Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Saito, Junichi; Kobayashi, Yohei*; Shibutani, Hideo*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 85(3), p.110 - 119, 2021/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.99(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Shimizu, Kazuyuki*; Hayashida, Hirotoshi*; Toda, Hiroyuki*; Kai, Tetsuya; Matsumoto, Yoshihiro*; Matsumoto, Yoshihisa*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 83(11), p.434 - 440, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:4.98(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Ogawa, Wataru*; Shobu, Takahisa; Kakehi, Mizue*; Kuratani, Fumiyasu*; Koide, Toshio*; Monju, Yoshiyuki*; Mizuta, Taiji*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 83(4), p.128 - 135, 2019/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:9.58(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Cymbals are percussion musical instruments with a simpler structure than other musical instruments. Therefore, their material composition basically decides the sound quality and decay time rather than the skill of the player. In this study, specimens of cymbals to which Titanium, Zirconium and Iron were added were prepared. From the difference of diffraction rings by synchrotron radiation X-rays, the crystal structure of the specimens of cymbals prepared by various manufacturing processes was analyzed in order to investigate the relationship between the crystal structure associated with the material and manufacturing process used and the damping of the sound of cymbals. As a result, it was found that the changes in the crystal structure were due to the manufacturing process used. In addition, it was clarified that the changes affected the damping of the sound of cymbals.
Kokubo, Hiroki*; Nishi, Tsuyoshi*; Ota, Hiromichi*; Yamano, Hidemasa
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 82(10), p.400 - 402, 2018/09
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:31.55(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)It is important to obtain the viscosity of a mixed alloy consisting of molten stainless steel and boron-carbide (SUS316L + B C alloy) for the improvement of severe accident assessment methodology for sodium-cooled fast reactors. In this study, the viscosities of the molten nickel (Ni) and stainless steel (SUS316L) were measured by the oscillating crucible method to confirm the performance of the viscosity measurement apparatus as a first step. The viscosities of molten Ni and SUS316L melts were measured up to 1823 K. It was found that the measured viscosity values of molten Ni and SUS316L were estimated from the deviation of the experimental data, were
C alloy) for the improvement of severe accident assessment methodology for sodium-cooled fast reactors. In this study, the viscosities of the molten nickel (Ni) and stainless steel (SUS316L) were measured by the oscillating crucible method to confirm the performance of the viscosity measurement apparatus as a first step. The viscosities of molten Ni and SUS316L melts were measured up to 1823 K. It was found that the measured viscosity values of molten Ni and SUS316L were estimated from the deviation of the experimental data, were  4% and
4% and  3%, respectively. It was also found that those of molten Ni and SUS316L were close to those of the literature values of molten Ni and similar composite stainless steels. Moreover, we tentatively measured the viscosity of molten SUS316L-5 mass%B
3%, respectively. It was also found that those of molten Ni and SUS316L were close to those of the literature values of molten Ni and similar composite stainless steels. Moreover, we tentatively measured the viscosity of molten SUS316L-5 mass%B C alloy. The fitted results of the viscosity for molten Ni and SUS316L were obtained.
C alloy. The fitted results of the viscosity for molten Ni and SUS316L were obtained.
Narita, Hirokazu*; Suzuki, Tomoya*; Motokawa, Ryuhei
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 81(4), p.157 - 167, 2017/04
Times Cited Count:16 Percentile:55.57(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)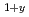 (Fe
(Fe Mn
Mn )
) (
(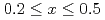 ,
, 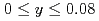 )
)Sakaki, Koji*; Kim, H.*; Machida, Akihiko; Watanuki, Tetsu; Nakamura, Yumiko*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 79(3), p.112 - 117, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:16.36(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)no abstracts in English
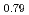 Ti
Ti Zr
Zr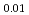
Kim, H.*; Sakaki, Koji*; Asano, Kota*; Ikeda, Kazutaka*; Otomo, Toshiya*; Machida, Akihiko; Watanuki, Tetsu; Nakamura, Yumiko*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 79(3), p.131 - 136, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)no abstracts in English
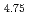 Sn
Sn by time resolved X-ray diffraction
by time resolved X-ray diffractionMachida, Akihiko; Higuchi, Kensuke*; Katayama, Yoshinori; Sakaki, Koji*; Kim, H.*; Nakamura, Yumiko*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 79(3), p.124 - 130, 2015/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.95(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Structural changes on hydrogen absorption process of hydrogen absorbing alloy LaNi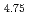 Sn
Sn have been investigated by time-resolved X-ray diffraction measurements using synchrotron radiation source. We have found the transient intermediate phase between the solid solution and hydride phases of LaNi
have been investigated by time-resolved X-ray diffraction measurements using synchrotron radiation source. We have found the transient intermediate phase between the solid solution and hydride phases of LaNi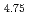 Sn
Sn under non-equilibrium hydrogen pressure condition at room temperature. LaNi
under non-equilibrium hydrogen pressure condition at room temperature. LaNi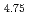 Sn
Sn has transformed into the hydride through three phase co-existing state. The hydrogen content of the intermediate phase estimated from the unit cell volume is independent of the induced hydrogen gas pressure. The variation of lattice constants indicate that the hydrogen atoms are located at the La
has transformed into the hydride through three phase co-existing state. The hydrogen content of the intermediate phase estimated from the unit cell volume is independent of the induced hydrogen gas pressure. The variation of lattice constants indicate that the hydrogen atoms are located at the La Ni
Ni (Ni,Sn)
(Ni,Sn) octahedron and La
octahedron and La (Ni,Sn)
(Ni,Sn) tetrahedron in the intermediate phase.
