Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 path-integral simulations of hydrogen-isotope diffusion in face-centred cubic metals
path-integral simulations of hydrogen-isotope diffusion in face-centred cubic metalsKimizuka, Hajime*; Ogata, Shigenobu*; Thomsen, B.; Shiga, Motoyuki
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 37(19), p.193001_1 - 193001_16, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)Calculations of hydrogen isotope diffusion coefficients for face-centred cubic lattice metals using  path integral methods show that the temperature dependence of the diffusion coefficients has an unusual shape. This is due to the competition between nuclear quantum effects with different temperature dependence, which explains the unusual crossover mechanism between the normal and inverse isotope effects. We also present the results of a path integral simulation that describes approximate quantum dynamics using machine learning-based interatomic potentials with almost the same accuracy as density functional theory calculations. This computational method paves the way for understanding the quantum behaviour of hydrogen isotopes in various solid-state materials.
path integral methods show that the temperature dependence of the diffusion coefficients has an unusual shape. This is due to the competition between nuclear quantum effects with different temperature dependence, which explains the unusual crossover mechanism between the normal and inverse isotope effects. We also present the results of a path integral simulation that describes approximate quantum dynamics using machine learning-based interatomic potentials with almost the same accuracy as density functional theory calculations. This computational method paves the way for understanding the quantum behaviour of hydrogen isotopes in various solid-state materials.
Seki, Takeshi*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Takanashi, Koki
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 36(33), p.333001_1 - 333001_11, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.05(Physics, Condensed Matter)Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Takata, Shinichi; Kawakita, Yukinobu; Fujimura, Yuki; Kondo, Keietsu
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 35(41), p.415403_1 - 415403_11, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter) inferred from muon study
inferred from muon studyKadono, Ryosuke*; Hiraishi, Masatoshi*; Okabe, Hirotaka*; Koda, Akihiro*; Ito, Takashi
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 35(28), p.285503_1 - 285503_13, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.32(Physics, Condensed Matter)Tatsumi, Kazuyoshi; Okudaira, Takuya*; Kofu, Maiko; Rozyczko, P.*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 36(37), p.375901_1 - 375901_13, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)Constantini, J.-M.*; Ogawa, Tatsuhiko; Gourier, D.*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 35(28), p.285701_1 - 285701_12, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)A novel analysis of luminescence is presented on the basis of virtual photon spectra (VPS) produced by charged particles (electrons or ions) passing by luminescent species such as defects or impurities, in wide band-gap ionic-covalent solids. The electron-energy dependence of experimental luminescence spectra of sapphire ( -Al
-Al O
O ) is discussed in relation to the computed VPS for the primary and secondary electrons. The experimental luminescence spectra of
) is discussed in relation to the computed VPS for the primary and secondary electrons. The experimental luminescence spectra of  -Al
-Al O
O are also analyzed in this framework for protons and helium ions in the MeV energy range. The variations of stopping power are consistent with the variation of the number of emitted VPs. The decay of luminescence yield versus ion stopping power is discussed on the basis of the variation of the computed VPS, and ionization and excitation induced by primary ions and secondary electrons. This decay is accounted for by a decrease of the yield of low-energy secondary electrons with the subsequent VP emission.
are also analyzed in this framework for protons and helium ions in the MeV energy range. The variations of stopping power are consistent with the variation of the number of emitted VPs. The decay of luminescence yield versus ion stopping power is discussed on the basis of the variation of the computed VPS, and ionization and excitation induced by primary ions and secondary electrons. This decay is accounted for by a decrease of the yield of low-energy secondary electrons with the subsequent VP emission.
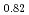 La
La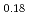 Fe
Fe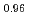 Ni
Ni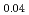 As
As
Xie, T.*; Liu, C.*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Li, S.*; Luo, H.*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 34(47), p.474001_1 - 474001_8, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)
Aoki, Dai*; Brison, J.-P.*; Flouquet, J.*; Ishida, Kenji*; Knebel, G.*; Tokunaga, Yo; Yanase, Yoichi*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 34(24), p.243002_1 - 243002_41, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:132 Percentile:90.46(Physics, Condensed Matter)
Haga, Yoshinori; Opletal, P.; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Sakai, Hironori
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 34(17), p.175601_1 - 175601_7, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:29 Percentile:86.06(Physics, Condensed Matter) Nb
Nb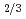 )O
)O
Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Taniguchi, Hiroki*; Noguchi, Yuji*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 33(3), p.035401_1 - 035401_8, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:22.00(Physics, Condensed Matter)Nanoscale structural analysis of relaxor Pb(Mg Nb
Nb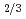 )O
)O (PMN) was performed using synchrotron high-energy X-ray diffraction measurements. Although PMN is a well-known relaxor ferroelectric material, the average structure is a cubic structure, and various models have been proposed to explain the ferroelectric microstructure. We performed a wide-range local structure analysis up to 20 nm using the pair distribution function (PDF). As a result, it was found that the structure of PMN changed depending on the distance and it was a glass-like structure.
