Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Morishita, Yuki; Miyamura, Hiroko; Sato, Yuki; Matsubara, Jun*; Sumali, B.*; Mitsukura, Yasue*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, p.170368_1 - 170368_16, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Decommissioning nuclear reactor sites presents challenges due to the presence of various radionuclides, including alpha emitters (e.g., Pu, Am, Cm) and beta emitters (e.g.,  Cs,
Cs,  Sr-
Sr- Y), which pose significant internal exposure risks to workers. Traditional measurement methods require multiple instruments and are time-consuming, particularly in high gamma-ray environments. To address these issues, we developed a remote alpha and beta discrimination measurement system that integrates a stilbene scintillator detector with a silicon photomultiplier, enabling simultaneous detection of both alpha and beta particles. This study further incorporates machine learning techniques, specifically Support Vector Machines (SVM), for automatic discrimination, eliminating the need for user-defined thresholds and ensuring consistent operational conditions. The system was tested with known radiation sources, demonstrating over 96% classification accuracy for alpha and beta particles. Measurements conducted in motion effectively identified contamination sources, confirming the system's capability for real-time analysis. This innovative approach enhances radiation safety and efficiency in nuclear decommissioning operations, making it particularly beneficial in environments where human access is limited.
Y), which pose significant internal exposure risks to workers. Traditional measurement methods require multiple instruments and are time-consuming, particularly in high gamma-ray environments. To address these issues, we developed a remote alpha and beta discrimination measurement system that integrates a stilbene scintillator detector with a silicon photomultiplier, enabling simultaneous detection of both alpha and beta particles. This study further incorporates machine learning techniques, specifically Support Vector Machines (SVM), for automatic discrimination, eliminating the need for user-defined thresholds and ensuring consistent operational conditions. The system was tested with known radiation sources, demonstrating over 96% classification accuracy for alpha and beta particles. Measurements conducted in motion effectively identified contamination sources, confirming the system's capability for real-time analysis. This innovative approach enhances radiation safety and efficiency in nuclear decommissioning operations, making it particularly beneficial in environments where human access is limited.
 experiment using a
experiment using a  Cf calibration source
Cf calibration sourceLee, D. H.*; Dodo, Taku; Haga, Katsuhiro; Harada, Masahide; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Kasugai, Yoshimi; Kinoshita, Hidetaka; Masuda, Shiho; Meigo, Shinichiro; Sakai, Kenji; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1072, p.170216_1 - 170216_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:98.29(Instruments & Instrumentation)Sasaki, Miyuki; Abe, Yuki*; Sanada, Yukihisa; Torii, Tatsuo*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1072, p.170207_1 - 170207_12, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)We have developed an omnidirectional radiation imager with fractal geometry named the FRIE system. This paper presents the development and evaluation of the FRIE system, designed to accurately estimate radioactivity distribution within decommissioning environments, such as the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The FRIE system is a unit of tetrahedral radiation sensors; 16 sensors are arranged in a Sierpinski tetrahedron shape, and the space between the sensors is filled with tungsten-based alloy for radiation shielding. This study assessed the performance of the FRIE system in estimating radiation distribution through simulations and actual measurement tests. From the results of the simulations and experimental data, it was confirmed that by maintaining a measurement density of at least 2 points/m , limiting the positional error to within
, limiting the positional error to within  10 cm, and the angular error to within
10 cm, and the angular error to within  10 degrees, it is possible to estimate the source location with an angular resolution of approximately 30 degrees. Future improvements in the arrangement of the FRIE system's crystals and shielding should enhance the performance metrics. This research signifies a pioneering implementation of fractal-based radiation imaging technology, offering a new direction in radiation measurement.
10 degrees, it is possible to estimate the source location with an angular resolution of approximately 30 degrees. Future improvements in the arrangement of the FRIE system's crystals and shielding should enhance the performance metrics. This research signifies a pioneering implementation of fractal-based radiation imaging technology, offering a new direction in radiation measurement.
