Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Xu, J.*; Lang, P.*; Liang, S.*; Zhang, J.*; Fei, Y.*; Wang, Y.*; Gao, D.*; Hattori, Takanori; Abe, Jun*; Dong, X.*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), p.2445 - 2451, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)The Alder-ene reaction is a chemical reaction between an alkene with an allylic hydrogen, and it provides an efficient method to construct the C-C bond. Traditionally, this reaction requires catalysts, high temperatures, or photocatalysis. In this study, we reported a high-pressure-induced solid-state Alder-ene reaction of 1-hexene at room temperature without a catalyst. 1-Hexene crystallizes at 4.3 GPa and polymerizes at 18 GPa, forming olefins. By exploring gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, we discovered that 1-hexene generates dimeric products through the Alder-ene reaction under high pressures. The in situ neutron diffraction shows that the reaction process did not obey the topochemical rule. A six-membered ring transition state including one C-H  bond and two alkene
bond and two alkene  bonds was evidenced by the theoretical calculation, whose energy obviously decreased when compressed to 20 GPa. Our work offers a novel and promising method to realize the Alder-ene reaction at room temperature without a catalyst, expanding the application of this important reaction.
bonds was evidenced by the theoretical calculation, whose energy obviously decreased when compressed to 20 GPa. Our work offers a novel and promising method to realize the Alder-ene reaction at room temperature without a catalyst, expanding the application of this important reaction.
Kato, Hiroyuki S.*; Muroyama, Mizuho*; Kobayakawa, Nano*; Muneyasu, Riku*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Murase, Natsumi*; Watanabe, Seiya*; Yamada, Takashi*; Kanematsu, Yusuke*; Tachikawa, Masanori*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 15(43), p.10769 - 10776, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:37.13(Chemistry, Physical) 7
7Kakiuchi, Takuhiro*; Anai, Ryota*; Saiki, Taiju*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 128(31), p.13052 - 13063, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)0xidation at the interface and the surface of Si(111) substrate with thin Hf films were studied using synchrotron radiation photoelectron spectroscopy in conjunction with supersonic oxygen molecular beams (SOMB). An Hf/Si(111) with a coverage of 0.5 monolayer (ML) included HfSi and HfSi . Following exposures to thermal oxygen molecules with a translational energy (Et) of 0.03 eV, HfSi was oxidized into Hf
. Following exposures to thermal oxygen molecules with a translational energy (Et) of 0.03 eV, HfSi was oxidized into Hf valence. Following SOMB irradiation with Et of 0.39 eV, the other HfSi
valence. Following SOMB irradiation with Et of 0.39 eV, the other HfSi could be oxidized into the Hf
could be oxidized into the Hf . Following the thermal O
. Following the thermal O exposures, the metallic Hf was nonlocally oxidized to HfO
exposures, the metallic Hf was nonlocally oxidized to HfO via trapping-mediated dissociative adsorption. Meanwhile, the segregated Si atoms were oxidized by SOMB irradiation with 2.2 eV and SiO
via trapping-mediated dissociative adsorption. Meanwhile, the segregated Si atoms were oxidized by SOMB irradiation with 2.2 eV and SiO was generated on the surface.
was generated on the surface.
Kumada, Takayuki; Iwahara, Daisuke*; Nishitsuji, Shotaro*; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Miura, Daisuke; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Sugita, Tsuyoshi; Torikai, Naoya*; Amino, Naoya*; Oku, Takayuki; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 128(21), p.8797 - 8802, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)We elucidated the entanglement of polybutadiene and silane coupling agent (SCA) molecules bound to Si substrates using spin-contrast-variation (SCV) neutron reflectivity (NR). In an annealed integral blend film of polybutadiene and SCA, a SCA layer generated on the Si substrate was composed of 70 vol. percent SCA molecules extended perpendicularly from the silicon substrate and entangled with 30 vol. percent polybutadiene molecules. By contrast, in an SCA-precoated polybutadiene film, the SCA-precoated layer is composed of densely packed SCA molecules forming crystal-like structure, and thus did not become entangled with the postcoated polybutadiene molecules. This poor entanglement resulted in poor binding between polybutadiene and Si substrate.
