Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Mn
Mn N and Fe
N and Fe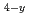 Co
Co N films
N filmsYin, W.*; Ito, Keita*; Tsubowa, Yusuke*; Tsujikawa, Masahito*; Shirai, Masafumi*; Umetsu, Rie*; Takanashi, Koki
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 628, p.173157_1 - 173157_8, 2025/09
Times Cited Count:0 neutron diffraction study
neutron diffraction studyYamashita, Takayuki*; Koga, Norimitsu*; Mao, W.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; Fujii, Hidetoshi*; Umezawa, Osamu*
Materials Science and Engineering A, 941, p.148602_1 - 148602_11, 2025/09
Cao, T.*; Wei, D.*; Gong, W.; Kawasaki, Takuro; Harjo, S.; 10 of others*
Materials Science and Engineering A, 940, p.148534_1 - 148534_16, 2025/09
Mochizuki, Akihito; Matsui, Hiroya; Nakayama, Masashi; Sakamoto, Ryo*; Shibata, Masahito*; Motoshima, Takayuki*; Jo, Mayumi*
Case Studies in Construction Materials, 22, p.e04648_1 - e04648_20, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0The properties of low-pH cement used in the geological disposal of radioactive waste may change through atmospheric carbonation and degradation caused by groundwater during the long-term operation of a repository. In this study, we investigated the effects of atmospheric carbonation and groundwater contact on the chemical, microstructural, and transport properties of shotcrete made from low-pH, high-fly-ash silica-fume cement (HFSC) over a period of 16 years in an underground research laboratory. In both carbonated and degraded zones of the HFSC shotcrete, capillary porosity increased for pores of  300 nm in diameter, and the total porosity was higher than in undegraded zones. These changes in porosity may be associated with the decalcification of calcium-silicate-hydrate and decomposition of ettringite. Such changes were minor in altered zones of OPC shotcrete, indicating that HFSC shotcrete is less resistant to atmospheric carbonation and groundwater leaching under the studied conditions. However, the hydraulic conductivity in HFSC was low enough to fulfill the specific functional requirements of low-pH cements for geological disposal.
300 nm in diameter, and the total porosity was higher than in undegraded zones. These changes in porosity may be associated with the decalcification of calcium-silicate-hydrate and decomposition of ettringite. Such changes were minor in altered zones of OPC shotcrete, indicating that HFSC shotcrete is less resistant to atmospheric carbonation and groundwater leaching under the studied conditions. However, the hydraulic conductivity in HFSC was low enough to fulfill the specific functional requirements of low-pH cements for geological disposal.
Gu, G. H.*; Jeong, S. G.*; Heo, Y.-U.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Cho, J.*; Kim, H. S.*; 4 of others*
Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 223, p.308 - 324, 2025/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Auh, Y. H.*; Neal, N. N.*; Arole, K.*; Regis, N. A.*; Nguyen, T.*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Tsuda, Yasutaka; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Radovic, M.*; Green, M. J.*; et al.
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 17(21), p.31392 - 31402, 2025/05
Naeem, M.*; Rehman, A. U.*; Romero Resendiz, L.*; Salamci, E.*; Aydin, H.*; Ansari, P.*; Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; Wang, X.-L.*; 3 of others*
Communications Materials (Internet), 6, p.65_1 - 65_13, 2025/04
Shiotani, Kohei; Niiyama, Tomoaki*; Shimokawa, Tomotsugu*
Materials Transactions, 66(6), p.704 - 711, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
 CaOsO
CaOsO studied by O
studied by O  -edge resonant inelastic X-ray scattering and Raman spectroscopy
-edge resonant inelastic X-ray scattering and Raman spectroscopyOkamoto, Jun*; Shibata, Goro; Fujimori, Atsushi; 9 of others*
npj Quantum Materials (Internet), 10, p.44_1 - 44_8, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 martensitic transformation in Ti-12Mo alloy
martensitic transformation in Ti-12Mo alloyChong, Y.*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Mitsuhara, Masatoshi*; Guo, B.*; Gholizadeh, R.*; Inoue, Koji*; Godfrey, A.*; Tsuji, Nobuhiro*
Communications Materials (Internet), 6, p.50_1 - 50_11, 2025/03
Strain-induced  martensitic phase transformation (SIMT) critically affects the mechanical properties of metastable
martensitic phase transformation (SIMT) critically affects the mechanical properties of metastable  titanium alloys. In this study, the effects of
titanium alloys. In this study, the effects of  grain size and oxygen content on SIMT in a Ti-12wt.%Mo alloy were systematically investigated. It is found that SIMT is promoted by a decrease in grain size and in oxygen content. The mechanistic origins of the anomalous grain size dependency and the acute oxygen content dependency of SIMT are discussed based on multi-scale microstructural characterization and state-of-the-art simulations. Grain refinement does not raise the energy barrier for SIMT but rather provides more nucleation sites for strain-induced
