Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Murakami, Masashi; Yoshida, Yukihiko; Nango, Nobuhito*; Kubota, Shogo*; Kurosawa, Takuya*; Sasaki, Toshiki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(7), p.650 - 661, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Uesawa, Shinichiro; Yamashita, Susumu; Sano, Yoshihiko*; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(6), p.523 - 541, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has developed a numerical method with the JUPITER code with a porous medium model to calculate the thermal behavior in PCVs of 1F. In this study, we performed an experiment and numerical simulation of the natural convective heat transfer with the porous medium to validate JUPITER with the porous medium model. In comparison of the temperature and velocity distributions between the experiment and simulation, the temperature distribution in the simulation was in good agreement with the distribution in the experiment except the temperature near the top surface of the porous medium. The velocity distribution also agreed qualitatively with the experimental result. In addition, we also performed the numerical simulations with various effective thermal conductivity models to discuss the effect of the conductivity based on the internal structure of porous media on the natural convective heat transfer. The result indicated that the temperature distribution in the porous medium and the velocity distribution of the natural convection were significantly different for each model, and thus the conductivity of the fuel debris was one of the key parameters of in the thermal behavior analysis in 1F.
Takei, Hayanori
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 45 Pages, 2025/06
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency is working on the research and development of an accelerator-driven nuclear transmutation system (ADS) for transmuting minor actinides. This system combines a subcritical nuclear reactor with a high-power superconducting proton linear accelerator (JADS-linac). One of the factors limiting the advancement of the JADS-linac is beam trips, which often induce thermal cycle fatigue, thereby damaging the components in the subcritical core. The average beam current of the JADS-linac is 32 times higher than that of the linear accelerator (linac) of the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC). Therefore, according to the development stage, comparing the beam trip frequency of the JADS-linac with the allowable beam trip frequency (ABTF) is necessary. Herein the beam trip frequency of the JADS-linac was estimated through a Monte Carlo program using the reliability functions based on the operational data of the J-PARC linac. The Monte Carlo program afforded the distribution of the beam trip duration, which cannot be obtained using traditional analytical methods. Results show that the frequency of the beam trips with a duration exceeding 5 min must be reduced to 27% of the current J-PARC linac level to be below the ABTF.
Uesawa, Shinichiro; Ono, Ayako; Nagatake, Taku; Yamashita, Susumu; Yoshida, Hiroyuki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(5), p.432 - 456, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)We performed electrostatic simulations of a wire-mesh sensor (WMS) for a single spherical bubble and bubbly flow to clarify the accuracy of the WMS. The electrostatic simulation for the single bubble showed the electric current density distribution and the electric current path from the excited transmitter to receivers for various bubble locations. It indicated systematic errors based on the nonuniform current density distribution around the WMS. The electrostatic simulation for the bubbly flow calculated by the computational fluid dynamics code, JAEA Utility Program for Interdisciplinary Thermal-hydraulics Engineering and Research (JUPITER), indicated that the WMS had difficulty in quantitatively measuring the intermediate values of the instantaneous void fraction between 0 and 1 because they cannot be estimated by previous transformation methods from the WMS signal to the void fraction, such as linear approximation or Maxwell's equation, and have a significant deviation of the void fraction of  0.2 for the WMS signal. However, the electrostatic simulation indicated that the time-averaged void fractions around the center of the flow channel can be estimated using linear approximation, and the time-averaged void fraction near the wall of the flow channel can be estimated using Maxwell's equation.
0.2 for the WMS signal. However, the electrostatic simulation indicated that the time-averaged void fractions around the center of the flow channel can be estimated using linear approximation, and the time-averaged void fraction near the wall of the flow channel can be estimated using Maxwell's equation.
Tomita, Ryohei; Tomita, Jumpei; Suzuki, Daisuke; Miyamoto, Yutaka; Yasuda, Kenichiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 10 Pages, 2025/05
A new automated particle measurement (APM) combined with micromanipulation using large geometry secondary ion mass spectrometry instrument was proposed and demonstrated to remove the particle mixing effect, which indicated that the aggregation of uranium particles was detected as a single uranium particle, from APM results. The results showed that the new APM method was more effective than the traditional APM method in removing the particle mixing effect from the APM results and determining the existence of minor uranium isotopes in the samples.
