Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 CuZn
CuZn P
P
May, A. F.*; Tabata, Chihiro; Okamoto, Satoshi*; Ortiz, B. R.*; Christianson, A. D.*; Yan, J.*; Kaneko, Koji; McGuire, M. A.*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 9(2), p.024406_1 - 024406_13, 2025/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) 3-Si phase on Al(111), studied by the multiple usages of positron diffraction and core-level photoemission spectroscopy
3-Si phase on Al(111), studied by the multiple usages of positron diffraction and core-level photoemission spectroscopySato, Yusuke*; Fukaya, Yuki; 14 of others*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 9(1), p.014002_1 - 014002_11, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English

 H
H O
OFujihara, Masayoshi; Hagihara, Masato; Koda, Akihiro*; Nakamura, Jumpei*; Matsuo, Akira*; Kindo, Koichi*; Ishikado, Motoyuki*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 9(1), p.014406_1 - 014406_9, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) MnSi
MnSi O
O
Kawamata, Masahiro*; Pang, X.*; Murakawa, Hiroshi*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Masuda, Hidetoshi*; Fujita, Masaki*; Hanasaki, Noriaki*; Onose, Yoshinori*; Nambu, Yusuke*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 9(1), p.014407_1 - 014407_6, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Yamamoto, Hajime*; Ikeda, Osamu*; Honda, Takashi*; Kimura, Kenta*; Aoyama, Takuya*; Ogushi, Kenya*; Suzuki, Akio*; Ishii, Kenji*; Matsumura, Daiju; Tsuji, Takuya; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 8(9), p.094402_1 - 094402_6, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:56.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)
Vali ka, M.*; Haidamak, T.*; Cabala, A.*; Posp
ka, M.*; Haidamak, T.*; Cabala, A.*; Posp
 il, J.*; Bastien, G.*; Sechovsk
il, J.*; Bastien, G.*; Sechovsk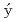 , V.*; Prokle
, V.*; Prokle ka, J.*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; et al.
ka, J.*; Yanagisawa, Tatsuya*; Opletal, P.; Sakai, Hironori; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 8(9), p.094415_1 - 094415_9, 2024/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:0.00(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Taniguchi, Koji*; Huang, P.-J.*; Sagayama, Hajime*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Oishi, Kazuki*; Kito, Shunsuke*; Nakamura, Yuiga*; Miyasaka, Hitoshi*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 8(2), p.024409_1 - 024409_10, 2024/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:56.91(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Zhang, Z.*; Gong, W.; Kawakita, Yukinobu; 9 of others*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(12), p.125402_1 - 125402_9, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.90(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Otsuki, Daiki*; Ishida, Tatsuhiro*; Tsutsumi, Naoya*; Kobayashi, Masaki*; Inagaki, Kodai*; Yoshida, Teppei*; Takeda, Yukiharu; Fujimori, Shinichi; Yasui, Akira*; Kitagawa, Saiki*; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(12), p.124601_1 - 124601_6, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.90(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Matsuzawa, Ikuya*; Fukutani, Katsuyuki; 5 of others*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(8), p.085003_1 - 085003_6, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:67.40(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Mori, Hideki*; Tsuru, Tomohito; Okumura, Masahiko; Matsunaka, Daisuke*; Shiihara, Yoshinori*; Itakura, Mitsuhiro
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(6), p.063605_1 - 063605_8, 2023/06
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:32.83(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The introduction of obstacles (e.g., precipitates) for controlling dislocation motion in molecular structures is a prevalent method for designing the mechanical strength of metals. Owing to the nanoscale size of the dislocation core ( 1 nm), atomic modeling is required to investigate the interactions between the dislocation and obstacles. However, conventional empirical potentials are not adequately accurate, in contrast to the calculations based on density functional theory (DFT). Therefore, the atomic-level details of the interactions between the dislocations and obstacles remain unclarified. To this end, this study applied an artificial neural network (ANN) framework to construct an atomic potential by leveraging the high accuracy of DFT. Using the constructed ANN potential, we investigated the dynamic interaction between the
1 nm), atomic modeling is required to investigate the interactions between the dislocation and obstacles. However, conventional empirical potentials are not adequately accurate, in contrast to the calculations based on density functional theory (DFT). Therefore, the atomic-level details of the interactions between the dislocations and obstacles remain unclarified. To this end, this study applied an artificial neural network (ANN) framework to construct an atomic potential by leveraging the high accuracy of DFT. Using the constructed ANN potential, we investigated the dynamic interaction between the 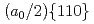 edge dislocation and obstacles in BCC iron. When the dislocation crossed the void, an ultrasmooth and symmetric half-loop was observed for the bowing-out dislocation. Except for the screw dislocation, the Peierls stress of all the dislocations predicted using the ANN was less than 100 MPa. More importantly, the results confirmed the formation of an Orowan loop in the interaction between a rigid sphere and dislocation. Furthermore, we discovered a phenomenon in which the Orowan loop disintegrated into two small loops during its interaction with the rigid sphere and dislocation.
