Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Machida, Akihiko*; Saito, Hiroyuki*; Aoki, Katsutoshi*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Machida, Shinichi*; Sato, Toyoto*; Orimo, Shinichi*
Physical Review B, 111(22), p.224413_1 - 224413_6, 2025/06
The crystal and magnetic structures of antiferromagnetic Mn deuterides formed by hydrogenating Mn metal at high temperature and high pressure, fcc  -MnDx and hcp
-MnDx and hcp  -MnDx, were investigated by in-situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms partially occupied the octahedral interstitial positions of the fcc and hcp metal lattices. The site occupancies increased rapidly with decreasing temperature from
-MnDx, were investigated by in-situ neutron powder diffraction. Deuterium atoms partially occupied the octahedral interstitial positions of the fcc and hcp metal lattices. The site occupancies increased rapidly with decreasing temperature from  700 to
700 to  450 K and remained down to 300 K. N
450 K and remained down to 300 K. N el temperature of 543(10) K was determined for
el temperature of 543(10) K was determined for  -MnD
-MnD . For
. For  -MnD
-MnD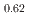 , saturation magnetic moment and N
, saturation magnetic moment and N el temperature were determined to be 0.82(1)
el temperature were determined to be 0.82(1) 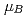 and 347(3) K, respectively. The N
and 347(3) K, respectively. The N el temperatures determined for
el temperatures determined for  -MnD
-MnD and
and  -MnD
-MnD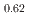 are consistent with those predicted by the respective Slater-Pauling curves proposed in previous studies. The updated N
are consistent with those predicted by the respective Slater-Pauling curves proposed in previous studies. The updated N el temperatures provide insights into the development of more accurate Slater-Pauling curves based on electronic band structure calculations.
el temperatures provide insights into the development of more accurate Slater-Pauling curves based on electronic band structure calculations.
 Co
Co )Sn studied by
)Sn studied by  SR
SRCai, Y.*; Yoon, S.*; Sheng, Q.*; Zhao, G.*; Seewald, E. F.*; Ghosh, S.*; Ingham, J.*; Pasupathy, A. N.*; Queiroz, R.*; Lei, H.*; et al.
Physical Review B, 111(21), p.214412_1 - 214412_17, 2025/06
Matsushita, Taiki*; Ozawa, Akihiro*; Araki, Yasufumi; Fujimoto, Junji*; Sato, Masatoshi*
Physical Review B, 111(24), p.245131_1 - 245131_11, 2025/06
 phases in undoped and Ca-modified sodium niobates
phases in undoped and Ca-modified sodium niobatesAso, Seiyu*; Matsuo, Hiroki*; Yoneda, Yasuhiro; Morikawa, Daisuke*; Tsuda, Kenji*; Oyama, Kenji*; Ishigaki, Toru*; Noguchi, Yuji*
Physical Review B, 111(17), p.174114_1 - 174114_12, 2025/05
We investigate the crystal structures, phase transitions, and phase stability of undoped and Ca-modified NaNbO through a combined analysis of high-resolution synchrotron radiation X-ray and neutron diffraction, convergent-beam electron diffraction, and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. It is demonstrated that the antiferroelectric (AFE)-
through a combined analysis of high-resolution synchrotron radiation X-ray and neutron diffraction, convergent-beam electron diffraction, and density functional theory (DFT) calculations. It is demonstrated that the antiferroelectric (AFE)- phase is stabilized over a wide temperature range of 200 to 800 K by Ca modification, and that the NaNbO
phase is stabilized over a wide temperature range of 200 to 800 K by Ca modification, and that the NaNbO is stabilized by temperature-driven isostatic pressure accompanied by lattice expansion, whereas the Ca-modified NaNbO
is stabilized by temperature-driven isostatic pressure accompanied by lattice expansion, whereas the Ca-modified NaNbO is induced by composition-induced chemical pressure along with lattice shrinkage.
is induced by composition-induced chemical pressure along with lattice shrinkage.