Sonehara, Masateru; Okano, Yasushi; Uchibori, Akihiro; Oki, Hiroshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(5), p.403 - 414, 2025/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)For sodium-cooled fast reactors, understanding sodium combustion behaviour is crucial for managing sodium leakage accidents. In this study, we perform benchmark analyses of the Sandia National Laboratories (SNL) T3 experiment using the multi-dimensional thermal hydraulic code AQUA-SF. Conducted in an enclosed space with a large vessel volume of 100 m and a sodium mass flow rate of 1 kg/s, the experiment highlighted the multi-dimensional effects of local temperature increase shortly after sodium injection. This study aims to extend the capabilities of AQUA-SF by focusing on the simulation of these multi-dimensional temperature variations, in particular the formation of high temperature regions at the bottom of the vessel. The proposed models include the temporary stopping of sodium droplet ignition and spray combustion of sodium splash on the floor. Furthermore, it has been shown that additional heat source near the floor is essential to enhance the reproduction of the high temperature region at the bottom. Therefore, case studies including sensitivity analyses of spray cone angle and prolonged combustion of droplets on the floor are conducted. This comprehensive approach provides valuable insights into the dynamics of sodium combustion and safety measures in sodium-cooled fast reactors.
and a sodium mass flow rate of 1 kg/s, the experiment highlighted the multi-dimensional effects of local temperature increase shortly after sodium injection. This study aims to extend the capabilities of AQUA-SF by focusing on the simulation of these multi-dimensional temperature variations, in particular the formation of high temperature regions at the bottom of the vessel. The proposed models include the temporary stopping of sodium droplet ignition and spray combustion of sodium splash on the floor. Furthermore, it has been shown that additional heat source near the floor is essential to enhance the reproduction of the high temperature region at the bottom. Therefore, case studies including sensitivity analyses of spray cone angle and prolonged combustion of droplets on the floor are conducted. This comprehensive approach provides valuable insights into the dynamics of sodium combustion and safety measures in sodium-cooled fast reactors.
Sato, Yuki; Terasaka, Yuta; Ichiba, Yuta*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(4), p.389 - 400, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Watanabe, Tomoaki; Tada, Kenichi; Endo, Tomohiro*; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 16 Pages, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study investigated the impact of nuclear data updates from JENDL-4.0 (J4) to JENDL-5 (J5) on the light-water reactor fuel burnup calculations. Burnup calculations were conducted with J4 and J5 for PWR pin-cell and BWR fuel assembly geometries. The calculation results revealed significant burnup-dependent differences in the neutron multiplication factor (k ). Across the burnup range of 0-50 GWd/t, k
). Across the burnup range of 0-50 GWd/t, k values of J5 were consistently smaller than those of J4 and the difference gradually increased as burnup progressed. Direct sensitivity calculations, in which each nuclide data was replaced from J4 to J5, indicated that updates to the cross-sections of
values of J5 were consistently smaller than those of J4 and the difference gradually increased as burnup progressed. Direct sensitivity calculations, in which each nuclide data was replaced from J4 to J5, indicated that updates to the cross-sections of  U,
U,  U, and
U, and  Pu and the thermal scattering law data of H in H
Pu and the thermal scattering law data of H in H O notably impacted the k
O notably impacted the k differences. For the BWR assembly geometry containing Gd fuels, large k
differences. For the BWR assembly geometry containing Gd fuels, large k differences were observed in the burnup range of 10-15 GWd/t. This difference was primarily attributed to updates in the
differences were observed in the burnup range of 10-15 GWd/t. This difference was primarily attributed to updates in the  U,
U,  Gd, and
Gd, and  Gd cross-sections, and thermal scattering law data of H in H
Gd cross-sections, and thermal scattering law data of H in H O. Furthermore, we investigated how the nuclear data updates affected the k
O. Furthermore, we investigated how the nuclear data updates affected the k differences by examining nuclide number densities, the energy-dependent sensitivities, and the neutron spectra.
differences by examining nuclide number densities, the energy-dependent sensitivities, and the neutron spectra.
 Fe(n,
Fe(n, )
) Fe
FeNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(3), p.300 - 307, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Segawa, Mariko; Toh, Yosuke; Maeda, Makoto; Kai, Tetsuya
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(3), p.268 - 277, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Kaburagi, Masaaki; Miyamoto, Yuta; Mori, Norimasa; Iwai, Hiroki; Tezuka, Masashi; Kurosawa, Shunsuke*; Tagawa, Akihiro; Takasaki, Koji
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(3), p.308 - 316, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Suzuki, Hideya*; Ban, Yasutoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(2), p.157 - 166, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Fujita, Tatsuya; Yamamoto, Akio*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(2), p.179 - 196, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study newly established a direct coupling code system consisting of the nuclear data processing code FRENDY version 2, and the three-dimensional heterogeneous transport code GENESIS (FRENDY-V2/GENESIS) for easy implementation of the random-sampling-based uncertainty quantification considering the implicit effect due to nuclear cross-section (XS) perturbations. The multi-group macroscopic XSs prepared for GENESIS were generated by FRENDY version 2, where the Dancoff factor was calculated by the neutron current method. Then the background XSs were evaluated based on the Carlvik two-term rational approximation. The infinite multiplication factor (k-infinity) and the fission reaction rate distribution in UO and MOX lattice geometries were compared with MVP3 to verify the calculation accuracy of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS. The sensitivity analyses on the discretization conditions such as the ray tracing of the method of characteristics were also carried out. Through several comparisons between FRENDY-V2/GENESIS and MVP3, FRENDY-V2/GENESIS with the SHEM 361-group structure calculates the k-infinity within approximately 50 pcm and the fission reaction rate distribution within approximately 0.1% by the root mean square, respectively. Consequently, the applicability of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS was verified, and FRENDY-V2/GENESIS can be used to discuss the implicit effect due to multi-group XS perturbations.
