Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Abe, Yosuke; Tsuru, Tomohito; Fujita, Yohei*; Otomo, Masahide*; Sasaki, Taisuke*; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Okubo, Nariaki; Ukai, Shigeharu
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 606, p.155606_1 - 155606_12, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the effect of Al addition on the formation of 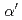 phase in Fe-Cr-Al model alloys by thermal aging. The Vickers hardness tests and a machine learning model indicate that the formation of the
phase in Fe-Cr-Al model alloys by thermal aging. The Vickers hardness tests and a machine learning model indicate that the formation of the 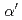 phase is promoted by low Al additions and suppressed by high Al additions. First-principles calculations, which indicate that Cr-Al-vacancy pairs are more stable than Cr-Cr pairs and that including Al atoms during
phase is promoted by low Al additions and suppressed by high Al additions. First-principles calculations, which indicate that Cr-Al-vacancy pairs are more stable than Cr-Cr pairs and that including Al atoms during 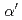 phase nucleation may be energetically advantageous. On the other hand, the formation of Al-Al pairs was very unstable. The formation of Al-Al pairs near the interface can be avoided when the amount of Al addition is small. However, it is inevitable when the amount of Al addition is significant, leading to the instability of the
phase nucleation may be energetically advantageous. On the other hand, the formation of Al-Al pairs was very unstable. The formation of Al-Al pairs near the interface can be avoided when the amount of Al addition is small. However, it is inevitable when the amount of Al addition is significant, leading to the instability of the 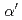 phase.
phase.
 O
O , FeUO
, FeUO , and UO
, and UO -Zr-stainless steel system samples generated in an oxidative atmosphere in the presence of malonic acid
-Zr-stainless steel system samples generated in an oxidative atmosphere in the presence of malonic acidTonna, Ryutaro*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Taishi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 605, p.155561_1 - 155561_9, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Abe, Yosuke; Sasaki, Taisuke*; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Okubo, Nariaki; Ukai, Shigeharu
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 600, p.155271_1 - 155271_12, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)To investigate the formation behavior of Cr-rich precipitates (CrRP) in Fe-Cr-Al (ODS) alloys being developed as accident tolerant fuel cladding for light water reactors, 14 Fe-Cr-Al alloys with systematically varied Cr and Al compositions were irradiated with 10.5 MeV Fe at
at 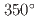 C at three damage levels. A three-dimensional atom probe analysis showed that the CrRP number density, volume fraction, and Cr concentration increase with increasing Cr composition, decreasing Al composition, and decreasing dose rate. The result of the multiple regression analysis on CrRP volume fractions indicates that in addition to the primary effects of these variables, there are several important interactions. It was also highlighted that to understand the dose rate effect on the CrRP formation behavior under neutron irradiation, it is useful to examine the irradiation time dependence, including the effective use of thermal aging data as a limit to the zero dose rate.
C at three damage levels. A three-dimensional atom probe analysis showed that the CrRP number density, volume fraction, and Cr concentration increase with increasing Cr composition, decreasing Al composition, and decreasing dose rate. The result of the multiple regression analysis on CrRP volume fractions indicates that in addition to the primary effects of these variables, there are several important interactions. It was also highlighted that to understand the dose rate effect on the CrRP formation behavior under neutron irradiation, it is useful to examine the irradiation time dependence, including the effective use of thermal aging data as a limit to the zero dose rate.