 under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation study
under hydrostatic pressure; A Combined neutron, X-ray, Raman, and first-principles calculation studyEfthimiopoulos, I.*; Klotz, S.*; Kunc, K.*; Baptiste, B.*; Chauvigne, P.*; Hattori, Takanori
Physical Review B, 111(13), p.134103_1 - 134103_13, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)We present a comprehensive study of the high pressure behaviour of ReO using X-ray and neutron diffraction, Raman scattering and first-principles calculations to 15 GPa. We show that the ambient pressure
using X-ray and neutron diffraction, Raman scattering and first-principles calculations to 15 GPa. We show that the ambient pressure 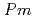
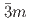 structure converts at 0.7 GPa in a continuous phase transition directly to a cubic phase with space group
structure converts at 0.7 GPa in a continuous phase transition directly to a cubic phase with space group 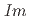
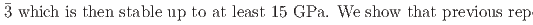 and rhombohedral
and rhombohedral 
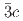 structures in this pressure range are an artifact due to an alteration of the sample by high-flux synchrotron X-ray radiation. The structural pressure dependence of the
structures in this pressure range are an artifact due to an alteration of the sample by high-flux synchrotron X-ray radiation. The structural pressure dependence of the 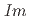
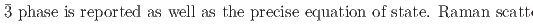 O samples are presented. The data shed light onto the unusual transition and densification mechanism due to progressive tilting of essentially rigid ReO
O samples are presented. The data shed light onto the unusual transition and densification mechanism due to progressive tilting of essentially rigid ReO octahedra.
octahedra.
Tamatsukuri, Hiromu; Uchihara, Takeru*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*; Ishii, Yuta*; Nakao, Hironori*; Takehana, Kanji*; Imanaka, Yasutaka*
Physical Review B, 111(13), p.134403_1 - 134403_9, 2025/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Sb
Sb with a honeycomb network
with a honeycomb networkAdachi, Tadashi*; Ogawa, Taiki*; Komiyama, Yota*; Sumura, Takuya*; Saito-Tsuboi, Yuki*; Takeuchi, Takaaki*; Mano, Kohei*; Manabe, Kaoru*; Kawabata, Koki*; Imazu, Tsuyoshi*; et al.
Physical Review B, 111(10), p.L100508_1 - L100508_6, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) with geometrically frustrated orthogonal antiferromagnetic dimer
with geometrically frustrated orthogonal antiferromagnetic dimerMetoki, Naoto; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Hagihara, Masato; Watanuki, Ryuta*; Kawamura, Seiko; Kofu, Maiko*; Nakajima, Kenji; Matsuda, Masaaki*
Physical Review B, 111(10), p.104424_1 - 104424_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Inelastic neutron scattering experiments were carried out to understand the unusual successive order in NdB with the frustrated Shatry-Sutherland (SS) lattice. The pseudo-quartet with
with the frustrated Shatry-Sutherland (SS) lattice. The pseudo-quartet with 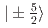 and
and 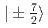 splits into four levels in the magnetically ordered states. The spectra can be explained with the on-site magnetic interaction
splits into four levels in the magnetically ordered states. The spectra can be explained with the on-site magnetic interaction 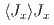 , the coupling of
, the coupling of 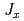 with quadrupole
with quadrupole 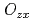 , and the uniaxial crystalline electric field. The
, and the uniaxial crystalline electric field. The  -electron states reproduce the temperature dependences of the in-plane moment
-electron states reproduce the temperature dependences of the in-plane moment 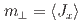 which is the primary order parameter, and a weakly induced
which is the primary order parameter, and a weakly induced 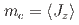 as the secondary order parameter. The magnetic-quadrupole coupling emerges and play essential role under the geometrical frustration, where the Heisenberg interactions are cancelled out.
as the secondary order parameter. The magnetic-quadrupole coupling emerges and play essential role under the geometrical frustration, where the Heisenberg interactions are cancelled out.