tetrahedron in the intermediate phase.
 O addition on lithium target for BNCT
O addition on lithium target for BNCTIshiyama, Shintaro; Baba, Yuji; Fujii, Ryo*; Nakamura, Masaru*; Imahori, Yoshio*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 78(8), p.317 - 321, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Low temperature synthesis of lithium-nitride compound was conducted on the lithium target for BNCT by N /H
/H O mixing gas squirt in the ultra high vacuum chamber, and the following results were derived; (1) Lithium-nitride compound was synthesized on the lithium target under 101.3 Pa N
O mixing gas squirt in the ultra high vacuum chamber, and the following results were derived; (1) Lithium-nitride compound was synthesized on the lithium target under 101.3 Pa N gas squirt at room temperature and in the ultra high vacuum chamber under the pressure of 1
gas squirt at room temperature and in the ultra high vacuum chamber under the pressure of 1 10
10 Pa. (2) Remarkable contamination by O and C was observed on the lithium-nitride compound synthesized under the squirt pressure of 13.3-80 Pa/1.33-4.7 Pa N
Pa. (2) Remarkable contamination by O and C was observed on the lithium-nitride compound synthesized under the squirt pressure of 13.3-80 Pa/1.33-4.7 Pa N /H
/H O mixing gas. (3) No contamination and synthesis of Li-N compound was observed under the squirt pressure of 0.013-0.027 Pa/0-0.005 Pa N
O mixing gas. (3) No contamination and synthesis of Li-N compound was observed under the squirt pressure of 0.013-0.027 Pa/0-0.005 Pa N /H
/H O mixing gas. (4) Contamination by O and C was enhanced with excessive addition of H
O mixing gas. (4) Contamination by O and C was enhanced with excessive addition of H O at the pressure of over 1.33 Pa.
O at the pressure of over 1.33 Pa.
 N synthesized on lithium target for boron neutron capture therapy
N synthesized on lithium target for boron neutron capture therapyIshiyama, Shintaro; Baba, Yuji; Fujii, Ryo*; Nakamura, Masaru*; Imahori, Yoshio*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 78(8), p.322 - 325, 2014/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)To remove high level of contaminants by O and C from Li N surface for boron neutron capture therapy target, high temperature thermal desorption was conducted up to 1123 K in ultra high vacuum and the following results were derived; (1) During thermal desorption up to 1023 K, typical three peaks of vacuum pressure disturbance due to vaporization of contaminants were observed in vacuum pressure-temperature curve. (2) Over-layered contaminants with high melting temperature below 1023 K on Li
N surface for boron neutron capture therapy target, high temperature thermal desorption was conducted up to 1123 K in ultra high vacuum and the following results were derived; (1) During thermal desorption up to 1023 K, typical three peaks of vacuum pressure disturbance due to vaporization of contaminants were observed in vacuum pressure-temperature curve. (2) Over-layered contaminants with high melting temperature below 1023 K on Li N surface is completely removed by high temperature thermal desorption up to 1123 K in ultra high vacuum. (3) From these desorption results, it is suggested that these contaminants corresponding to these vaporization peaks are H
N surface is completely removed by high temperature thermal desorption up to 1123 K in ultra high vacuum. (3) From these desorption results, it is suggested that these contaminants corresponding to these vaporization peaks are H O and Li compounds with high melting temperature below 1023 K, of which LiOH and Li
O and Li compounds with high melting temperature below 1023 K, of which LiOH and Li CO
CO were synthesized by decomposition process of Li
were synthesized by decomposition process of Li N with residual H
N with residual H O and CO
O and CO in low temperature.
in low temperature.