 molecule generation from dissociatively adsorbed water on TiO
molecule generation from dissociatively adsorbed water on TiO through photoexcitation
through photoexcitationKato, Koichi*; Nagatsuka, Naoki*; Fukutani, Katsuyuki
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 128(20), p.8188 - 8198, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:30.18(Chemistry, Physical)Shinohara, Yuya*; Iwashita, Takuya*; Nakanishi, Masahiro*; Osti, N. C.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nirei, Masami; Dmowski, W.*; Egami, Takeshi*
Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 128(6), p.1544 - 1549, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:44.97(Chemistry, Physical)Okazaki, Hiroyuki*; Idesaki, Akira*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi*; Matsumura, Daiju; Ikeda, Takashi*; Yamamoto, Shunya*; Yamaki, Tetsuya*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 127(49), p.23628 - 23633, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.61(Chemistry, Physical)Tsuji, Hayato*; Nakahata, Masaki*; Hishida, Mafumi*; Seto, Hideki*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Inoue, Takeru*; Egawa, Yasunobu*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 14(49), p.11235 - 11241, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:61.28(Chemistry, Physical)Tamura, Kazuhisa
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 127(46), p.22733 - 22739, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.61(Chemistry, Physical)The underpotential deposition of Bi on Au(111) electrode in 1 M HClO solution and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate was investigated using visible light reflectance measurement and surface X-ray scattering techniques. The electrosorption valency of the UPD reaction of Bi was elucidated and it was found that in both 1 M HClO
solution and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate was investigated using visible light reflectance measurement and surface X-ray scattering techniques. The electrosorption valency of the UPD reaction of Bi was elucidated and it was found that in both 1 M HClO and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate the electrosorption valency was smaller than 3, but the detail process in the UPD reaction was different between in two electrolytes. The difference may be originated from the difference in the solvation status of Bi
and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate the electrosorption valency was smaller than 3, but the detail process in the UPD reaction was different between in two electrolytes. The difference may be originated from the difference in the solvation status of Bi rather than the electrical double layer structure.
rather than the electrical double layer structure.
 neutron diffraction
neutron diffractionKobayashi, Hiroki*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Ito, Hayate*; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori; Kagi, Hiroyuki*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 14(47), p.10664 - 10669, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:26.29(Chemistry, Physical)Ice IV is a metastable high-pressure phase of ice in which the water molecules exhibit orientational disorder. Although orientational ordering is commonly observed for other ice phases, it has not been reported for ice IV. We conducted  powder neutron diffraction experiments for DCl-doped D
powder neutron diffraction experiments for DCl-doped D O ice IV to investigate hydrogen ordering in ice IV. We found abrupt changes in the temperature derivative of unit cell volume, dV/dT, at about 120 K, and revealed their slightly ordered structure at low temperatures based on the Rietveld method. The occupancy of the D1 site deviates from 0.5; it increased when samples were cooled at higher pressures and reached 0.282(5) at 2.38 GPa, 58 K. Our results evidence the presence of a low-symmetry hydrogen-ordered state corresponding to ice IV. It seems, however, difficult to experimentally access the completely ordered phase corresponding to ice IV by slow cooling at high pressure.
O ice IV to investigate hydrogen ordering in ice IV. We found abrupt changes in the temperature derivative of unit cell volume, dV/dT, at about 120 K, and revealed their slightly ordered structure at low temperatures based on the Rietveld method. The occupancy of the D1 site deviates from 0.5; it increased when samples were cooled at higher pressures and reached 0.282(5) at 2.38 GPa, 58 K. Our results evidence the presence of a low-symmetry hydrogen-ordered state corresponding to ice IV. It seems, however, difficult to experimentally access the completely ordered phase corresponding to ice IV by slow cooling at high pressure.
Kumada, Takayuki; Nakagawa, Hiroshi; Miura, Daisuke; Sekine, Yurina; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Hiroi, Kosuke; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Oku, Takayuki; Oishi, Kazuki*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 14(34), p.7638 - 7643, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)The structure of nano-ice crystals in rapidly frozen glucose solution was elucidated by using spin-contrast-variation small-angle neutron scattering, which distinguishes the nano-ice crystal signal from the frozen amorphous solution signal by the polarization-dependent neutron scattering. The analysis revealed that the nano-ice crystals form a planar structure with a diameter exceeding tens of nanometers and a thickness of 1 nm, which is close to the critical nucleation size. This result suggests that the glucose molecules are preferentially bound to a specific face of nano-ice crystals, and then block the crystal growth perpendicular to that face.