Guembou Shouop, C. J.; Tsuchiya, Harufumi
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1072, p.170189_1 - 170189_14, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:52.60(Instruments & Instrumentation) Sr/
Sr/ Y inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Unit 3 reactor building using a liquid light guide Cherenkov counter
Y inside the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Unit 3 reactor building using a liquid light guide Cherenkov counterTerasaka, Yuta; Sato, Yuki; Furuta, Yoshihiro*; Kubo, Shin*; Ichiba, Yuta*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1070, Part 2 , p.170021_1 - 170021_9, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Jinno, Satoshi; Matsubara, Akihiro*; Fujita, Natsuko; Kimura, Kenji
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 557, p.165545_1 - 165545_4, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)This study introduces the development of a downsized Accelerator Mass Spectrometry (AMS) system aiming to enhance accessibility and cost-effectiveness in radiocarbon analysis. The "crystal surface stripper method" is introduced as a solution to challenges in AMS downsizing, demonstrating effective ion detection with a smaller angular spread compared to conventional gas stripper methods. The experimental results provide insights into charge conversion capabilities, scattering angle broadening, and energy loss associated with surface scattering.
Iwamoto, Yosuke; Matsuda, Hiroki*; Meigo, Shinichiro; Yonehara, Katsuya*; Pellemoine, F.*; Liu, Z.*; Lynch, K.*; Yoshida, Makoto*; Yabuuchi, Atsushi*; Yoshiie, Toshimasa*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 557, p.165543_1 - 165543_8, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The number of displacements per atom is widely used as an indicator of irradiation damage to materials in proton accelerator facilities. Experiments have been carried out on protons below 3 GeV to verify the dpa of metallic materials. However, the dpa for high-energy protons above 3 GeV has not been measured. In order to validate the displacement cross sections of metals in the high-energy region, the electrical resistivity changes of aluminium, copper and tungsten wires at a temperature of 8 K were measured using protons with energy of 120 GeV. The results show that the conventional irradiation damage model of PHITS overestimates the experimental data. On the other hand, the calculation results using the athermal recombination correction model were in agreement with the experimental data.
Sato, Tatsuhiko; Hashimoto, Shintaro; M rquez Dami
rquez Dami n, J. I.*; Niita, Koji*
n, J. I.*; Niita, Koji*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 557, p.165535_1 - 165535_8, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Teshigawara, Makoto; Lee, Y.*; Tatsumoto, Hideki*; Hartl, M.*; Aso, Tomokazu; Iverson, E. B.*; Ariyoshi, Gen; Ikeda, Yujiro*; Hasegawa, Takumi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 557, p.165534_1 - 165534_10, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)At Japanese Spallation Neutron Source in J-PARC, the para-hydrogen fraction was measured by using Raman spectroscopy in-situ for an integrated beam power of 9.4 MW h at 1 MW operation, to evaluate the functionality of the ferric oxyhydroxide catalyst. This result showed that full functionality of the catalyst was retained up to the 1 MW operation. We attempted to study the effect of neutron scattering driven para to ortho-hydrogen back-conversion rate in the absence of the catalyst effect with a bypass line without catalyst. The measured increase of ortho-hydrogen fraction was 0.44% for an integrated beam power of 2.4 MW
h at 1 MW operation, to evaluate the functionality of the ferric oxyhydroxide catalyst. This result showed that full functionality of the catalyst was retained up to the 1 MW operation. We attempted to study the effect of neutron scattering driven para to ortho-hydrogen back-conversion rate in the absence of the catalyst effect with a bypass line without catalyst. The measured increase of ortho-hydrogen fraction was 0.44% for an integrated beam power of 2.4 MW h at 500 kW operation, however, which was considered to be due to not only to neutron collisions in cold moderators but also to the high ortho-hydrogen fraction of initially static liquid hydrogen in the bypass line and passive exudation of quasi-static hydrogen in the catalyst vessel to the main loop.
h at 500 kW operation, however, which was considered to be due to not only to neutron collisions in cold moderators but also to the high ortho-hydrogen fraction of initially static liquid hydrogen in the bypass line and passive exudation of quasi-static hydrogen in the catalyst vessel to the main loop.
