Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Takeuchi, Sachiko*; Takizawa, Makoto*
Journal of Physics G; Nuclear and Particle Physics, 47(5), p.053001_1 - 053001_67, 2020/05
Times Cited Count:67 Percentile:88.17(Physics, Nuclear) -decay study of
-decay study of 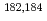 Tl
TlVan Beveren, C.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Barzakh, A. E.*; Cocolios, T. E.*; de Groote, R. P.*; Fedorov, D.*; Fedosseev, V. N.*; Ferrer, R.*; Ghys, L.*; Huyse, M.*; et al.
Journal of Physics G; Nuclear and Particle Physics, 43(2), p.025102_1 - 025102_22, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:60.04(Physics, Nuclear)Kajino, Toshitaka*; Mathews, G. J.*; Hayakawa, Takehito
Journal of Physics G; Nuclear and Particle Physics, 41(4), p.044007_1 - 044007_34, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:27 Percentile:81.83(Physics, Nuclear)Neutrino interactions are a key component of the mechanism for supernova explosions. They also play an important role in the associated nucleosynthesis. Nevertheless, a number of issues remain to be resolved. In this review we summarize research by our group and others on some of these issues. Much effort is now invested in understanding the transport of neutrinos from the core and the role of neutrino heated convection in the outer envelopes. In addition to the neutrino transport issues, we review some current topics in neutrino induced nucleosynthesis (the neutrino and p processes). We review some current issues regarding the synthesis of the neutirno-process isotopes  Ta and
Ta and 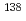 La and summarize the application of the neutrino -process chronometers,
La and summarize the application of the neutrino -process chronometers, 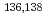 Ce,
Ce, 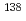 La, and
La, and 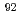 Nb. We also consider other aspects.
Nb. We also consider other aspects.
Oryu, Shinsho*; Hiratsuka, Yasuhiro*; Nishinohara, Satoshi*; Chiba, Satoshi
Journal of Physics G; Nuclear and Particle Physics, 39(4), p.045101_1 - 045101_12, 2012/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:27.19(Physics, Nuclear)We present a two-body calculation method for a rigorous treatment of Coulomb interaction in momentum ( -)space. The method is based on a modified Coulomb potential which is equivalent to the genuine Coulomb potential in configuration (
-)space. The method is based on a modified Coulomb potential which is equivalent to the genuine Coulomb potential in configuration ( -)space. We also use the two-potential theory with the auxiliary potential. The calculated proton-proton phase shifts are in very good agreement with the experimental data for the states
-)space. We also use the two-potential theory with the auxiliary potential. The calculated proton-proton phase shifts are in very good agreement with the experimental data for the states 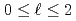 . The phase shifts for the
. The phase shifts for the 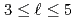 states are also calculated. Practical applications of our method in a few hadron problems are discussed.
states are also calculated. Practical applications of our method in a few hadron problems are discussed.
 [503] band of
[503] band of  Pt
PtLi, G. S.*; Zhou, X. H.*; Zhang, Y. H.*; Zheng, Y.*; Liu, M. L.*; Hua, W.*; Zhou, H. B.*; Ding, B.*; Wang, H. X.*; Lei, X. G.*; et al.
Journal of Physics G; Nuclear and Particle Physics, 38(9), p.095105_1 - 095105_9, 2011/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.38(Physics, Nuclear)High-spin states in  Pt have been investigated by means of in beam
Pt have been investigated by means of in beam  -ray spectroscopic method at the JAEA tandem facility. Low-spin signature inversion is revealed in the 7/2
-ray spectroscopic method at the JAEA tandem facility. Low-spin signature inversion is revealed in the 7/2 [503] band. The inversion can be interpreted as a configuration change from the 7/2
[503] band. The inversion can be interpreted as a configuration change from the 7/2 [503] orbital to the 7/2
[503] orbital to the 7/2 [514] orbital with increasing spin, which is supported by a theoretical calculation of the semi-classical Donau and Frauendorf approach.
[514] orbital with increasing spin, which is supported by a theoretical calculation of the semi-classical Donau and Frauendorf approach.
Maruyama, Toshiki; Chiba, Satoshi; Schulze, H.-J.*; Tatsumi, Toshitaka*
Journal of Physics G; Nuclear and Particle Physics, 35(10), p.104076_1 - 104076_4, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.73(Physics, Nuclear)We investigate the property of the hadron-quark mixed phase using the Brueckner-Hartree-Fock model for hadron (hyperon) phase and the MIT bag model for quark phase. To satisfy the Gibbs conditions, charge density as well as baryon number density becomes non-uniform in the mixed phase. Taking into account the density distribution and the Coulomb interaction in a self-consistent way, we clarify the roles of the surface tension and the charge screening effect. We will show that the screened Coulomb interaction makes the EOS similar to the one given by the Maxwell construction. We demonstrate that hyperons are suppressed in the mixed phase, because hadron phase is positively charged. This is a novel mechanism of hyperon suppression in compact stars. Finally we will discuss some consequences of our EOS on the structure and the maximum mass of NS.
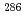 114 and
114 and 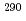 114 using low-energy fusion channels
114 using low-energy fusion channelsGherghescu, R. A.*; Poenaru, D. N.*; Greiner, W.*; Nagame, Yuichiro
Journal of Physics G; Nuclear and Particle Physics, 32(11), p.L73 - L84, 2006/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.64(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Titov, A. I.; Fujiwara, Mamoru*; Kawase, Keigo*
Journal of Physics G; Nuclear and Particle Physics, 32(8), p.1097 - 1103, 2006/08
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:70.04(Physics, Nuclear)We show that the asymmetries in the nuclear resonance fluorescence processes with a circular polarized photon beam may be used as a tool for studying the parity nonconservation (PNC) in nuclei. The PNC asymmetry measurements both in excitingthe parity doublet states and in exciting the discrete states near the ground states with parity mixing are discussed. We derived the formulae needed for measuring the PNC asymmetries.
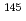 Tb
TbZheng, Y.*; Zhou, X. H.*; Zhang, Y. H.*; Hayakawa, Takehito; Oshima, Masumi; Toh, Yosuke; Shizuma, Toshiyuki; Katakura, Junichi; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Matsuda, Makoto; et al.
Journal of Physics G; Nuclear and Particle Physics, 30(4), p.465 - 479, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:47.43(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Fujiwara, Mamoru; Kawabata, Takahiro*; Mohr, P.*
Journal of Physics G; Nuclear and Particle Physics, 28(4), p.643 - 648, 2002/04
Times Cited Count:13 Percentile:57.78(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
 Ge beam
Ge beamToh, Yosuke; Czosnyka, T.*; Oshima, Masumi; Hayakawa, Takehito; Kusakari, Hideshige*; Sugawara, Masahiko*; Osa, Akihiko; Koizumi, Mitsuo; Hatsukawa, Yuichi; Katakura, Junichi; et al.
Journal of Physics G; Nuclear and Particle Physics, 27(7), p.1475 - 1480, 2001/07
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:84.99(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English
Maruyama, Tomoyuki*; Chiba, Satoshi
Journal of Physics G; Nuclear and Particle Physics, 25(12), p.2361 - 2369, 1999/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:45.17(Physics, Nuclear)no abstracts in English