Toyama, Takeshi*; Tanno, Takashi; Yano, Yasuhide; Inoue, Koji*; Nagai, Yasuyoshi*; Otsuka, Satoshi; Miyazawa, Takeshi; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; Nakashima, Hideharu*; Onuma, Masato*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 599, p.155252_1 - 155252_14, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the stability of oxide nano particles in oxide dispersion-strengthened (ODS) steel, which is a promising candidate material for next-generation reactors, under neutron irradiation at high temperature to high doses. MA957, a 14Cr-ODS steel, was irradiated with Joyo in Japan Atomic Energy Agency under irradiation conditions of 130 dpa at 502 C, 154 dpa at 589
C, 154 dpa at 589 C, and 158 dpa at 709
C, and 158 dpa at 709 C. Three-dimensional atom probe (3D-AP) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) observation were performed to characterize the oxide particles in the ODS steels. A high number density of Y-Ti-O particle was observed in the unirradiated and irradiated samples. Almost no change in the morphology of the oxide particles, i.e. average diameter, number density, and chemical composition, has been observed in the samples irradiated to 130 dpa at 502
C. Three-dimensional atom probe (3D-AP) and transmission electron microscope (TEM) observation were performed to characterize the oxide particles in the ODS steels. A high number density of Y-Ti-O particle was observed in the unirradiated and irradiated samples. Almost no change in the morphology of the oxide particles, i.e. average diameter, number density, and chemical composition, has been observed in the samples irradiated to 130 dpa at 502 C and to 154 dpa at 589
C and to 154 dpa at 589 C. A slight decrease in number density was observed in the sample irradiated to 158 dpa at 709
C. A slight decrease in number density was observed in the sample irradiated to 158 dpa at 709 CC. The hardness of any of the irradiated samples was almost unchanged from that of the unirradiated sample. It was revealed that the oxide particles existed stable, and the strength of the material was sufficiently maintained even after being neutron irradiated to high dose of
CC. The hardness of any of the irradiated samples was almost unchanged from that of the unirradiated sample. It was revealed that the oxide particles existed stable, and the strength of the material was sufficiently maintained even after being neutron irradiated to high dose of  160 dpa at high temperature up to 700
160 dpa at high temperature up to 700 C. A part of this study includes the results of MEXT Innovative Nuclear Research and Development Program Grant Number JPMXD0219214482.
C. A part of this study includes the results of MEXT Innovative Nuclear Research and Development Program Grant Number JPMXD0219214482.
Vauchy, R.; Hirooka, Shun; Horii, Yuta; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 599, p.155233_1 - 155233_11, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The fluorite exsolution/recombination in U Pu
Pu O
O (y = 0.30 and 0.45) and PuO
(y = 0.30 and 0.45) and PuO was investigated using differential scanning calorimetry. The results are in relatively good agreement with the literature data, except for plutonia. Our values indicate that the critical temperature of the miscibility gap in Pu-O is 30
was investigated using differential scanning calorimetry. The results are in relatively good agreement with the literature data, except for plutonia. Our values indicate that the critical temperature of the miscibility gap in Pu-O is 30 50 K lower than previously reported. Finally, the systematic experimental procedure allowed us refining the locus of the solvus existing in hypostoichiometric U
50 K lower than previously reported. Finally, the systematic experimental procedure allowed us refining the locus of the solvus existing in hypostoichiometric U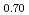 0Pu
0Pu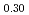 O
O , U
, U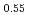 Pu
Pu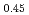 O
O , and PuO
, and PuO dioxides.
dioxides.
 Am
Am O
O at 1473, 1573, and 1673 K
at 1473, 1573, and 1673 KWatanabe, Masashi; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Vauchy, R.; Kato, Masato; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Seki, Takayuki*; Hino, Tetsushi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 599, p.155232_1 - 155232_5, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:75.80(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Oxygen potential data of U Am
Am O
O were measured at 1473, 1573, and 1673 K by thermogravimetry. In U
were measured at 1473, 1573, and 1673 K by thermogravimetry. In U An
An O
O , where An stands for Pu or Am, and for a given value of y and Oxygen/Metal ratio, the oxygen potential of U
, where An stands for Pu or Am, and for a given value of y and Oxygen/Metal ratio, the oxygen potential of U Am
Am O
O is higher than that of U
is higher than that of U Pu
Pu O
O . The valence of cations in the hypostoichiometric region is similar to that of Nd-doped UO
. The valence of cations in the hypostoichiometric region is similar to that of Nd-doped UO . At the stoichiometric composition, it is estimated to be Am
. At the stoichiometric composition, it is estimated to be Am , U
, U , and U
, and U (for charge compensation of Am
(for charge compensation of Am ). The experimental data were analyzed using a defect chemistry model, and a relationship connecting the oxygen-to-metal ratio, the temperature, and the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure was proposed.