and MOX lattice geometries were compared with MVP3 to verify the calculation accuracy of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS. The sensitivity analyses on the discretization conditions such as the ray tracing of the method of characteristics were also carried out. Through several comparisons between FRENDY-V2/GENESIS and MVP3, FRENDY-V2/GENESIS with the SHEM 361-group structure calculates the k-infinity within approximately 50 pcm and the fission reaction rate distribution within approximately 0.1% by the root mean square, respectively. Consequently, the applicability of FRENDY-V2/GENESIS was verified, and FRENDY-V2/GENESIS can be used to discuss the implicit effect due to multi-group XS perturbations.
 and Fe-Zr melt
and Fe-Zr meltNakajima, Kunihisa; Takano, Masahide
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(1), p.78 - 85, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)At TEPCO's Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, it is estimated that considerable amounts of cesium still remain in the reactors from the analysis results using the severe accident analysis codes and the reverse analysis from contaminated water. Since cesium is known to form stable compounds with uranium and zirconium, chemisorption experiments with uranium dioxide pellets and iron-zirconium melts for cesium hydroxide vapor were carried out. As the results, formations of cesium uranate, Cs UO
UO , and cesium zirconate, Cs
, and cesium zirconate, Cs ZrO
ZrO , were confirmed, indicating that cesium was chemisorbed on both of the uranium dioxide pellets and the iron-zirconium melts in an Ar-H
, were confirmed, indicating that cesium was chemisorbed on both of the uranium dioxide pellets and the iron-zirconium melts in an Ar-H -H
-H O flow and an Ar-H
O flow and an Ar-H flow, respectively. Therefore, it was considered that cesium released from fuel might be trapped by chemisorption with fuels and/or iron-zirconium melts during light water reactor severe accidents.
flow, respectively. Therefore, it was considered that cesium released from fuel might be trapped by chemisorption with fuels and/or iron-zirconium melts during light water reactor severe accidents.
Nakamura, Satoshi; Ishii, Sho*; Kato, Hitoshi*; Ban, Yasutoshi; Hiruta, Kenta; Yoshida, Takuya; Uehara, Hiroyuki; Obata, Hiroki; Kimura, Yasuhiko; Takano, Masahide
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 62(1), p.56 - 64, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:51.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)A dissolution method for analyzing the elemental composition of fuel debris using the sodium peroxide (Na O
O ) fusion technique has been developed. Herein, two different types of simulated debris materials (such as solid solution of (Zr,RE)O
) fusion technique has been developed. Herein, two different types of simulated debris materials (such as solid solution of (Zr,RE)O and molten core-concrete interaction products (MCCI)) were taken. At various temperatures, these debris materials were subsequently fused with Na
and molten core-concrete interaction products (MCCI)) were taken. At various temperatures, these debris materials were subsequently fused with Na O
O in crucibles, which are made of different materials, such as Ni, Al
in crucibles, which are made of different materials, such as Ni, Al O
O , Fe, and Zr. Then, the fused samples are dissolved in nitric acid. Furthermore, the effects of the experimental conditions on the elemental composition analysis were evaluated using inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES), which suggested the use of a Ni crucible at 923 K as an optimum testing condition. The optimum testing condition was then applied to the demonstration tests with Three Mile Island unit-2 (TMI-2) debris in a shielded concrete cell, thereby achieving complete dissolution of the debris. The elemental composition of TMI-2 debris revealed by the proposed dissolution method has good reproducibility and has an insignificant contradiction in the mass balance of the sample. Therefore, this newly developed reproducible dissolution method can be effectively utilized in practical applications by dissolving fuel debris and estimating its elemental composition.