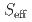 =
=  antiferromagnetic tetramer compound Yb
antiferromagnetic tetramer compound Yb SiO
SiO
Hase, Masashi*; Kaneko, Koji; Tabata, Chihiro; Yamauchi, Hiroki; Tsujii, Naohito*; D nni, A.*
nni, A.*
Physical Review B, 111(9), p.094403_1 - 094403_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) with
with  = 2.1 K revealed by
= 2.1 K revealed by  Te NMR
Te NMRMatsumura, Hiroki*; Tokunaga, Yo; Sakai, Hironori; Kambe, Shinsaku; 13 of others*
Physical Review B, 111(9), p.094507_1 - 094507_9, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Fe
Fe O
O
Ba, Y.*; Yamamoto, Kei; 6 of others*
Physical Review B, 111(10), p.104401_1 - 104401_15, 2025/03
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Jin, H.*; Choi, E. S.*; Wu, H.-C.*; Curro, N. J.*; Nawa, Kazuhiro*; Sato, Taku*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ohara, Takashi; Klavins, P.*; Taufour, V.*
Physical Review B, 111(3), p.035103_1 - 035103_7, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Fe
Fe O
O
Mori, Michiyasu; Tomasello, B.*; Ziman, T.*
Physical Review B, 111(1), p.014407_1 - 014407_12, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Yamane, Yuta*; Araki, Yasufumi; Fukami, Shunsuke*
Physical Review B, 111(14), p.144412_1 - 144412_9, 2025/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Fujisawa, Yuita*; Krishnadas, A*; Nakamura, Tomonori*; Hsu, C.-H.*; Smith, B. R. M.*; Pardo-Almanza, M*; Hiyane, Hoshu*; Nagai, Yuki; Machida, Tadashi*; Okada, Yoshinori*
Physical Review B, 110(22), p.224511_1 - 224511_5, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Understanding the nature of vortices in type-II superconductors has been vital for deepening the physics of exotic superconductors and applying superconducting materials to future electronic devices. A recent study has shown that the LiTi O
O (111) thin film offers a unique experimental platform to unveil the nature of the vortex along the curved Josephson junction. This study successfully visualized individual Josephson vortices along the curved Josephson junctions using in-situ spectroscopic scanning tunneling microscopy on LiTi
(111) thin film offers a unique experimental platform to unveil the nature of the vortex along the curved Josephson junction. This study successfully visualized individual Josephson vortices along the curved Josephson junctions using in-situ spectroscopic scanning tunneling microscopy on LiTi O
O (111) epitaxial thin films. Notably, the local curvature of the Josephson junction was discovered to control the position of Josephson vortices. Furthermore, the numerical simulation reproduces the critical role of the curvature of the Josephson junction. This study provides guidelines to control Josephson vortices through geometrical ways, such as mechanical controlling of superconducting materials and their devices.
(111) epitaxial thin films. Notably, the local curvature of the Josephson junction was discovered to control the position of Josephson vortices. Furthermore, the numerical simulation reproduces the critical role of the curvature of the Josephson junction. This study provides guidelines to control Josephson vortices through geometrical ways, such as mechanical controlling of superconducting materials and their devices.
 SR study on the noncentrosymmetric superconductor NbGe
SR study on the noncentrosymmetric superconductor NbGe
Jiao, J. C.*; Chen, K. W.*; Hillier, A. D.*; Ito, Takashi; Higemoto, Wataru; Li, Z.*; Lv, B.*; Xu, Z.-A.*; Shu, L.*
Physical Review B, 110(21), p.214516_1 - 214516_9, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Kotegawa, Hisashi*; Nakamura, Akira*; Huyen, V. T. N.*; Arai, Yuki*; To, Hideki*; Sugawara, Hitoshi*; Hayashi, Junichi*; Takeda, Keiki*; Tabata, Chihiro; Kaneko, Koji; et al.
Physical Review B, 110(21), p.214417_1 - 214417_8, 2024/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Chi, Z.*; Shibata, Goro; Fujimori, Atsushi; 15 of others*
Physical Review B, 110, p.184401_1 - 184401_8, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Gd
Gd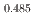 Mn
Mn O
O
Ishii, Yuta*; Sakakura, Terutoshi*; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Lustikova, J.*; Aoyama, Takuya*; Ogushi, Kenya*; Wakabayashi, Yusuke*; Kimura, Hiroyuki*; Noda, Yukio*
Physical Review B, 110(18), p.184404_1 - 184404_7, 2024/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Furuya, Shunsuke*; Matsuo, Mamoru; Kato, Takeo*
Physical Review B, 110(16), p.165129_1 - 165129_13, 2024/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)