Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
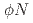 correlation function
correlation functionAbreu, L. M.*; Gubler, P.; Khemchandani, K. P.*; Mart nez Torres, A.*; Hosaka, Atsushi
nez Torres, A.*; Hosaka, Atsushi
Physics Letters B, 860, p.139175_1 - 139175_7, 2025/01
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:52.60(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Li, P. J.*; Utsuno, Yutaka; Yoshida, Kazuki; 85 of others*
Physics Letters B, 855, p.138828_1 - 138828_11, 2024/08
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:74.11(Astronomy & Astrophysics) condensed state in
condensed state in  Mg using the
Mg using the  C+
C+ C scattering
C scatteringFujikawa, Y.*; Kawabata, T.*; Adachi, S.*; Hirose, Kentaro; Makii, Hiroyuki; Nishio, Katsuhisa; Orlandi, R.; Suzaki, Fumi; 13 of others*
Physics Letters B, 848, p.138384_1 - 138384_6, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:73.96(Astronomy & Astrophysics)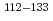 Sb
SbLechner, S.*; Miyagi, Takayuki*; Xu, Z. Y.*; Bissell, M. L.*; Blaum, K.*; Cheal, B.*; Devlin, C. S.*; Garcia Ruiz, R. F.*; