Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
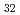 (Al, Zn)
(Al, Zn) Approximant crystal; Influence of chemical disorder
Approximant crystal; Influence of chemical disorderShimizu, Kazuyuki*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Akamaru, Satoshi*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Abe, Rion*; Sasaki, Taisuke*; Wang, Y.*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Scripta Materialia, 265, p.116730_1 - 116730_7, 2025/08
Times Cited Count:0Zheng, R.*; Gong, W.; 6 of others*
Acta Materialia, 293, p.121098_1 - 121098_12, 2025/07
Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Gao, S.*; Ito, Tatsuya; Yamashita, Takayuki*; Harjo, S.; Zhao, L.*; Wang, Q.*
Scripta Materialia, 264, p.116726_1 - 116726_6, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0Lin, Z. M.*; Liu, B. X.*; Ming, K. S.*; Xu, P. G.; Yin, F. X.*; Zheng, S. J.*
Scripta Materialia, 263, p.116692_1 - 116692_7, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Park, M.-H.*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Harjo, S.; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 292, p.121061_1 - 121061_13, 2025/06
Times Cited Count:1Wang, Y.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; 7 of others*
Acta Materialia, 288, p.120840_1 - 120840_14, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction studyIto, Tatsuya; Ogawa, Yuhei*; Gong, W.; Mao, W.*; Kawasaki, Takuro; Okada, Kazuho*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Harjo, S.
Acta Materialia, 287, p.120767_1 - 120767_16, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yoshida, Shuhei*; Gong, W.; 9 of others*
Acta Materialia, 283, p.120498_1 - 120498_15, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:63.37(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Itakura, Mitsuhiro; Tsuru, Tomohito
Scripta Materialia, 255, p.116366_1 - 116366_5, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Reduction of grain boundary cohesive energy by hydrogen has been considered as one of the candidate causes of grain boundary fracture in steels and aluminum alloys. Recently, the effects of grain boundary segregation elements have been investigated by first-principles calculations, but there are few studies that quantitatively estimate the grain boundary cohesive energy. In this study, we describe a quantitative evaluation method using first-principles calculation results and show some examples of experimental calculations.
Okada, Kazuho*; Shibata, Akinobu*; Kimura, Yuji*; Yamaguchi, Masatake; Ebihara, Kenichi; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 280, p.120288_1 - 120288_14, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Mao, W.*; Gao, S.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Ito, Tatsuya; Harjo, S.; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 278, p.120233_1 - 120233_13, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:87.44(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Ying, H.*; Yang, X.*; He, H.*; Yan, A.*; An, K.*; Ke, Y.*; Wu, Z.*; Tang, S.*; Zhang, Z.*; Dong, H.*; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 250, p.116181_1 - 116181_7, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:41.92(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Fang, W.*; Liu, C.*; Zhang, J.*; Xu, P. G.; Peng, T.*; Liu, B.*; Morooka, Satoshi; Yin, F.*
Scripta Materialia, 249, p.116046_1 - 116046_6, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:63.37(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Somekawa, Hidetoshi*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Naito, Kimiyoshi*; Singh, A.*
Scripta Materialia, 249, p.116173_1 - 116173_6, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:41.92(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)The segregated  twin boundaries play a role in obstruction of dislocation slips. Thus, they contribute to increase in hardness. Internal friction tests reveal that, irrespective of the solute elements, induced twin boundaries are effective in enhancing damping capacity, owing to their reversible motion, i.e., growth and shrinkage. In contrast, by comparison of the loss factor of specimens with/without twin boundary segregation, segregation leads to a decrease in damping capacity. The energy barrier required for twin boundary sliding to occur is closely related to the loss factor.
twin boundaries play a role in obstruction of dislocation slips. Thus, they contribute to increase in hardness. Internal friction tests reveal that, irrespective of the solute elements, induced twin boundaries are effective in enhancing damping capacity, owing to their reversible motion, i.e., growth and shrinkage. In contrast, by comparison of the loss factor of specimens with/without twin boundary segregation, segregation leads to a decrease in damping capacity. The energy barrier required for twin boundary sliding to occur is closely related to the loss factor.