edge dislocation and obstacles in BCC iron. When the dislocation crossed the void, an ultrasmooth and symmetric half-loop was observed for the bowing-out dislocation. Except for the screw dislocation, the Peierls stress of all the dislocations predicted using the ANN was less than 100 MPa. More importantly, the results confirmed the formation of an Orowan loop in the interaction between a rigid sphere and dislocation. Furthermore, we discovered a phenomenon in which the Orowan loop disintegrated into two small loops during its interaction with the rigid sphere and dislocation.
 Fe
Fe O
O grown on Al
grown on Al O
O ; Effects of postdeposition annealing studied by XMCD
; Effects of postdeposition annealing studied by XMCDNonaka, Yosuke*; Wakabayashi, Yuki*; Shibata, Goro; Sakamoto, Shoya*; Ikeda, Keisuke*; Chi, Z.*; Wan, Y.*; Suzuki, Masahiro*; Tanaka, Arata*; Tanaka, Masaaki*; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(4), p.044413_1 - 044413_10, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:50.30(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Sc
Sc )
) O
O determined by single-crystal neutron diffraction
determined by single-crystal neutron diffractionTanaka, Seiya*; Kiyanagi, Ryoji; Ishikawa, Yoshihisa*; Amako, Yasushi*; Iiyama, Taku*; Futamura, Ryusuke*; Maruyama, Kenichi*; Utsumi, Shigenori*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(1), p.014403_1 - 014403_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:10.57(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Terasawa, Tomoo; Matsunaga, Kazuya*; Hayashi, Naoki*; Ito, Takahiro*; Tanaka, Shinichiro*; Yasuda, Satoshi; Asaoka, Hidehito
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(1), p.014002_1 - 014002_10, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:62.75(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Au(001) surfaces exhibit a complex reconstructed structure [Hex-Au(001)] comprising a hexagonal surface and square bulk lattices, yielding a quasi-one-dimensional corrugated surface. When graphene was grown on this surface, the periodicity of the corrugated surface was predicted to change the electronic structure of graphene, forming bandgaps and new Dirac points. Furthermore, the graphene-Au interface is promising for bandgap generation and spin injection due to band hybridization. Here, we report the angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy and density functional calculation of graphene on a Hex-Au(001) surface. The crossing point of the original and replica graphene  bands showed no bandgap, suggesting that the one-dimensional potential was too small to modify the electronic structure. A bandgap of 0.2 eV was observed at the crossing point of the graphene
bands showed no bandgap, suggesting that the one-dimensional potential was too small to modify the electronic structure. A bandgap of 0.2 eV was observed at the crossing point of the graphene  and Au
and Au 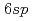 bands, indicating that the bandgap is generated using hybridization of the graphene
bands, indicating that the bandgap is generated using hybridization of the graphene  and Au
and Au 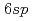 bands. We discussed the hybridization mechanism and concluded that the R30 configuration between graphene and Au and an isolated electronic structure of Au are essential for effective hybridization between graphene and Au. We anticipate that hybridization between graphene
bands. We discussed the hybridization mechanism and concluded that the R30 configuration between graphene and Au and an isolated electronic structure of Au are essential for effective hybridization between graphene and Au. We anticipate that hybridization between graphene  and Au
and Au 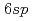 would result in spin injection into graphene.
would result in spin injection into graphene.
