Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sheng, L.*; Yamamoto, Kei; 18 of others*
Nature Physics, 8 Pages, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:82.94(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Han, J.*; Uchimura, Tomohiro*; Araki, Yasufumi; Yoon, J.-Y.*; Takeuchi, Yutaro*; Yamane, Yuta*; Kanai, Shun*; Ieda, Junichi; Ohno, Hideo*; Fukami, Shunsuke*
Nature Physics, 20(7), p.1110 - 1117, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:96.80(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Quantum metric and Berry curvature are two fundamental and distinct factors to describe the geometry of quantum eigenstates. While Berry curvature is known for playing crucial roles in several condensed-matter states, quantum metric, which was predicted to induce new classes of topological phenomena, has rarely been touched, particularly in an ambient circumstance. Using a topological chiral antiferromagnet Mn Sn adjacent to Pt, at room temperature, we successfully manipulate the quantum-metric structure of electronic states through its interplay with the nanoscale spin texture at the Mn
Sn adjacent to Pt, at room temperature, we successfully manipulate the quantum-metric structure of electronic states through its interplay with the nanoscale spin texture at the Mn Sn/Pt interface. This is manifested by a time-reversal-odd second-order Hall effect that is robust against extrinsic electron scattering, in contrast to any transport effects from the Berry curvature. We also verify the flexibility of controlling the quantum-metric structure, as the interacting spin texture can be tuned by moderate magnetic fields or by interface engineering via spin-orbit interactions. Our work paves a way for harnessing the quantum-metric structure to unveil emerging topological physics in practical environments and to build applicable nonlinear devices.
Sn/Pt interface. This is manifested by a time-reversal-odd second-order Hall effect that is robust against extrinsic electron scattering, in contrast to any transport effects from the Berry curvature. We also verify the flexibility of controlling the quantum-metric structure, as the interacting spin texture can be tuned by moderate magnetic fields or by interface engineering via spin-orbit interactions. Our work paves a way for harnessing the quantum-metric structure to unveil emerging topological physics in practical environments and to build applicable nonlinear devices.
Zeng, Z.*; Zhou, C.*; Zhou, H.*; Han, L.*; Chi, R.*; Li, K.*; Kofu, Maiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Wei, Y.*; Zhang, W.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 20(7), p.1097 - 1102, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:94.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Ichikawa, Tsubasa*; Hakoshima, Hideaki*; Inui, Koji*; Ito, Kosuke*; Matsuda, Ryo*; Mitarai, Kosuke*; Miyamoto, Koichi*; Mizukami, Wataru*; Mizuta, Kaoru*; Mori, Toshio*; et al.
Nature Reviews Physics (Internet), 6(6), p.345 - 347, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:99.15(Physics, Applied)Zhao, K.*; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Chen, H.*; Gegenwart, P.*
Nature Physics, 20(3), p.442 - 449, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:94.31(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In magnetic crystals, despite the explicit breaking of time-reversal symmetry, two equilibrium states related by time reversal are always energetically degenerate. In ferromagnets, this time-reversal degeneracy is reflected in the hysteresis of the magnetic field dependence of the magnetization and, if metallic, in that of the anomalous Hall effect (AHE). Under time-reversal, both these quantities change signs but not their magnitude. Here we show that a time-reversal-like degeneracy appears in the metallic kagome spin ice HoAgGe when magnetic fields are applied parallel to the kagome plane. We find vanishing hysteresis in the field dependence of the magnetization at low temperature, but finite hysteresis in the field-dependent AHE. This suggests the emergence of states with nearly the same energy and net magnetization but different sizes of the AHE and of the longitudinal magnetoresistance. By analysing the experimental data and a minimal tight-binding model, we identify a time-reversal-like operation connecting these near-degenerate states, which is related to the non-trivial distortion of the kagome lattice in HoAgGe. Our work demonstrates the diagnostic power of transport phenomena for identifying hidden symmetries in frustrated spin systems.
Shangguan, Y.*; Bao, S.*; Dong, Z.-Y.*; Xi, N.*; Gao, Y.-P.*; Ma, Z.*; Wang, W.*; Qi, Z.*; Zhang, S.*; Huang, Z.*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(12), p.1883 - 1889, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:93.50(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Takagi, Hirotaka*; Takagi, Rina*; Minami, Susumu*; Nomoto, Takuya*; Oishi, Kazuki*; Suzuki, Michito*; Yanagi, Yuki*; Hirayama, Motoaki*; Khanh, N.*; Karube, Kosuke*; et al.
Nature Physics, 19(7), p.961 - 968, 2023/07
Times Cited Count:55 Percentile:99.13(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Nishi, Takahiro*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; 46 of others*
Nature Physics, 19(6), p.788 - 793, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:15 Percentile:90.62(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Aidala, C.*; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Imai, Kenichi; Sako, Hiroyuki; Sato, Susumu; Tanida, Kiyoshi; PHENIX Collaboration*; 312 of others*
Nature Physics, 15(3), p.214 - 220, 2019/03
Times Cited Count:110 Percentile:97.33(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Marsh, B. A.*; Day Goodacre, T.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Andreyev, A. N.; 41 of others*
Nature Physics, 14(12), p.1163 - 1167, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:127 Percentile:96.96(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Shiomi, Yuki*; Lustikova, J.*; Watanabe, Shingo*; Hirobe, Daichi*; Takahashi, Saburo*; Saito, Eiji
Nature Physics, 15(1), p.22 - 26, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:21 Percentile:75.53(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Bi
Bi Se
Se
Yonezawa, Shingo*; Tajiri, Kengo*; Nakata, Suguru*; Nagai, Yuki; Wang, Z.*; Segawa, Koji*; Ando, Yoichi*; Maeno, Yoshiteru*
Nature Physics, 13(2), p.123 - 126, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:217 Percentile:98.78(Physics, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Hirobe, Daichi*; Sato, Masahiro*; Kawamata, Takayuki*; Shiomi, Yuki*; Uchida, Kenichi*; Iguchi, Ryo*; Koike, Yoji*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Nature Physics, 13(1), p.30 - 34, 2017/01
Times Cited Count:122 Percentile:96.97(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Takahashi, Ryo*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Ono, Masao; Harii, Kazuya; Chudo, Hiroyuki; Okayasu, Satoru; Ieda, Junichi; Takahashi, Saburo*; Maekawa, Sadamichi; Saito, Eiji
Nature Physics, 12, p.52 - 56, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:121 Percentile:96.21(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Si
Si
Yamashita, Takuya*; Shimoyama, Yusuke*; Haga, Yoshinori; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Onuki, Yoshichika; Sumiyoshi, Hiroaki*; Fujimoto, Satoshi*; Levchenko, A.*; Shibauchi, Takasada*; et al.