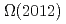 from QCD sum rules
from QCD sum rulesSu, N.*; Chen, H.-X.*; Gubler, P.; Hosaka, Atsushi
Nuclear and Particle Physics Proceedings, 347, p.2 - 5, 2024/12
Minowa, Kazuki*; Watanabe, So; Nakase, Masahiko*; Takahatake, Yoko; Miyazaki, Yasunori; Ban, Yasutoshi; Matsuura, Haruaki*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 556, p.165496_1 - 165496_6, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)In this study, X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) spectral analysis and column experiments were used to verify the selectivity of rare earth (RE) ions by alkyl diamide amine (ADAAM) adsorbent. In addition, the interactions between the N atoms of ADAAM and RE ions were evaluated to determine whether any of the RE ions are a valid simulant for developing a mutual separation process for minor actinides (MAs) in highly radioactive liquid waste. It was confirmed that La and Ce interacted with the amine N atom of ADAAM and they showed a peak shift of the N-K edge XANES spectrum; this finding suggested that a soft interaction is an essential factor influencing ion selectivity. Therefore, the selection factor of RE ions by ADAAM adsorbent was similar to that of MAs. It was concluded that RE ions are reasonable species to simulate MAs.
Oguri, Kaori; Hagura, Naoto*; Yamaguchi, Akiko; Okumura, Masahiko; Matsuura, Haruaki*; Tsunashima, Yasumichi; Aoki, Katsumi; Arai, Yoichi; Watanabe, So
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 556, p.165516_1 - 165516_8, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ningyo-toge is the uranium mine that has been operated in Japan. Various radioactive elements such as Uranium (U), and Radium (Ra) are still present in the mine ground water with very small amount, and behavior of those elements is not fully understood. In this study, we investigated the composition of metal oxides and clay minerals in a soil of slag deposit at the mine, and systematics of adsorption structure of various ions were examined. Identifying the composition and chemical forms of minerals present in the soil of slag can provide useful information for the safety assessment and evaluation of influence on the surrounding environment.
Arai, Yoichi; Watanabe, So; Watanabe, Masayuki; Arai, Tsuyoshi*; Katsuki, Kenta*; Agou, Tomohiro*; Fujikawa, Hisaharu*; Takeda, Keisuke*; Fukumoto, Hiroki*; Hoshina, Hiroyuki*; et al.
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 554, p.165448_1 - 165448_10, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)
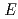 -
- 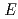 telescope ERDA
telescope ERDAHarayama, Isao; Hirose, Yasushi*; Sekiba, Daiichiro*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 554, p.165435_1 - 165435_6, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)
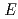 -
-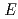 telescope elastic recoil detection analysis (ERDA) is a helpful ion beam analysis (IBA) technique for the absolute quantification of multiple light elements in thin films. We have developed a compact
telescope elastic recoil detection analysis (ERDA) is a helpful ion beam analysis (IBA) technique for the absolute quantification of multiple light elements in thin films. We have developed a compact 
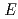 -
-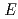 telescope ERDA system to estimate a composition ratio of oxygen and nitrogen in metal oxynitride thin films. Our
telescope ERDA system to estimate a composition ratio of oxygen and nitrogen in metal oxynitride thin films. Our 
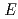 -
-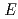 telescope ERDA system employs a gas ionization chamber (GIC), which consisted of a U-shaped cathode, while a planar shaped cathode is widely utilized for GICs. The shape of U-shaped cathode is useful to downsize the GIC. The difference of performance between the U-shaped and planar shaped cathodes, however, has not been studied well, yet. In this study, we quantitatively evaluated the influence using the U-shaped cathode on
telescope ERDA system employs a gas ionization chamber (GIC), which consisted of a U-shaped cathode, while a planar shaped cathode is widely utilized for GICs. The shape of U-shaped cathode is useful to downsize the GIC. The difference of performance between the U-shaped and planar shaped cathodes, however, has not been studied well, yet. In this study, we quantitatively evaluated the influence using the U-shaped cathode on 
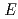 -
-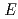 telescope ERDA. In order to compare the performance of the U-shaped and planar shaped cathode, we measured SrTiO
telescope ERDA. In order to compare the performance of the U-shaped and planar shaped cathode, we measured SrTiO bulk samples as a standard with them. There is no significant difference between the two cathodes from the viewpoint of O recoil yields. These results show that the U-shaped cathode can also be used safely for
bulk samples as a standard with them. There is no significant difference between the two cathodes from the viewpoint of O recoil yields. These results show that the U-shaped cathode can also be used safely for 
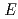 -
-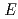 telescope ERDA, and that GICs have a flexibility in the electrode shape, which is useful to make GICs more compact.
telescope ERDA, and that GICs have a flexibility in the electrode shape, which is useful to make GICs more compact.
