Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Miyahara, Kaname; Tokizawa, Takayuki; Nakayama, Shinichi
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1518, p.245 - 256, 2013/10
After the Fukushima Dai-ichi accident, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was chosen by the Government to conduct decontamination model projects at selected sites. Despite tight boundary conditions in terms of timescale and resources, the decontamination model projects provide a good basis for developing recommendations on how to assure clean-up efficiency and reduce time, cost, subsequent waste management and environmental impact. This can be summarised in terms of site characterisation and data interpretation, clean-up and waste minimisation and storage.
 (aq)/NH
(aq)/NH

Kobayashi, Taishi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Ueda, Kenyo*; Kitamura, Akira
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1518, p.231 - 236, 2013/10
For the nuclear waste management of TRU waste, it is necessary to assess the impact of nitrate salts contained in the waste. In the present study, the sorption behavior of Ni and Pd on the pumice tuff was investigated in the presence of NH (aq)/NH
(aq)/NH
 . Under different NH
. Under different NH (aq)/NH
(aq)/NH
 concentration, pH and ionic strength conditions, distribution coefficient (
concentration, pH and ionic strength conditions, distribution coefficient ( ) of Ni and Pd on the pumice tuff was determined by batch experiment. For Ni system, the
) of Ni and Pd on the pumice tuff was determined by batch experiment. For Ni system, the  values showed no significant dependence on the initial NH
values showed no significant dependence on the initial NH
 concentration in neutral pH region, agrees with the prediction from thermodynamic data. For Pd system, the
concentration in neutral pH region, agrees with the prediction from thermodynamic data. For Pd system, the  values decreased with an increase of [NH
values decreased with an increase of [NH
 ]ini, suggesting the formation of stable ammine complex (Pd(NH
]ini, suggesting the formation of stable ammine complex (Pd(NH )
)
 (
( : 1 - 4)). The obtained
: 1 - 4)). The obtained  values for Ni and Pd were analyzed using the surface complexation model. By taking complexes predicted by thermodynamic data into account, the sorption behavior of Ni and Pd in the presence of NH
values for Ni and Pd were analyzed using the surface complexation model. By taking complexes predicted by thermodynamic data into account, the sorption behavior of Ni and Pd in the presence of NH (aq)/NH
(aq)/NH
 were well explained.
were well explained.
Yoshikawa, Hideki; Iijima, Kazuki; Sasamoto, Hiroshi; Fujiwara, Kenso; Mitsui, Seiichiro; Kitamura, Akira; Kurikami, Hiroshi; Tokizawa, Takayuki; Yui, Mikazu; Nakayama, Shinichi
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1518, p.269 - 275, 2013/10
Following the release of radionuclides into the environment as a result of the accident at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant, Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) had to develop an immediate and effective method of reducing the dose rate received by students in school facilities. A demonstration of a reducing method was carried out by JAEA at a junior high school ground and kindergarten yard in the center of Fukushima-city. Dose rates of the released radionuclides are largely controlled by the ground level contamination and accumulation of mainly cesium-137 ( Cs) and cesium-134 (
Cs) and cesium-134 ( Cs) in populated areas. An effective means of reducing dose rate was to remove the surface soil and to bury it on-site under fresh uncontaminated soil or soil collected under deep depth at the site for shielding. The dose rate at1 m above ground level was reduced from 2.5
Cs) in populated areas. An effective means of reducing dose rate was to remove the surface soil and to bury it on-site under fresh uncontaminated soil or soil collected under deep depth at the site for shielding. The dose rate at1 m above ground level was reduced from 2.5  Sv/h to 0.15
Sv/h to 0.15  Sv/h.
Sv/h.