 N thin layer on lithium target surface for BNCT in N
N thin layer on lithium target surface for BNCT in N gaseous conditions
gaseous conditionsIshiyama, Shintaro; Baba, Yuji; Fujii, Ryo*; Nakamura, Masaru*; Imahori, Yoshio*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 78(4), p.137 - 141, 2014/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)To prevent vaporization damage of BNCT (Boron Neutron Capture Therapy) lithium target during operation, direct synthesis of Li N thin layer on lithium target surface was demonstrated in 0.1 MPa N
N thin layer on lithium target surface was demonstrated in 0.1 MPa N gas at temperature below 548 K and the following conclusions were derived; (1) Synthesis of Li
gas at temperature below 548 K and the following conclusions were derived; (1) Synthesis of Li N thin layer on lithium surface was confirmed after nitridation at 276
N thin layer on lithium surface was confirmed after nitridation at 276 548 K with surface contamination by oxygen and carbon. (2) Rapid nitridation over 1-5wt.%/min was observed above Li melting temperature, whereas slow reaction under 0.02-0.5 wt.%/min below melting temperature. (3) During nitridation, removal of oxygen contamination on Li
548 K with surface contamination by oxygen and carbon. (2) Rapid nitridation over 1-5wt.%/min was observed above Li melting temperature, whereas slow reaction under 0.02-0.5 wt.%/min below melting temperature. (3) During nitridation, removal of oxygen contamination on Li N thin layer is taken place by nitrogen below Li melting temperature.
N thin layer is taken place by nitrogen below Li melting temperature.
Ioka, Ikuo; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi*; Takizawa, Masayuki*; Ito, Takeshi*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 78(1), p.16 - 22, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)A multi-axis stress field is indispensable to quick and quantitative evaluation of stress corrosion cracking for constructional materials and weld joints of existing industrial plants. The applicability of multi-axis residual stress field into SCC tests was evaluated. The hard sphere ball was stuffed into small flat-plate of type 304SS. Numerical analysis was conducted in order to compare with the experimental results. The numerical analysis was comparatively in agreement with the experimental results. Parameters of the test were selected by numerical analysis to optimize the residual stress of specimen. SCC test in MgCl was performed using the specimen with optical residual stress condition. It is confirmed that the multi-axis residual stress field was useful in quick and quantitative SCC test by comparing the initiation of cracks with the distribution of residual stress obtained by numerical analysis.
was performed using the specimen with optical residual stress condition. It is confirmed that the multi-axis residual stress field was useful in quick and quantitative SCC test by comparing the initiation of cracks with the distribution of residual stress obtained by numerical analysis.
Tsuru, Tomohito; Aoyagi, Yoshiteru*; Kaji, Yoshiyuki; Shimokawa, Tomotsugu*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 78(1), p.45 - 51, 2014/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:5.95(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Huge-scale atomistic simulations of shear deformation tests to the aluminum polycrystalline thin film containing the Frank-Read source are performed to elucidate the relationship between the inter- and intragranular plastic deformation processes and the mechanical properties of ultrafine-grained metals. While the first plastic deformation occurs by the dislocation bow-out motion within the grain region for both models, the subsequent plastic deformation is strongly influenced by the resistance of the slip transfer by dislocation transmission through grain boundaries. The influence of the competition between the intragranular dislocation nucleation and intergranular slip transfer on the material strength is considered.
 on dehydrogenation of magnesium borohydride Mg(BH
on dehydrogenation of magnesium borohydride Mg(BH )
)
Li, H.-W.*; Matsumura, Daiju; Nishihata, Yasuo; Akiba, Etsuo*; Orimo, Shinichi*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 77(12), p.627 - 630, 2013/12
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:26.04(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)no abstracts in English
 lithium deposition and ion implantation
lithium deposition and ion implantationIshiyama, Shintaro; Baba, Yuji; Fujii, Ryo*; Nakamura, Masaru*; Imahori, Yoshio*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 77(11), p.509 - 513, 2013/11
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:9.97(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)To testify thermal stability of the BNCT neutron target synthesized by  lithium deposition and ion implantation, laser heating test of the Li
lithium deposition and ion implantation, laser heating test of the Li N/Li/Cu tri-layered target was conducted in high vacuum chamber of 10
N/Li/Cu tri-layered target was conducted in high vacuum chamber of 10 Pa and thermal stability of the tri-layered target was characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Following conclusions were derived; (1) The Li
Pa and thermal stability of the tri-layered target was characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Following conclusions were derived; (1) The Li N/Li/Cu tri- layered target with very low oxide and carbon contamination was synthesized by
N/Li/Cu tri- layered target with very low oxide and carbon contamination was synthesized by  lithium deposition and ion implantation techniques without H
lithium deposition and ion implantation techniques without H O and O
O and O additions (2) The starting temperature of evaporation of the Li
additions (2) The starting temperature of evaporation of the Li N/Li/Cu tri-layered target increased by 120 K compared to that of the Li/Cu target and (3) frequent repair synthesis of the damaged Li
N/Li/Cu tri-layered target increased by 120 K compared to that of the Li/Cu target and (3) frequent repair synthesis of the damaged Li N/Li/Cu tri-layered target caused by evaporation is possible.