Nakahara, Masaumi; Watanabe, So; Ishii, Yasuyuki*; Yamagata, Ryohei*; Yuri, Yosuke*; Yuyama, Takahiro*; Ishizaka, Tomohisa*; Koka, Masashi*; Yamada, Naoto*; Hagura, Naoto*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 554, p.165449_1 - 165449_5, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Ion beam induced luminescence analysis of lanthanide complexes in the organic solvents for minor actinides recovery process was carried out to investigate the structures of complexes. In this study, hydrogen ion beam obtained from the single-ended accelerator and argon ion beam obtained from the azimuthally varying field cyclotron were used in Takasaki Ion Accelerators for Advanced Radiation Application in National Institutes for Quantum Science and Technology. In the experiments, ion beam induced luminescence spectra of lanthanide complexes in the organic solvents were measured, and the relationship between the obtained spectra and the structures of complexes was studied.
Morishita, Yuki; Tomioka, Akifumi; Fujisawa, Makoto; Izaki, Kenji
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1065, p.169527_1 - 169527_5, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)It is important to differentiate between natural and artificial radioactive materials such as plutonium in nuclear facilities. In this study, a scintillator-based alpha-particle detector was developed using YAP:Ce scintillator and Multi-Anode PhotoMultiplier Tube. The detector was used to measure various naturally occurring radioactive materials (NORM) samples including radon progeny, lead plate, lantern mantle, and radium ceramic ball. The measurement results were compared with Monte Carlo simulation calculations and were found to be in agreement. The energy resolution of the detector is 8.6%FWHM. In the measurement results of radon progeny, peaks of 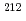 Bi (6.1 MeV),
Bi (6.1 MeV),  Po (7.7 MeV), and
Po (7.7 MeV), and 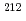 Po (8.8 MeV) can be observed. The lead plate contains
Po (8.8 MeV) can be observed. The lead plate contains  Po and emits 5.3 MeV alpha particle. The simulation with the same energy was able to reproduce the actual measurement. The results showed the energy and distribution of the alpha particles emitted by the NORM samples. The study successfully demonstrated the capability of the developed alpha-particle detector in identifying NORM.
Po and emits 5.3 MeV alpha particle. The simulation with the same energy was able to reproduce the actual measurement. The results showed the energy and distribution of the alpha particles emitted by the NORM samples. The study successfully demonstrated the capability of the developed alpha-particle detector in identifying NORM.
 Li-glass detector to gamma rays by a coincidence method
Li-glass detector to gamma rays by a coincidence methodIto, Fumiaki*; Lee, J.; Hironaka, Kota; Takahashi, Tone; Suzuki, Satoshi*; Mochimaru, Takanori*; Hori, Junichi*; Terada, Kazushi*; Koizumi, Mitsuo
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1064, p.169465_1 - 169465_9, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)Balibrea-Correa, J.*; Kimura, Atsushi; 133of others*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1064, p.169385_1 - 169385_13, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:86.15(Instruments & Instrumentation)Hattori, Takanori; Suzuki, Koji*; Miyo, Tatsuya*; Ito, Takayoshi*; Machida, Shinichi*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1064, p.169448_1 - 169448_9, 2024/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Instruments & Instrumentation)The authors regret that the abstract and summary explain that the cup diameter of a standard double-toroidal anvils is 1.5 mm. This is incorrect; the standard diameter is 4.0 mm. The authors would like to apologise for any inconvenience caused.
Sato, Yuki; Kakuto, Takeshi*; Tanaka, Takayuki*; Shimano, Hiroyuki*; Morohashi, Yuko; Hatakeyama, Tomoyoshi*; Nakajima, Junsaku; Ishiyama, Masahiro
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1063, p.169300_1 - 169300_7, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:86.15(Instruments & Instrumentation)