Nature Physics, 11(1), p.17 - 20, 2015/01
Times Cited Count:60 Percentile:90.28(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Kambe, Shinsaku; Sakai, Hironori; Tokunaga, Yo; Lapertot, G.*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Knebel, G.*; Flouquet, J.*; Walstedt, R. E.*
Nature Physics, 10(11), p.840 - 844, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:18 Percentile:69.41(Physics, Multidisciplinary)In new observations reported here, we find that coexisting, static Fermi liquid and non-Fermi liquid states are a key feature of the QCPT in YbRh Si
Si . By means of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spin-lattice relaxation time measurements on a single crystal sample, it is revealed that the FL and NFL states are invariant,while their relative proportion in a crossover is field dependent near the QCPT. Such a pair of states has remained hidden in Ce compounds, owing presumably to short lifetimes for the two states. A new scaling law for the occupation ratio of the two states is derived, and could be widely applicable to Kondo-lattice systems
. By means of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spin-lattice relaxation time measurements on a single crystal sample, it is revealed that the FL and NFL states are invariant,while their relative proportion in a crossover is field dependent near the QCPT. Such a pair of states has remained hidden in Ce compounds, owing presumably to short lifetimes for the two states. A new scaling law for the occupation ratio of the two states is derived, and could be widely applicable to Kondo-lattice systems
Watanabe, Shun*; Ando, Kazuya*; Kang, K.*; Mooser, S.*; Vaynzof, Y.*; Kurebayashi, Hidekazu*; Saito, Eiji; Sirringhaus, H.*
Nature Physics, 10(4), p.308 - 313, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:189 Percentile:97.81(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Hiraishi, Masatoshi*; Iimura, Soshi*; Kojima, Kenji*; Yamaura, Junichi*; Hiraka, Haruhiro*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Miao, P.*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Torii, Shuki*; Miyazaki, Masanori*; et al.
Nature Physics, 10(4), p.300 - 303, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:108 Percentile:95.02(Physics, Multidisciplinary) Si
Si
Ikeda, Hiroaki*; Suzuki, Michito; Arita, Ryotaro*; Takimoto, Tetsuya*; Shibauchi, Takasada*; Matsuda, Yuji*
Nature Physics, 8(7), p.528 - 533, 2012/07
Times Cited Count:138 Percentile:95.89(Physics, Multidisciplinary)The origin of the hidden-order phase transition of URu Si
Si has been a long-standing mystery in condensed matter physics. We examine the complete set of multipole correlations allowed in URu
has been a long-standing mystery in condensed matter physics. We examine the complete set of multipole correlations allowed in URu Si
Si based on a first-principles theoretical approach. The results uncover that the hidden-order parameter is a rank-5 multipole (dotriacontapole) order with nematic
based on a first-principles theoretical approach. The results uncover that the hidden-order parameter is a rank-5 multipole (dotriacontapole) order with nematic 
 symmetry. This naturally provides comprehensive explanations of all key features in the hidden-order phase including anisotropic magnetic excitations, nearly degenerate antiferromagnetic-ordered state, and spontaneous rotational symmetry breaking.
symmetry. This naturally provides comprehensive explanations of all key features in the hidden-order phase including anisotropic magnetic excitations, nearly degenerate antiferromagnetic-ordered state, and spontaneous rotational symmetry breaking.
Mounce, A. M.*; Oh, S.*; Mukhopadhyay, S.*; Halperin, W. P.*; Reyes, A. P.*; Kuhns, P. L.*; Fujita, Kazuhiro*; Ishikado, Motoyuki; Uchida, Shinichi*
Nature Physics, 7(2), p.125 - 128, 2011/02
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:49.50It has been predicted that superconducting vortices should be electrically charged and that this effect is particularly enhanced for high-temperature superconductors. Hall effect and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiments suggest the existence of charge accumulation in the vortex core, but the effects are small and the interpretation controversial. Here we show that the Abrikosov vortex lattice, characteristic of the mixed state of superconductors, will become unstable at a sufficiently high magnetic field if there is charge trapped on the vortex core. Our NMR measurements of the magnetic fields generated by vortices in Bi Sr
Sr CaCu
CaCu O
O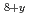 single crystals provide evidence for an electrostatically driven vortex lattice reconstruction with the magnitude of charge on each vortex pancake of
single crystals provide evidence for an electrostatically driven vortex lattice reconstruction with the magnitude of charge on each vortex pancake of 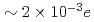 , depending on doping, in line with theoretical estimates.
, depending on doping, in line with theoretical estimates.