhiro; Nishiyama, Tadao*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 108(1), p.1 - 12, 2013/02
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:39.24(Mineralogy)The spatial variation in initial 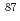 Sr/
Sr/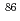 Sr ratios (SrI) in the Toki granite, Central Japan, shows heterogeneity ranging from 0.708942 to 0.710069, which provides information on formation processes of plutons. The Toki granite has three mineralogy-based rock facies: muscovite-biotite granite (MBG), hornblende-biotite granite (HBG) and biotite granite (BG). Large SrI values were found to be distributed at the western margin (west MBG) and the lithologically central region (central BG), while small SrI values were found at the northeast margin (northeast MBG). Regions with high and low Sr concentrations were also found in the Toki granite. In the Sr-rich samples, SrI (0.708942-0.709789) increases with 100/Sr (0.7-1.5). This geochemical trend extends towards the country sedimentary rocks of the Mino Terrane, which can be interpreted to result from assimilation and fractional crystallization (AFC) between the original granitic magma and the Mino sedimentary rocks. The SrI values in the Sr-rich regions show a correlation with the Alumina Saturation Index (ASI). In particular, the west MBG, with large SrI values, is classified as a peraluminous granitoid, suggesting that the western margin of the pluton was strongly affected by assimilation during the intrusion process. The Sr-poor samples are present both in the central BG, with large SrI values, and in the northeast MBG, with small SrI values. The Sr-poor samples have small ASI and large differentiation indices, indicating that the central BG and the northeast MBG were generated either by different AFC process with different amounts of contaminants or by the intrusion and fractionation of different source magma with different SrI values. Overall, the geochemical spatial variations found in the Toki granite can be explained by various degrees of assimilation and fractional crystallization in the magma chamber and/or multi-stage intrusions with different degrees of crystallization of plural source magmas.
Sr ratios (SrI) in the Toki granite, Central Japan, shows heterogeneity ranging from 0.708942 to 0.710069, which provides information on formation processes of plutons. The Toki granite has three mineralogy-based rock facies: muscovite-biotite granite (MBG), hornblende-biotite granite (HBG) and biotite granite (BG). Large SrI values were found to be distributed at the western margin (west MBG) and the lithologically central region (central BG), while small SrI values were found at the northeast margin (northeast MBG). Regions with high and low Sr concentrations were also found in the Toki granite. In the Sr-rich samples, SrI (0.708942-0.709789) increases with 100/Sr (0.7-1.5). This geochemical trend extends towards the country sedimentary rocks of the Mino Terrane, which can be interpreted to result from assimilation and fractional crystallization (AFC) between the original granitic magma and the Mino sedimentary rocks. The SrI values in the Sr-rich regions show a correlation with the Alumina Saturation Index (ASI). In particular, the west MBG, with large SrI values, is classified as a peraluminous granitoid, suggesting that the western margin of the pluton was strongly affected by assimilation during the intrusion process. The Sr-poor samples are present both in the central BG, with large SrI values, and in the northeast MBG, with small SrI values. The Sr-poor samples have small ASI and large differentiation indices, indicating that the central BG and the northeast MBG were generated either by different AFC process with different amounts of contaminants or by the intrusion and fractionation of different source magma with different SrI values. Overall, the geochemical spatial variations found in the Toki granite can be explained by various degrees of assimilation and fractional crystallization in the magma chamber and/or multi-stage intrusions with different degrees of crystallization of plural source magmas.
Yuguchi, Takashi; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Nishiyama, Tadao*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 106(3), p.130 - 141, 2011/06
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:50.74(Mineralogy)Petrographical studies examining the development and variations of sub-solidus reactions recorded in the Toki granite represent the three-dimensional cooling pattern of this zoned pluton in Central Japan. Samples collected from 19 boreholes in the Toki granite show characteristics indicative of spatial variations in the extent of sub-solidus reactions. Exsolution coarsening has produced microperthite including albite-rich lamellae in this pluton, while deuteric coarsening has resulted in patchperthite, myrmekite, and the reaction rim. The extent of deuteric coarsening reactions can be evaluated by the width and spacing of albite-rich patch in patchperthite, and by the thickness of myrmekite and the reaction rim. The width, spacing and thickness of these textural features increase systematically with elevation and also increase gradually in the horizontal inward in the western part but not in the eastern part of the pluton. The systematic variations in textural development indicate that the Toki granite cooled effectively from the roof and from the western margin during the deuteric coarsening stage. The deuteric coarsening may have occurred at temperatures below 500 C based on ternary feldspar thermometry.
C based on ternary feldspar thermometry.
Yuguchi, Takashi; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Nishiyama, Tadao*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 106(2), p.61 - 78, 2011/04
Times Cited Count:22 Percentile:52.67(Mineralogy)Oikawa, Teruki; Umeda, Koji; Kanazawa, Sunao; Matsuzaki, Tatsuji*
Journal of Mineralogical and Petrological Sciences, 101(1), p.23 - 28, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:3.98(Mineralogy)The authors report biotite K-Ar, zircon FT, and apatite FT ages from four sites in the Ichifusayama Granodiorite in the Outer Zone acidic rocks of Southwest Japan, Southern Kyushu. All the K-Ar ages and FT ages are concentrated on 13-10Ma. The difference in the apatite FT ages was caused by an influence of paleotopography such as a deep valley. The rapid cooling of the granodiorite in ca. 13 Ma occurred by uplift throughout the Outer Zone of Southwest Japan in Kyushu. It is considered that obduction to the Philippine Sea Plate of the Outer Zone of Kyushu also occurred in ca. 13 Ma. It is considered that obduction to the Philippine Sea Plate of the Outer Zone of Kyushu also occurred in ca. 13 Ma.