, Fe, and Zr. Then, the fused samples are dissolved in nitric acid. Furthermore, the effects of the experimental conditions on the elemental composition analysis were evaluated using inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectroscopy (ICP-AES), which suggested the use of a Ni crucible at 923 K as an optimum testing condition. The optimum testing condition was then applied to the demonstration tests with Three Mile Island unit-2 (TMI-2) debris in a shielded concrete cell, thereby achieving complete dissolution of the debris. The elemental composition of TMI-2 debris revealed by the proposed dissolution method has good reproducibility and has an insignificant contradiction in the mass balance of the sample. Therefore, this newly developed reproducible dissolution method can be effectively utilized in practical applications by dissolving fuel debris and estimating its elemental composition.
Yano, Yasuhide; Miyazawa, Takeshi; Tanno, Takashi; Akasaka, Naoaki; Yoshitake, Tsunemitsu; Kaito, Takeji; Otsuka, Satoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 8 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The effects of strain rate on tensile properties of irradiated modified 316 stainless steel (PNC316) claddings were investigated. PNC316 claddings were irradiated at the experimental fast reactor Joyo using CRT402 control rod assembly at 400 C up to 25 dpa. Post-irradiation ring tensile tests were carried out at strain rates of 3.3
C up to 25 dpa. Post-irradiation ring tensile tests were carried out at strain rates of 3.3 10
10 , 3.3
, 3.3 10
10 and 3.3
and 3.3 10
10 s
s at a test temperature of 350
at a test temperature of 350 C. The results showed no obvious dependence of all strain rates on tensile properties, although a slight decrease in total elongation was observed at the slowest strain rate of 3.3
C. The results showed no obvious dependence of all strain rates on tensile properties, although a slight decrease in total elongation was observed at the slowest strain rate of 3.3 10
10 s
s . In addition, only a part of fracture surface at the slowest strain rate showed intergranular type region in the inner surface area, although the grain boundary separation occurred on inner surfaces near the fracture region at all strain rates. It is suggested that presence of a high content of helium near the inner surfaces would be related to the fracture behavior.
. In addition, only a part of fracture surface at the slowest strain rate showed intergranular type region in the inner surface area, although the grain boundary separation occurred on inner surfaces near the fracture region at all strain rates. It is suggested that presence of a high content of helium near the inner surfaces would be related to the fracture behavior.
Sakamoto, Masahiro; Okumura, Keisuke; Kanno, Ikuo; Matsumura, Taichi; Terashima, Kenichi; Riyana, E. S.; Kaneko, Junichi*; Mizokami, Masato*; Mizokami, Shinya*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 10 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) Er(n,
Er(n, )
)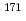 Er and
Er and  Hf(n,
Hf(n, )
) Hf reactions
Hf reactionsNakamura, Shoji; Shibahara, Yuji*; Endo, Shunsuke; Rovira Leveroni, G.; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 14 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology) -,
-,  - and X-ray spectra
- and X-ray spectraOshima, Masumi*; Goto, Jun*; Hayakawa, Takehito*; Asai, Masato; Shinohara, Hirofumi*; Suzuki, Katsuyuki*; Shen, H.*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 10 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)The spectrum determination method (SDM) is the method to determine radioactivities by analyzing full spectral shape of  - or
- or  rays through least-squares fitting by referring to standard
rays through least-squares fitting by referring to standard  - and
- and  spectra. In this paper, we have newly applied the SDM to a unified spectrum composed of two spectra measured with a Ge detector and a liquid scintillation counter. By analyzing the unified spectrum, uncertainties of deduced radioactivities have been improved. We applied this method to the unified spectrum including 40 radionuclides with equal intensities, and have deduced their radioactivities correctly.
spectra. In this paper, we have newly applied the SDM to a unified spectrum composed of two spectra measured with a Ge detector and a liquid scintillation counter. By analyzing the unified spectrum, uncertainties of deduced radioactivities have been improved. We applied this method to the unified spectrum including 40 radionuclides with equal intensities, and have deduced their radioactivities correctly.
Sudo, Ayako; Sato, Takumi; Takano, Masahide
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 9 Pages, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)During the progression of the severe accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, seawater flowed down and was predicted to react with molten corium and concrete. For the removal and storage of fuel debris, knowing the effects of seawater components on the characteristics of reaction products in the fuel debris is crucial. To understand changes in the microstructure of fuel debris, a reaction test was conducted by introducing sea salt to simulated corium and concrete under a temperature gradient. Among the components of sea salt, sulfur formed iron sulfide during metallic precipitation. Analysis of vaporized species indicated that most of Cl, some Na and K in the sea salt might volatilize during heating rather than react with simulated corium and concrete. Calcium and a small amount of Mg, Na, and K in the sea salt might be trapped in the silicate glass.