(PMN) was performed using synchrotron high-energy X-ray diffraction measurements. Although PMN is a well-known relaxor ferroelectric material, the average structure is a cubic structure, and various models have been proposed to explain the ferroelectric microstructure. We performed a wide-range local structure analysis up to 20 nm using the pair distribution function (PDF). As a result, it was found that the structure of PMN changed depending on the distance and it was a glass-like structure.
Kataoka, Noriyuki*; Tanaka, Masashi*; Hosoda, Wataru*; Taniguchi, Takumi*; Fujimori, Shinichi; Wakita, Takanori*; Muraoka, Yuji*; Yokoya, Takashi*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 33(3), p.035501_1 - 035501_6, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:22.00(Physics, Condensed Matter) single unit-cell FeSe superconductor
single unit-cell FeSe superconductorFukaya, Yuki; Zhou, G.*; Zheng, F.*; Zhang, P.*; Wang, L.*; Xue, Q.-K.*; Shamoto, Shinichi
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 31(5), p.055701_1 - 055701_6, 2019/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:26.76(Physics, Condensed Matter)no abstracts in English
 and 5
and 5 materials studied by angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy
materials studied by angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopyFujimori, Shinichi
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 28(15), p.153002_1 - 153002_31, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:39 Percentile:38.92(Physics, Condensed Matter)Chen, Y.-T.*; Takahashi, Saburo*; Nakayama, Hiroyasu*; Althammer, M.*; Goennenwein, S. T. B.*; Saito, Eiji; Bauer, G. E. W.*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 28(10), p.103004_1 - 103004_15, 2016/03
Times Cited Count:93 Percentile:61.66(Physics, Condensed Matter)We review the so-called spin Hall magnetoresistance (SMR) in bilayers of a magnetic insulator and a metal, in which spin currents are generated in the normal metal by the spin Hall effect. The associated angular momentum transfer to the ferromagnetic layer and thereby the electrical resistance is modulated by the angle between the applied current and the magnetization direction. The SMR provides a convenient tool to non-invasively measure the magnetization direction and spin-transfer torque to an insulator. We introduce the minimal theoretical instruments to calculate the SMR, i.e. spin diffusion theory and quantum mechanical boundary conditions. This leads to a small set of parameters that can be fitted to experiments. We discuss the limitations of the theory as well as alternative mechanisms such as the ferromagnetic proximity effect and Rashba spin-orbit torques, and point out new developments.
 Pt
Pt As
As (Fe
(Fe Pt
Pt As)
As)
Ikeuchi, Kazuhiko*; Kobayashi, Yoshiaki*; Suzukia, Kazunori*; Ito, Masayuki*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Bourges, P.*; Christianson, A. D.*; Nakamura, Hiroki; Machida, Masahiko; Sato, Masatoshi*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 27(46), p.465701_1 - 465701_7, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.75(Physics, Condensed Matter)We report the results of inelastic neutron scattering measurements on particular phonons of a superconducting (SC) Ca Pt
Pt As
As (Fe
(Fe Pt
Pt As)
As) with the onset transition temperature
with the onset transition temperature 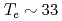 K to investigate mainly what roles orbital fluctuation plays in Cooper pairing, where we observed a slight softening of the in-plane transverse acoustic mode corresponding to the elastic constant
K to investigate mainly what roles orbital fluctuation plays in Cooper pairing, where we observed a slight softening of the in-plane transverse acoustic mode corresponding to the elastic constant 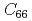 . This softening starts at temperature
. This softening starts at temperature  well above the SC
well above the SC  , as
, as  decreases. An anomalously strong change of the scattering intensity of in-plane optical modes was observed at the M point of the pseudo tetragonal reciprocal space in the range of 35
decreases. An anomalously strong change of the scattering intensity of in-plane optical modes was observed at the M point of the pseudo tetragonal reciprocal space in the range of 35 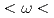 40 meV with decreasing
40 meV with decreasing  from far above
from far above  . Because this
. Because this  region mainly corresponds to the motion of Fe and As atoms in the FeAs planes, the finding presents information on the coupling between the orbital fluctuation of Fe
region mainly corresponds to the motion of Fe and As atoms in the FeAs planes, the finding presents information on the coupling between the orbital fluctuation of Fe 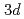 electrons and the lattice system, useful for studying the possible roles of orbital fluctuation in the pairing mechanism and/or the appearance of the so-called nematic phase.
