Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshida, Keisuke; Kato, Shingo; Okuyama, Shinichi; Ishimori, Yuu; Inoue, Mutsuo*
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences (Internet), 24, p.1 - 12, 2024/08
Tokunaga, Kohei; Takahashi, Yoshio*; Kozai, Naofumi
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences (Internet), 23, p.14 - 19, 2023/00
Kusaka, Ryoji
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences (Internet), 20, p.28 - 31, 2020/06
Miyamoto, Yutaka; Yasuda, Kenichiro
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences (Internet), 18, p.13 - 15, 2018/07
A sequential separation technique using an anion-exchange column developed in the previous works have the potential to completely separate picograms of Am from the lanthanides using mixtures of acetic acid, hydrochloric acid, and nitric acid as the eluents, without any functional ligands or special columns. This experimental result implies that ultra-trace actinides, including Am, Pu, U, and Th in environmental samples can be sequentially separated by combination of these mixed-media eluents and an anion exchange column.
Kaneko, Masashi; Watanabe, Masayuki; Miyashita, Sunao*; Nakashima, Satoru*
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences (Internet), 17, p.9 - 15, 2017/03
Density functional calculations were applied to the complexation of Eu(III) and Am(III) ions with phosphinic acid (O-donor) and dihiophosphinic acid (S-donor) from the viewpoint of the bonding nature of valence orbitals in metal ion. Two and four conformers for S-donor and O-donor complexes, respectively were optimized. Their stabilization energies by complex formation toward [M(H O)
O) ]
] were estimated. As the result, the energies reproduced the experimental Am(III)/Eu(III) selectivity that O-donor ligand preferably coordinates to Eu(III) ion, whereas S-donor ligand selectively coordinates to Am(III) ion. Focused on the bonding natures of d and f-orbital electrons, it was indicated that the d-orbital electrons in both Eu and Am complexes participate in the covalency as bonding-type nature and have the almost same contribution. Meanwhile, the contribution of the f-orbital electrons was different between Eu and Am complexes and indicated that in the case of S-donor complex, non-bonding type and bonding type contributions were observed for Eu and Am complexes, respectively and in the case of O-donor complex, bonding type and anti-bonding type contributions were observed for Eu and Am complexes, respectively. This result suggested that the bonding natures of d-orbital electrons contribute to the geometrical similarity of molecular structures for Eu and Am complexes and the bonding natures of f-orbital electrons contribute to the difference in the selectivity of Eu and Am ions.
were estimated. As the result, the energies reproduced the experimental Am(III)/Eu(III) selectivity that O-donor ligand preferably coordinates to Eu(III) ion, whereas S-donor ligand selectively coordinates to Am(III) ion. Focused on the bonding natures of d and f-orbital electrons, it was indicated that the d-orbital electrons in both Eu and Am complexes participate in the covalency as bonding-type nature and have the almost same contribution. Meanwhile, the contribution of the f-orbital electrons was different between Eu and Am complexes and indicated that in the case of S-donor complex, non-bonding type and bonding type contributions were observed for Eu and Am complexes, respectively and in the case of O-donor complex, bonding type and anti-bonding type contributions were observed for Eu and Am complexes, respectively. This result suggested that the bonding natures of d-orbital electrons contribute to the geometrical similarity of molecular structures for Eu and Am complexes and the bonding natures of f-orbital electrons contribute to the difference in the selectivity of Eu and Am ions.
 Nb and
Nb and 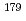 Ta as homologues of element 105, Db, on cation exchanger in HF/HNO
Ta as homologues of element 105, Db, on cation exchanger in HF/HNO solution
solutionKasamatsu, Yoshitaka*; Toyoshima, Atsushi; Tome, Hayato*; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Asai, Masato; Haba, Hiromitsu*; Nagame, Yuichiro
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences (Internet), 13(1), p.9 - 12, 2013/06
Adsorption behavior of the group-5 elements,  Nb and
Nb and 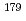 Ta, on cation-exchange resin was studied in mixed solution of HF and HNO
Ta, on cation-exchange resin was studied in mixed solution of HF and HNO as a model experiment of their heavier homologue, element 105 (dubnium, Db). Chemical reactions of these elements in the cation exchange rapidly reached the equilibrium. It was found that distribution coefficients of Nb and Ta decrease with increasing the fluoride ion concentration in the studied range of 10
as a model experiment of their heavier homologue, element 105 (dubnium, Db). Chemical reactions of these elements in the cation exchange rapidly reached the equilibrium. It was found that distribution coefficients of Nb and Ta decrease with increasing the fluoride ion concentration in the studied range of 10 - 10
- 10 M. Clear difference between Nb and Ta was observed in the variations of the distribution coefficients against the fluoride ion concentration. This would originate from their different chemical species of fluoride complexes. We propose the cation-exchange experiment of Db based on the present experimental results to understand its fluoride complex formation.
M. Clear difference between Nb and Ta was observed in the variations of the distribution coefficients against the fluoride ion concentration. This would originate from their different chemical species of fluoride complexes. We propose the cation-exchange experiment of Db based on the present experimental results to understand its fluoride complex formation.
 I and
I and  Cs in soil samples and a simplified calculation of cascade summing corrections for volume source
Cs in soil samples and a simplified calculation of cascade summing corrections for volume sourceAsai, Masato; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Sato, Tetsuya; Tsukada, Kazuaki; Oe, Kazuhiro; Sato, Nozomi; Toyoshima, Atsushi
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences (Internet), 12(1), p.5 - 10, 2012/06
To measure radioactivities in soil contaminated by the accident of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, efficiency calibration of Ge detectors for  I,
I,  Cs, and
Cs, and  Cs in volume sources was investigated.
Cs in volume sources was investigated.  -ray detection efficiencies for these nuclei were determined precisely using standard soil samples containing
-ray detection efficiencies for these nuclei were determined precisely using standard soil samples containing  Cs,
Cs,  Cs,
Cs, 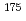 Hf, and
Hf, and  Zr. These standard sources were prepared by admixing radioactive solutions with soil, and point sources were made from the same solutions to determine their radioactivity concentrations. Cascade summing corrections for
Zr. These standard sources were prepared by admixing radioactive solutions with soil, and point sources were made from the same solutions to determine their radioactivity concentrations. Cascade summing corrections for  rays of
rays of  Cs in soil samples were evaluated experimentally. To easily calculate the cascade summing corrections for volume sources, we examined a simplified method using averaged efficiencies, and evaluated its validity through a comparison of the calculated correction factors with the experimental ones.
Cs in soil samples were evaluated experimentally. To easily calculate the cascade summing corrections for volume sources, we examined a simplified method using averaged efficiencies, and evaluated its validity through a comparison of the calculated correction factors with the experimental ones.