 Rh
Rh Sn
Sn
Iwasa, Kazuaki*; Suyama, Kazuya*; Kawamura, Seiko; Nakajima, Kenji; Raymond, S.*; Steffens, P.*; Yamada, Akira*; Matsuda, Tatsuma*; Aoki, Yuji*; Kawasaki, Ikuto; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 7(1), p.014201_1 - 014201_11, 2023/01
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:42.21(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Sn
Sn S
S submicrometer-wide wire devices
submicrometer-wide wire devicesShiogai, Junichi*; Ikeda, Junya*; Fujiwara, Kohei*; Seki, Takeshi*; Takanashi, Koki; Tsukazaki, Atsushi*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(11), p.114203_1 - 114203_9, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:34.44(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) Cu
Cu (PO
(PO )
) SO
SO
 5H
5H O as a model antiferromagnetic spin-1/2 Heisenberg
O as a model antiferromagnetic spin-1/2 Heisenberg 
 -
-
 chain
chainFujihara, Masayoshi; Jeschke, H. O.*; Morita, Katsuhiro*; Kuwai, Tomohiko*; Koda, Akihiro*; Okabe, Hirotaka*; Matsuo, Akira*; Kindo, Koichi*; Mitsuda, Setsuo*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(11), p.114408_1 - 114408_8, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:12.90(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)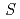 = 1/2 Heisenberg
= 1/2 Heisenberg 
 -
-
 chain antiferromagnets have been investigated extensively due to their exotic magnetic states. Here, we report the magnetic behavior of birchite Cd
chain antiferromagnets have been investigated extensively due to their exotic magnetic states. Here, we report the magnetic behavior of birchite Cd Cu
Cu (PO
(PO )
) SO
SO
 5H
5H O and its effective spin model. Experimental studies by magnetic susceptibility, magnetization, heat capacity, and
O and its effective spin model. Experimental studies by magnetic susceptibility, magnetization, heat capacity, and  SR measurements indicate the absence of long-range order down to 0.4 K. Theoretical studies reveal that birchite is a model compound for the
SR measurements indicate the absence of long-range order down to 0.4 K. Theoretical studies reveal that birchite is a model compound for the 
 -
-
 antiferromagnetic chain: the intrachain interactions
antiferromagnetic chain: the intrachain interactions 
 and
and 
 are antiferromagnetic and their magnitude is about 100 times larger than the interchain interactions. The magnitude of
are antiferromagnetic and their magnitude is about 100 times larger than the interchain interactions. The magnitude of 
 is two to three times larger than that of
is two to three times larger than that of 
 , thus the spin gap is expected to be only a few percent of that of
, thus the spin gap is expected to be only a few percent of that of 
 . The temperature dependence of the specific heat shows a broad peak at about 1 K (
. The temperature dependence of the specific heat shows a broad peak at about 1 K ( 0.036
0.036 
 ), which suggests the presence of a spin gap.
), which suggests the presence of a spin gap.
 Y
Y Fe
Fe O
O films
filmsKikkawa, Takashi*; Saito, Eiji; 6 of others*
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(10), p.104402_1 - 104402_13, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:46.06(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary) by molten salt flux method
by molten salt flux methodSakai, Hironori; Opletal, P.; Tokiwa, Yoshifumi; Yamamoto, Etsuji; Tokunaga, Yo; Kambe, Shinsaku; Haga, Yoshinori
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(7), p.073401_1 - 073401_10, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:50 Percentile:95.07(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The molten salt flux method is applied as a new synthetic route for the single crystals of the spin-triplet superconductor UTe . The single crystals under an optimized growth condition with excess uranium exhibit a superconducting transition at
. The single crystals under an optimized growth condition with excess uranium exhibit a superconducting transition at 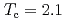 K, which is the highest
K, which is the highest  reported for this compound. The obtained crystals show a remarkably large residual resistivity ratio with respect to the room temperature value and a small residual electronic contribution in specific heat well below
reported for this compound. The obtained crystals show a remarkably large residual resistivity ratio with respect to the room temperature value and a small residual electronic contribution in specific heat well below  . These results indicate that the increase of
. These results indicate that the increase of  in UTe
in UTe can be achieved by reducing the disorder associated with uranium vacancies. The excess uranium in the molten salt acts as a reducing agent, preventing tetravalent uranium from becoming pentavalent and suppressing creation of uranium vacancies. At the same time, the relatively low growth temperature can suppress Te volatilization.
can be achieved by reducing the disorder associated with uranium vacancies. The excess uranium in the molten salt acts as a reducing agent, preventing tetravalent uranium from becoming pentavalent and suppressing creation of uranium vacancies. At the same time, the relatively low growth temperature can suppress Te volatilization.
Busi, M.*; Polatidis, E.*; Malamud, F.*; Kockelmann, W.*; Morgano, M.*; Kaestner, A.*; Tremsin, A.*; Kalentics, N.*; Log , R.*; Leinenbach, C.*; et al.
, R.*; Leinenbach, C.*; et al.
Physical Review Materials (Internet), 6(5), p.053602_1 - 053602_8, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:65.51(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)