grain size and oxygen content on SIMT in a Ti-12wt.%Mo alloy were systematically investigated. It is found that SIMT is promoted by a decrease in grain size and in oxygen content. The mechanistic origins of the anomalous grain size dependency and the acute oxygen content dependency of SIMT are discussed based on multi-scale microstructural characterization and state-of-the-art simulations. Grain refinement does not raise the energy barrier for SIMT but rather provides more nucleation sites for strain-induced  martensite, thereby promoting SIMT in fine-grained Ti-12wt.%Mo alloy. In contrast, for the Ti-12wt.%Mo-0.3 wt.%O alloy, oxygen atoms substantially increase the energy barrier for SIMT, due to a change in the local configuration of oxygen atoms during the phase transformation. In addition, atom probe tomography reveals for the first time that oxygen atoms segregate at
martensite, thereby promoting SIMT in fine-grained Ti-12wt.%Mo alloy. In contrast, for the Ti-12wt.%Mo-0.3 wt.%O alloy, oxygen atoms substantially increase the energy barrier for SIMT, due to a change in the local configuration of oxygen atoms during the phase transformation. In addition, atom probe tomography reveals for the first time that oxygen atoms segregate at 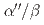 phase boundaries, thereby further restricting the growth of
phase boundaries, thereby further restricting the growth of  martensite.
martensite.
Masuki, Yuma*; Katsuta, Nagayoshi*; Naito, Sayuri*; Murakami, Takuma*; Umemura, Ayako*; Fujita, Natsuko; Matsubara, Akihiro*; Minami, Masayo*; Niwa, Masakazu; Yoshida, Hidekazu*; et al.
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 485, p.136843_1 - 136843_10, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Engineering, Environmental)Lacustrine deposits have 30-fold higher As abundance than the average crustal deposit. Arsenic is mostly concentrated as discrete horizons deposited in spring and autumn. As-rich layers contain FeAsS, AsS, and As S
S but As-rich hotspots mostly contain FeAsS. As accumulation to sediment is controlled by redox potential with organic matter.
but As-rich hotspots mostly contain FeAsS. As accumulation to sediment is controlled by redox potential with organic matter.
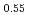 Pu
Pu Am
Am )O
)O
Yokoyama, Keisuke; Watanabe, Masashi; Usui, Akane; Seki, Takayuki*; Onishi, Takashi; Kato, Masato
Nuclear Materials and Energy (Internet), 42, p.101908_1 - 101908_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nuclear Science & Technology)Oxygen potential of high Am content MOX, (U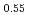 Pu
Pu Am
Am )O
)O , was measured at 1273 K, 1473 K, 1573 K, and 1623 K. by gas equilibrium method using thermogravimeter. Comparing the measured data with the literature data, it was found that the addition of 15% Am increases the oxygen potential of (U, Pu)O
, was measured at 1273 K, 1473 K, 1573 K, and 1623 K. by gas equilibrium method using thermogravimeter. Comparing the measured data with the literature data, it was found that the addition of 15% Am increases the oxygen potential of (U, Pu)O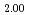 by 100-150 kJ/mol for the same Pu content and O/M ratio. The proportion of cations in the stoichiometric composition was determined as (U
by 100-150 kJ/mol for the same Pu content and O/M ratio. The proportion of cations in the stoichiometric composition was determined as (U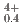 U
U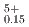 Pu
Pu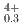 Am
Am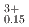 )O
)O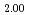 , assuming the presence of Am
, assuming the presence of Am and partial oxidation of U
and partial oxidation of U to U
to U . The relationship between oxygen partial pressure and deviation x from stoichiometry in (U
. The relationship between oxygen partial pressure and deviation x from stoichiometry in (U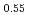 Pu
Pu Am
Am )O
)O was analyzed by defect chemistry model. The equation to represent the O/M ratio was derived as a function of temperature and oxygen partial pressure. A part of this study includes the results of MEXT Innovative Nuclear Research and Development Program Grant Number JPMXD0219214921.
was analyzed by defect chemistry model. The equation to represent the O/M ratio was derived as a function of temperature and oxygen partial pressure. A part of this study includes the results of MEXT Innovative Nuclear Research and Development Program Grant Number JPMXD0219214921.