N/Li/Cu tri-layered target caused by evaporation is possible.
Takeda, Masayasu; Suzuki, Junichi*; Akiya, Takahiro*; Kato, Hiroaki*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 76(3), p.165 - 176, 2012/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:79.02(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Saito, Hiroyuki; Machida, Akihiko; Katayama, Yoshinori; Aoki, Katsutoshi; Akiba, Etsuo*
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 76(2), p.139 - 143, 2012/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.06(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Ando, Masami; Wakai, Eiichi; Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Kawasaki, Yasushi
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 72(10), p.785 - 788, 2008/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:12.65(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)no abstracts in English
 3(111) grain boundary
3(111) grain boundaryYamaguchi, Masatake
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 72(9), p.657 - 666, 2008/09
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:71.40(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)The microscopic mechanism of the grain boundary embrittlement in metals by solute segregation has been not well understood for many years. From first-principles calculations, we show here that the calculated cohesive energy (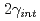 ) of bcc iron
) of bcc iron  3(111) symmetrical tilt grain boundary is reduced by the segregation of sulfur (S) or phosphorous (P), while it is increased by the segregation of boron (B) or carbon (C). The rate of the decrease/increase in the
3(111) symmetrical tilt grain boundary is reduced by the segregation of sulfur (S) or phosphorous (P), while it is increased by the segregation of boron (B) or carbon (C). The rate of the decrease/increase in the 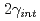 was excellently proportional to the experimental ductile-to-brittle transition temparature (DBTT) shift with increasing segregation; this demonstrates that the grain boundary embrittlement is governed by the change in the 2
was excellently proportional to the experimental ductile-to-brittle transition temparature (DBTT) shift with increasing segregation; this demonstrates that the grain boundary embrittlement is governed by the change in the 2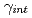 .
.
Kurata, Yuji; Futakawa, Masatoshi
Nihon Kinzoku Gakkai-Shi, 72(6), p.470 - 476, 2008/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.13(Metallurgy & Metallurgical Engineering)Corrosion tests of CrN-coated steels for nuclear reactors were conducted in liquid lead-bismuth (Pb-Bi) at 450 C and 550
C and 550 C for 3000 h to investigate the applicability of CrN coating to a liquid Pb-Bi environment. CrN coatings on F82H (Fe-8Cr-2W-0.3V-0.04Ta-0.1C) and 316SS exhibited good compatibility in liquid Pb-Bi during corrosion test at 450
C for 3000 h to investigate the applicability of CrN coating to a liquid Pb-Bi environment. CrN coatings on F82H (Fe-8Cr-2W-0.3V-0.04Ta-0.1C) and 316SS exhibited good compatibility in liquid Pb-Bi during corrosion test at 450 C. The CrN coating layer suffered heavy damage such as cracking and spalling, and showed no effectiveness as a protective layer in corrosion test at 550
C. The CrN coating layer suffered heavy damage such as cracking and spalling, and showed no effectiveness as a protective layer in corrosion test at 550 C. Nickel and chromium in 316SS dissolved into Pb-Bi through the damaged coating layer at 550
C. Nickel and chromium in 316SS dissolved into Pb-Bi through the damaged coating layer at 550 C. The cracking and spalling were not found after heating CrN-coated steels in Ar gas at 550
C. The cracking and spalling were not found after heating CrN-coated steels in Ar gas at 550 C. It is considered that stresses caused by the difference of thermal expansion coefficients between CrN and steels led to cracking and spalling of the CrN coating through corrosion attack by liquid Pb-Bi at 550
C. It is considered that stresses caused by the difference of thermal expansion coefficients between CrN and steels led to cracking and spalling of the CrN coating through corrosion attack by liquid Pb-Bi at 550 C.
C.