Ma, Y.*; Naeem, M.*; Zhu, L.*; He, H.*; Sun, X.*; Yang, Z.*; He, F.*; Harjo, S.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Wang, X.-L.*
Acta Materialia, 270, p.119822_1 - 119822_13, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:95.42(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Mn
MnShimizu, Kazuyuki*; Nishimura, Katsuhiko*; Matsuda, Kenji*; Akamaru, Satoshi*; Nunomura, Norio*; Namiki, Takahiro*; Tsuchiya, Taiki*; Lee, S.*; Higemoto, Wataru; Tsuru, Tomohito; et al.
Scripta Materialia, 245, p.116051_1 - 116051_6, 2024/05
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:63.37(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Hydrogen at the mass ppm level causes hydrogen embrittlement in metallic materials, but it is extremely difficult to experimentally elucidate the hydrogen trapping sites. We have taken advantage of the fact that positive muons can act as light isotopes of hydrogen to study the trapping state of hydrogen in matter. Zero-field muon spin relaxation experiments and the density functional theory (DFT) calculations for hydrogen trapping energy are carried out for Al Mn. The DFT calculations for hydrogen in Al
Mn. The DFT calculations for hydrogen in Al Mn have found four possible trapping sites in which the hydrogen trapping energies are 0.168 (site 1), 0.312 (site 2), 0.364 (site 3), and 0.495 (site 4) in the unit of eV/atom. Temperature variations of the deduced dipole field width (
Mn have found four possible trapping sites in which the hydrogen trapping energies are 0.168 (site 1), 0.312 (site 2), 0.364 (site 3), and 0.495 (site 4) in the unit of eV/atom. Temperature variations of the deduced dipole field width ( ) indicated step-like changes at temperatures, 94, 193, and 236 K. Considering their site densities, the observed
) indicated step-like changes at temperatures, 94, 193, and 236 K. Considering their site densities, the observed  change temperatures are interpreted by trapping muons at sites 1, 3, and 4.
change temperatures are interpreted by trapping muons at sites 1, 3, and 4.
Guo, B.*; Chen, H.*; Chong, Y.*; Mao, W.; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Zhang, Z.*; Jonas, J. J.*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Acta Materialia, 268, p.119780_1 - 119780_11, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:92.77(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Tang, J.*; Wang, Y.*; Fujihara, Hiro*; Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hirayama, Kyosuke*; Ebihara, Kenichi; Takeuchi, Akihisa*; Uesugi, Masayuki*; Toda, Hiroyuki*
Scripta Materialia, 239, p.115804_1 - 115804_5, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:82.25(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology)Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) behaviors induced by the combination of external and internal hydrogen (H) in an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy were systematically investigated via in situ 3D characterization techniques. SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy could initiate and propagate in the potential crack region where the H concentration exceeded a critical value, in which the nanoscopic H-induced decohesion of  -MgZn
-MgZn precipitates resulted in macroscopic cracking. External H that penetrated the alloy from the environment played a crucial role during the SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy by generating gradient-distributed H-affected zones near the crack tips, which made Al alloys in water environment more sensitive to SCC. Additionally, the pre-existing internal H was driven toward the crack tips during plastic deformation. It was involved in the SCC and made contributions to both the cracks initiation and propagation.
precipitates resulted in macroscopic cracking. External H that penetrated the alloy from the environment played a crucial role during the SCC of the Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy by generating gradient-distributed H-affected zones near the crack tips, which made Al alloys in water environment more sensitive to SCC. Additionally, the pre-existing internal H was driven toward the crack tips during plastic deformation. It was involved in the SCC and made contributions to both the cracks initiation and propagation.
Vauchy, R.; Hirooka, Shun; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Materialia, 32, p.101943_1 - 101943_8, 2023/12
Vauchy, R.; Hirooka, Shun; Murakami, Tatsutoshi
Materialia, 32, p.101934_1 - 101934_12, 2023/12