). The experimental data were analyzed using a defect chemistry model, and a relationship connecting the oxygen-to-metal ratio, the temperature, and the equilibrium oxygen partial pressure was proposed.
 Pu
Pu )O
)O (x = 0, 0.18, 0.45, and 1) and analysis of heat capacity
(x = 0, 0.18, 0.45, and 1) and analysis of heat capacityHirooka, Shun; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Matsumoto, Taku; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Kato, Masato; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 598, p.155188_1 - 155188_9, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Pshenichnikov, A.; Zubekhina, B.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 597, p.155136_1 - 155136_12, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Pu
Pu O
O powder using master sintering curve theory
powder using master sintering curve theoryNakamichi, Shinya; Sunaoshi, Takeo*; Hirooka, Shun; Vauchy, R.; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 595, p.155072_1 - 155072_11, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Miyazawa, Takeshi; Tanno, Takashi; Imagawa, Yuya; Hashidate, Ryuta; Yano, Yasuhide; Kaito, Takeji; Otsuka, Satoshi; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Onuma, Masato*; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 593, p.155008_1 - 155008_16, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Irisawa, Eriko; Kato, Chiaki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 591, p.154914_1 - 154914_10, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:86.15(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The amount of corrosion of austenitic stainless-steel R-SUS304ULC was evaluated considering the changes in solution composition and boiling during actual concentration operations. Austenitic stainless-steel R-SUS304ULC is the structural material of the highly radioactive liquid waste concentrator in Japanese spent fuel reprocessing plant, which treats highly corrosive nitric acid solutions during enrichment operations. The study results show that it is necessary to focus on nitric acid concentrations, oxidizing metal ion concentrations, and decompression boiling as factors that accelerate the corrosion rate of stainless steel because of cathodic reaction activation.
Cantarel, V.; Chupin, F.; Ortega-Charlot, M.*; Yamagishi, Isao; Ueno, Fumiyoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 592, p.154969_1 - 154969_9, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Tonna, Ryutaro*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Taishi*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Kirishima, Akira*; Sato, Nobuaki*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 589, p.154862_1 - 154862_10, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The dissolution behavior of FeUO compounds formed by a high-temperature reaction of UO
compounds formed by a high-temperature reaction of UO with iron, a stainless-steel component of reactor structural materials, was investigated under atmospheric conditions. The compounds were prepared in an electric furnace using U
with iron, a stainless-steel component of reactor structural materials, was investigated under atmospheric conditions. The compounds were prepared in an electric furnace using U O
O and Fe
and Fe O
O as starting materials, and their solid states were analyzed using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. The concentration of nuclides dissolved in water was examined by performing static leaching tests of FeUO
as starting materials, and their solid states were analyzed using X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, and X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy. The concentration of nuclides dissolved in water was examined by performing static leaching tests of FeUO compounds for up to three months. A redox reaction was proposed to occur between trivalent Fe and pentavalent U ions in the early stage of FeUO
compounds for up to three months. A redox reaction was proposed to occur between trivalent Fe and pentavalent U ions in the early stage of FeUO dissolution. It was thermodynamically deduced that the reduced divalent Fe ion was finally oxidized into a trivalent ion in the presence of dissolved oxygen, and iron hydroxide limited the solubility of Fe. Meanwhile, the concentration of hexavalent U (i.e., uranyl ion) was limited owing to the presence of secondary minerals such as metaschoepite and sodium uranate and subsequently decreased, possibly owing to sorption on Fe oxides, for example. The concentrations of multivalent ions of fission products, such as Ru and Ce, also decreased, likely for the reason above. By contrast, the concentration of soluble Cs ions did not decrease. The validity of this interpretation was supported by comparing the results with the dissolution behavior of a reference sample (Fe-free U
dissolution. It was thermodynamically deduced that the reduced divalent Fe ion was finally oxidized into a trivalent ion in the presence of dissolved oxygen, and iron hydroxide limited the solubility of Fe. Meanwhile, the concentration of hexavalent U (i.e., uranyl ion) was limited owing to the presence of secondary minerals such as metaschoepite and sodium uranate and subsequently decreased, possibly owing to sorption on Fe oxides, for example. The concentrations of multivalent ions of fission products, such as Ru and Ce, also decreased, likely for the reason above. By contrast, the concentration of soluble Cs ions did not decrease. The validity of this interpretation was supported by comparing the results with the dissolution behavior of a reference sample (Fe-free U O
O ).