electrons and the lattice system, useful for studying the possible roles of orbital fluctuation in the pairing mechanism and/or the appearance of the so-called nematic phase.
Li, H.; Maekawa, Masaki; Kawasuso, Atsuo; Tanimura, Naoki*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 27(24), p.246001_1 - 246001_5, 2015/06
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:29.96(Physics, Condensed Matter)Uchida, Kenichi*; Ishida, Masahiko*; Kikkawa, Takashi*; Kirihara, Akihiro*; Murakami, Tomoo*; Saito, Eiji
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 26(34), p.343202_1 - 343202_15, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:232 Percentile:84.79(Physics, Condensed Matter)Mori, Michiyasu; Koshibae, Wataru*; Hikino, Shinichi*; Maekawa, Sadamichi
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 26(25), p.255702_1 - 255702_5, 2014/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:13.77(Physics, Condensed Matter) explored using
explored using  In nuclear quadrupole resonance
In nuclear quadrupole resonanceChudo, Hiroyuki; Koutroulakis, G.*; Yasuoka, Hiroshi; Bauer, E. D.*; Tobash, P. H.*; Mitchell, J. N.*; Thompson, J. D.*
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 26(3), p.036001_1 - 036001_5, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:22.43(Physics, Condensed Matter)The results of  In nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR) measurements on PuIn
In nuclear quadrupole resonance (NQR) measurements on PuIn are reported. Three of the four NQR lines of
are reported. Three of the four NQR lines of  In expected for nuclear spin
In expected for nuclear spin  =9/2 are observed. The equal spacing of these lines at 20 K yields the NQR frequency of
=9/2 are observed. The equal spacing of these lines at 20 K yields the NQR frequency of 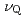 =10.45 MHz, and the asymmetry parameter of the electric field gradient,
=10.45 MHz, and the asymmetry parameter of the electric field gradient,  =0. The NQR line profile and the nuclear spin-lattice relaxation rate
=0. The NQR line profile and the nuclear spin-lattice relaxation rate  display an abrupt change at 14 K, which is associated with the onset of long-range antiferromagnetic order. The temperature dependences of the staggered magnetization
display an abrupt change at 14 K, which is associated with the onset of long-range antiferromagnetic order. The temperature dependences of the staggered magnetization 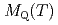 , extracted from the NQR spectra, and
, extracted from the NQR spectra, and  below
below  =14 K are well explained by the self-consistent renormalization (SCR) theory for spin fluctuations. In addition, scaling between
=14 K are well explained by the self-consistent renormalization (SCR) theory for spin fluctuations. In addition, scaling between 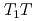 and
and 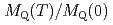 is also consistent with the predictions of SCR theory, providing further evidence that PuIn
is also consistent with the predictions of SCR theory, providing further evidence that PuIn is a weak itinerant antiferromagnet in which spin fluctuations around the antiferromagnetic wave vector play a major role in the system's behavior at finite temperatures.
is a weak itinerant antiferromagnet in which spin fluctuations around the antiferromagnetic wave vector play a major role in the system's behavior at finite temperatures.
 Si
Si and DyCu
and DyCu Si
Si
Mitsumoto, Keisuke*; Goto, Saori*; Nemoto, Yuichi*; Akatsu, Mitsuhiro*; Goto, Terutaka*; Dung, N. D.*; Matsuda, Tatsuma; Haga, Yoshinori; Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Sugiyama, Kiyohiro*; et al.
Journal of Physics; Condensed Matter, 25(29), p.296002_1 - 296002_8, 2013/07
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.37(Physics, Condensed Matter)