 GeTe
GeTe homojunctions
homojunctionsObata, Reiji*; Saito, Eiji; Kikkawa, Takashi; 13 of others*
Advanced Materials, 37(8), p.2411459_1 - 2411459_11, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary) O
O , FeUO
, FeUO , and UO
, and UO -Zr-stainless steel system samples generated in an oxidative atmosphere in the presence of malonic acid
-Zr-stainless steel system samples generated in an oxidative atmosphere in the presence of malonic acidTonna, Ryutaro*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Okamoto, Yoshihiro; Kobayashi, Taishi*
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 605, p.155561_1 - 155561_9, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Abe, Yosuke; Tsuru, Tomohito; Fujita, Yohei*; Otomo, Masahide*; Sasaki, Taisuke*; Yamashita, Shinichiro; Okubo, Nariaki; Ukai, Shigeharu
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 606, p.155606_1 - 155606_12, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We investigated the effect of Al addition on the formation of 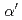 phase in Fe-Cr-Al model alloys by thermal aging. The Vickers hardness tests and a machine learning model indicate that the formation of the
phase in Fe-Cr-Al model alloys by thermal aging. The Vickers hardness tests and a machine learning model indicate that the formation of the 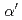 phase is promoted by low Al additions and suppressed by high Al additions. First-principles calculations, which indicate that Cr-Al-vacancy pairs are more stable than Cr-Cr pairs and that including Al atoms during
phase is promoted by low Al additions and suppressed by high Al additions. First-principles calculations, which indicate that Cr-Al-vacancy pairs are more stable than Cr-Cr pairs and that including Al atoms during 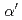 phase nucleation may be energetically advantageous. On the other hand, the formation of Al-Al pairs was very unstable. The formation of Al-Al pairs near the interface can be avoided when the amount of Al addition is small. However, it is inevitable when the amount of Al addition is significant, leading to the instability of the
phase nucleation may be energetically advantageous. On the other hand, the formation of Al-Al pairs was very unstable. The formation of Al-Al pairs near the interface can be avoided when the amount of Al addition is small. However, it is inevitable when the amount of Al addition is significant, leading to the instability of the 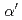 phase.
phase.
Naeem, M.*; Ma, Y.*; Tian, J.*; Kong, H.*; Romero-Resendiz, L.*; Fan, Z.*; Jiang, F.*; Gong, W.; Harjo, S.; Wu, Z.*; et al.
Materials Science & Engineering A, 924, p.147819_1 - 147819_10, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Nanoscience & Nanotechnology) CuZn
CuZn P
P
May, A. F.*; Tabata, Chihiro; Okamoto, Satoshi*; Ortiz, B. R.*; Christianson, A. D.*; Yan, J.*; Kaneko, Koji; McGuire, M. A.*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 9(2), p.024406_1 - 024406_13, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Nozaki, Yukio*; Sukegawa, Hiroaki*; Watanabe, Shinichi*; Yunoki, Seiji*; Horaguchi, Taisuke*; Nakayama, Hayato*; Yamanoi, Kazuto*; Wen, Z.*; He, C.*; Song, J.*; et al.
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 26(1), p.2428153_1 - 2428153_39, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) neutron imaging and diffraction analysis revealing spatial lithiation phase evolution in an ultra-thick graphite electrode
neutron imaging and diffraction analysis revealing spatial lithiation phase evolution in an ultra-thick graphite electrodeStrobl, M.*; Baur, M. E.*; Samothrakitis, S.*; Molamud, F.*; Zhang, X.*; Tung, P. K. M.*; Schmidt, S.*; Woracek, R.*; Lee, J.*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; et al.
Advanced Energy Materials, p.2405238_1 - 2405238_9, 2025/01
Im, S.*; Jee, H.*; Kanematsu, Manabu*; Morooka, Satoshi; Choe, H.*; Nishio, Yuhei*; Machida, Akihiko*; Tominaga, Aki; Jeon, B. H.*; Bae, S.*
Construction and Building Materials, 459, p.139742_1 - 139742_17, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Construction & Building Technology)