).
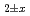 mixed oxides
mixed oxidesVauchy, R.; Matsumoto, Taku; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; et al.
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 588, p.154786_1 - 154786_13, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.29(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Horii, Yuta; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Furusawa, Naoya*; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 588, p.154799_1 - 154799_20, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:88.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The thermal conductivities of near-stoichiometric (U,Pu,Am)O doped with Nd
doped with Nd O
O /Sm
/Sm O
O , which is major fission product (FP) generated by a uranium-plutonium mixed oxides (MOX) fuel irradiation, as simulated fission products are evaluated at 1073-1673 K. The thermal conductivities are calculated from the thermal diffusivities that are measured using the laser flash method. To evaluate the thermal conductivity from a homogeneity viewpoint of Nd/Sm cations in MOX, the specimens with different homogeneity of Nd/Sm are prepared using two kinds of powder made by ball-mill and fusion methods. A homogeneous Nd/Sm distribution decreases the thermal conductivity of MOX with increasing Nd/Sm content, whereas heterogeneous Nd/Sm has no influence. The effect of Nd/Sm on the thermal conductivity is studied using the classical phonon transport model (A+BT)
, which is major fission product (FP) generated by a uranium-plutonium mixed oxides (MOX) fuel irradiation, as simulated fission products are evaluated at 1073-1673 K. The thermal conductivities are calculated from the thermal diffusivities that are measured using the laser flash method. To evaluate the thermal conductivity from a homogeneity viewpoint of Nd/Sm cations in MOX, the specimens with different homogeneity of Nd/Sm are prepared using two kinds of powder made by ball-mill and fusion methods. A homogeneous Nd/Sm distribution decreases the thermal conductivity of MOX with increasing Nd/Sm content, whereas heterogeneous Nd/Sm has no influence. The effect of Nd/Sm on the thermal conductivity is studied using the classical phonon transport model (A+BT) . The dependences of the coefficients A and B on the Nd/Sm content (C
. The dependences of the coefficients A and B on the Nd/Sm content (C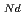 and C
and C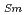 , respectively) are evaluated as: A(mK/W)=1.70
, respectively) are evaluated as: A(mK/W)=1.70  10
10 + 0.93C
+ 0.93C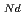 + 1.20C
+ 1.20C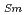 , B(m/W)=2.39
, B(m/W)=2.39  10
10 .
.
Narukawa, Takafumi; Kondo, Keietsu; Fujimura, Yuki; Kakiuchi, Kazuo; Udagawa, Yutaka; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 587, p.154736_1 - 154736_8, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.92(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Watanabe, So; Takahatake, Yoko; Ogi, Hiromichi*; Osugi, Takeshi; Taniguchi, Takumi; Sato, Junya; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Kajinami, Akihiko*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 585, p.154610_1 - 154610_6, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Vauchy, R.; Hirooka, Shun; Watanabe, Masashi; Yokoyama, Keisuke; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 584, p.154576_1 - 154576_11, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:84.29(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ukai, Shigeharu; Sakamoto, Kan*; Otsuka, Satoshi; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Kimura, Akihiko*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 583, p.154508_1 - 154508_24, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:32 Percentile:95.63(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Narukawa, Takafumi; Kondo, Keietsu; Fujimura, Yuki; Kakiuchi, Kazuo; Udagawa, Yutaka; Nemoto, Yoshiyuki
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 582, p.154467_1 - 154467_12, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:59.85(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)