Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ishitobi, Takayuki
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(7), p.075001_1 - 075001_2, 2025/07
Kubo, Katsunori
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(7), p.074701_1 - 074701_5, 2025/07
Ishitobi, Takayuki
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(7), p.073703_1 - 073703_4, 2025/06
Kadono, Ryosuke*; Ito, Takashi
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(6), p.064601_1 - 064601_11, 2025/06
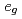 orbital system on a simple cubic lattice
orbital system on a simple cubic latticeKubo, Katsunori
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(5), p.054703_1 - 054703_7, 2025/05

Yamauchi, Hiroki; Metoki, Naoto; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Hong, T.*; Fernandez-Baca, J. A.*; Hagihara, Masato; Masuda, Takatsugu*; Yoshizawa, Hideki*; Ito, Shinichi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(5), p.054705_1 - 054705_8, 2025/04
Hidaka, Hiroyuki*; Yanagiya, Shun*; Onodera, Shintaro*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*; Tanida, Hiroshi*; Ishitobi, Takayuki
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(3), p.034706_1 - 034706_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Rajeev, H. S.*; Hu, X.*; Chen, W.-L.*; Zhang, D.*; Chen, T.*; Kofu, Maiko*; Kajimoto, Ryoichi; Nakamura, Mitsutaka; Chen, A. Z.*; Johnson, G. C.*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(3), p.034602_1 - 034602_14, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Maeda, Mizuho*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Haga, Yoshinori; Shirasaki, Kenji*; Kimura, Noriaki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 94(2), p.024707_1 - 024707_6, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nagai, Yuki; Tomiya, Akio*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(11), p.114007_1 - 114007_8, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:43.84(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We proposed a new self-learning Monte Carlo method using Transformer, a key technology in generative AI. By using Transformer's Attention mechanism, which can infer the relevance of distant words in a sentence, we have constructed an effective model that can efficiently capture the long-range correlations that are important in the phase transitions in electronic systems. Furthermore, we reduce the number of parameters by incorporating symmetries that the system must satisfy, such as spin rotation and spatial translation, into the network. We also found a scaling law that the loss decreases as the number of layers is increased.
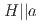 in the early-stage sample of spin-triplet superconductor UTe
in the early-stage sample of spin-triplet superconductor UTe
Kitagawa, Shunsaku*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; 11 of others*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(12), p.123701_1 - 123701_5, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nakajima, Taro*; Saito, Hiraku*; Kobayashi, Naoki*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Nakamura, Tatsuya; Furukawa, Hazuki*; Asai, Shinichiro*; Masuda, Takatsugu*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(9), p.091002_1 - 091002_5, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:64.46(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Akiba, Hiroshi*; Omasa, Yoshinori*; Kofu, Maiko*; Zhang, M.*; Sato, Shun*; Yamamuro, Osamu*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(9), p.091010_1 - 091010_6, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ozawa, Akihiro*; Araki, Yasufumi; Nomura, Kentaro*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(9), p.094704_1 - 094704_9, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Modulation of magnetization in magnetic Weyl semimetals leads to the shift of Weyl points in momentum space, which effectively serves as the chirality-dependent gauge field for the Weyl fermions. Here, we theoretically study such a magnetization-induced chiral gauge field, in a fully spin-polarized Weyl ferromagnet Co Sn
Sn S
S . From a tight-binding model of Co
. From a tight-binding model of Co Sn
Sn S
S on stacked kagome lattice with magnetism, we calculate the magnetization-dependent evolution of the Weyl points in momentum space, resulting in the chiral gauge field. In the presence of the magnetic domain wall structure, we evaluate the chiral magnetic field arising from the spatial profile of the chiral gauge field. We find that a magnetic domain wall in Co
on stacked kagome lattice with magnetism, we calculate the magnetization-dependent evolution of the Weyl points in momentum space, resulting in the chiral gauge field. In the presence of the magnetic domain wall structure, we evaluate the chiral magnetic field arising from the spatial profile of the chiral gauge field. We find that a magnetic domain wall in Co Sn
Sn S
S gives rise to a giant chiral magnetic field for the Weyl fermions, which reaches the order of a few hundred tesla to induce the Landau quantization. Such a giant chiral magnetic field may also influence the novel transport phenomena, such as the charge pumping by the domain wall motion, compatible with the spinmotive force.
gives rise to a giant chiral magnetic field for the Weyl fermions, which reaches the order of a few hundred tesla to induce the Landau quantization. Such a giant chiral magnetic field may also influence the novel transport phenomena, such as the charge pumping by the domain wall motion, compatible with the spinmotive force.

Takeuchi, Tetsuya*; Honda, Fuminori*; Aoki, Dai*; Haga, Yoshinori; Kida, Takanori*; Narumi, Yasuo*; Hagiwara, Masayuki*; Kindo, Koichi*; Karube, Kosuke*; Harima, Hisatomo*; et al.
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(4), p.044708_1 - 044708_10, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Si
Si
Kon, Fusako*; Tabata, Chihiro; Saito, Hiraku*; Nakajima, Taro*; Hidaka, Hiroyuki*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Amitsuka, Hiroshi*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(4), p.044701_1 - 044701_11, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ito, Takashi; Kadono, Ryosuke*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(4), p.044602_1 - 044602_7, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:75.95(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kubo, Katsunori
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(2), p.024708_1 - 024708_8, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:82.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary)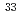 S-nuclear magnetic resonance measurements
S-nuclear magnetic resonance measurementsYoshida, Shogo*; Haga, Yoshinori; Fujii, Takuto*; Nakai, Yusuke*; Mito, Takeshi*; 8 of others*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 93(1), p.013702_1 - 013702_5, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Mo for production of medical
Mo for production of medical  Tc by
Tc by  Mo(
Mo(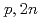 )
) Tc
TcHashimoto, Shintaro; Nagai, Yasuki*
Journal of the Physical Society of Japan, 92(12), p.124202_1 - 124202_11, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Tc, which is a daughter nuclide of
Tc, which is a daughter nuclide of  Mo, is used worldwide for medical imaging. However, there is a problem with the supply of
Mo, is used worldwide for medical imaging. However, there is a problem with the supply of  Tc (
Tc ( Mo) due to the replacement of aging reactors. A method to produce
Mo) due to the replacement of aging reactors. A method to produce  Tc by irradiating
Tc by irradiating  Mo with protons using medical cyclotrons has been proposed. In this study, we presented a method to determine individual excitation functions for Mo(
Mo with protons using medical cyclotrons has been proposed. In this study, we presented a method to determine individual excitation functions for Mo(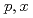 )Tc using measured excitation functions for
)Tc using measured excitation functions for  Mo(
Mo(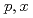 )Tc. The method was validated by comparing estimated radionuclide purities of
)Tc. The method was validated by comparing estimated radionuclide purities of  Tc in enriched
Tc in enriched  Mo samples using the determined excitation functions with measured ones. In this study, we found that the content of
Mo samples using the determined excitation functions with measured ones. In this study, we found that the content of 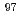 Mo,
Mo, 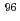 Mo, and
Mo, and  Mo should be low in order to produce
Mo should be low in order to produce  Tc with high radionuclide purity. The results of this study play an important role in discussion of the required Mo compositions in enriched
Tc with high radionuclide purity. The results of this study play an important role in discussion of the required Mo compositions in enriched  Mo, taking into account the constraints of each facility.
Mo, taking into account the constraints of each facility.