 ortho-para conversion on a metal surface; Interplay between electron and phonon systems
ortho-para conversion on a metal surface; Interplay between electron and phonon systemsUeta, Hirokazu; Fukutani, Katsuyuki
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 14(34), p.7591 - 7596, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.83(Chemistry, Physical)Inagawa, Kohei*; Matsumura, Daiju; Taniguchi, Masashi*; Uegaki, Shinya*; Nakayama, Tomohito*; Urano, Junnosuke*; Aotani, Takuro*; Tanaka, Hirohisa*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 127(24), p.11542 - 11549, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:20.33(Chemistry, Physical)Massey, D.*; Williams, C. D.*; Mu, J.*; Masters, A. J.*; Motokawa, Ryuhei; Aoyagi, Noboru; Ueda, Yuki; Antonio, M. R.*
Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 127(9), p.2052 - 2065, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:14.56(Chemistry, Physical)Balois-Oguchi, M. V.*; Hayazawa, Norihiko*; Yasuda, Satoshi; Ikeda, Katsuyoshi*; Nguyen, T. Q.*; Esca o, M. C.*; Tanaka, Takuo*
o, M. C.*; Tanaka, Takuo*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 127(12), p.5982 - 5990, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:75.53(Chemistry, Physical)Micrometer-sized wrinkles in graphene are known to affect the electronic properties of graphene due to their shape and the strain variations they create. Here, we analyze the strain distribution and doping of a graphene wrinkle having 1.9 nm width using tip-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (TERS) in ambient conditions. We found a strong correlation between the TERS images of the graphene wrinkle and the electronic Raman scattering (eRS) of the Au(111) substrate. Our work demonstrates that the as-fabricated physical and electronic properties of nanometer-sized features, such as wrinkles, can be probed and studied in detail with TERS which is essential for nanodevice characterization.
Ye, X.*; Shimokawa, Kohei*; Kezuka, Yuto*; Hatakeyama, Takuya*; Li, H.*; Ichitsubo, Tetsu
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 127(11), p.5210 - 5218, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.33(Chemistry, Physical) Cs NMR chemical shift of clay minerals via machine learning and DFT-GIPAW calculations
Cs NMR chemical shift of clay minerals via machine learning and DFT-GIPAW calculationsOkubo, Takahiro*; Takei, Akihiro*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta; Deguchi, Kenzo*; Oki, Shinobu*; Shimizu, Tadashi*
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 127(4), p.973 - 986, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:69.12(Chemistry, Physical)The identification of adsorption sites of Cs on clay minerals has been studied in the fields of environmental chemistry. The nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiments allow direct observations of the local structures of adsorbed Cs. The NMR parameters of  Cs, derived from solid-state NMR experiments, are sensitive to the local neighboring structures of adsorbed Cs. However, determining the Cs positions from NMR data alone is difficult. This paper describes an approach for identifying the expected atomic positions of Cs adsorbed on clay minerals by combining machine learning (ML) with experimentally observed chemical shifts. A linear ridge regression model for ML is constructed from the smooth overlap of atomic positions descriptor and gauge-including projector augmented wave (GIPAW) ab initio data. The
Cs, derived from solid-state NMR experiments, are sensitive to the local neighboring structures of adsorbed Cs. However, determining the Cs positions from NMR data alone is difficult. This paper describes an approach for identifying the expected atomic positions of Cs adsorbed on clay minerals by combining machine learning (ML) with experimentally observed chemical shifts. A linear ridge regression model for ML is constructed from the smooth overlap of atomic positions descriptor and gauge-including projector augmented wave (GIPAW) ab initio data. The  Cs chemical shifts can be instantaneously calculated from the Cs positions on any clay layers using ML. The inverse analysis from the ML model can derive the atomic positions from experimentally observed chemical shifts.
Cs chemical shifts can be instantaneously calculated from the Cs positions on any clay layers using ML. The inverse analysis from the ML model can derive the atomic positions from experimentally observed chemical shifts.
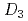 point group symmetry (M(II) = Zn(II) and Mg(II))
point group symmetry (M(II) = Zn(II) and Mg(II))Masuda, Yuka*; Sakata, Shiomi*; Kayahara, Saori*; Irie, Natsumi*; Kofu, Maiko; Kono, Yohei*; Sakakibara, Toshiro*; Horii, Yoji*; Kajiwara, Takashi*
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 127(6), p.3295 - 3306, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:39.92(Chemistry, Physical) NH and CaNH thin films by reactive magnetron sputtering under hydrogen partial pressure control
NH and CaNH thin films by reactive magnetron sputtering under hydrogen partial pressure controlChon, S.*; Fukutani, Katsuyuki; 8 of others*
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 13(43), p.10169 - 10174, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Physical)Kusaka, Ryoji; Watanabe, Masayuki
Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters (Internet), 13(30), p.7065 - 7071, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:71.30(Chemistry, Physical)