Sato, Haruo; Niizato, Tadafumi; Amano, Kenji; Tanaka, Shingo; Aoki, Kazuhiro
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1518, p.277 - 282, 2013/10
The accident of the TEPCO Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant occurred by the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake on 11 March, 2011. It is estimated that 1.2-1.5 10
10 Bq for
Bq for  Cs and 1.5-1.6
Cs and 1.5-1.6 10
10 Bq for I-131 were released until the beginning of April and those radionuclides (RN) were deposited on soil surface and forest etc. widely around Fukushima Pref. This work was carried out as one of the investigations for making the distribution maps of radiation dose rate and soil contaminated by RNs which the MEXT promotes. The Geoslicer investigation on the depth distribution of RNs in soil was carried out after 3 months from the accident. The investigation was conducted at 11 locations in Nihonmatsu City, Kawamata Town and Namie Town, and soil samples of depth 50 cm to 1 m were taken. Both of
Bq for I-131 were released until the beginning of April and those radionuclides (RN) were deposited on soil surface and forest etc. widely around Fukushima Pref. This work was carried out as one of the investigations for making the distribution maps of radiation dose rate and soil contaminated by RNs which the MEXT promotes. The Geoslicer investigation on the depth distribution of RNs in soil was carried out after 3 months from the accident. The investigation was conducted at 11 locations in Nihonmatsu City, Kawamata Town and Namie Town, and soil samples of depth 50 cm to 1 m were taken. Both of  Cs and
Cs and  Cs were detected in all investigated locations, and
Cs were detected in all investigated locations, and 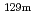 Te and
Te and 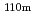 Ag were detected only in areas where radiation dose rates are high. At many locations investigated, radiocaesium more than 99% distributed within a depth of 10 cm in soil in the surface layer. On the other hand, RNs tended to distribute to deeper part in soil at locations that are supposed to have been used as farmland than in soil in the surface layer, and radiocaesium more than 99% in soil at locations that are supposed to have been used as farmland also distributed within a depth of around 14 cm. The apparent diffusion coefficients of RNs derived from penetration profiles near the surface layer showed a tendency to be higher in soil at locations that are supposed to have been used as farmland than in soil in the surface layer. The distribution coefficients by a batch method were also obtained for Cs and I, and the relationship between D
Ag were detected only in areas where radiation dose rates are high. At many locations investigated, radiocaesium more than 99% distributed within a depth of 10 cm in soil in the surface layer. On the other hand, RNs tended to distribute to deeper part in soil at locations that are supposed to have been used as farmland than in soil in the surface layer, and radiocaesium more than 99% in soil at locations that are supposed to have been used as farmland also distributed within a depth of around 14 cm. The apparent diffusion coefficients of RNs derived from penetration profiles near the surface layer showed a tendency to be higher in soil at locations that are supposed to have been used as farmland than in soil in the surface layer. The distribution coefficients by a batch method were also obtained for Cs and I, and the relationship between D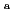 and K
and K was discussed.
was discussed.
Takeda, Seiji; Inoue, Yoshihisa; Kimura, Hideo
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1518, p.237 - 242, 2013/10
The sensitive analysis of radionuclide migration for the scenarios on deterioration or loss of safety functions expected in HLW disposal system due to the human error (initial defective scenarios) is performed in this study. Release rates for Cs-135 and Se-79 are estimated from Monte Carlo-based analysis. Maximum release rates of radionuclides for initial defective scenarios, buffer (colloidal transport case) and sealing plugs (pathway of short-circuit), are about one or two order magnitude higher than that normal scenario. From a viewpoint of future safety review, these results especially indicate the need to understand the feasibility on two types of initial defective scenario for the buffer and sealing plugs, leading to the loss of restraint of colloidal migration in the buffer and the loss of restraint with the plugs from migration through dominant pathway in tunnels and their vicinity.
Sasaki, Toshiki; Kaminishi, Shuji*; Miyamoto, Yasuaki; Funasaka, Hideyuki
Materials Research Society Symposium Proceedings, Vol.1518, p.257 - 268, 2013/10
The Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station accident and restoration works have produced significant volume of radioactive waste. The waste has very different characteristics from usual radioactive waste produced in nuclear power stations and it requires extensive research and development for management of the waste. R&D works such as radionuclide analysis of the waste, hydrogen generation/diffusion analysis of a storage vessel, corrosion evaluation of storage vessels, etc. have been performed for characterization and safe storage of the waste. The detailed R&D plan for processing and disposal waste will be established by the end of FY2012.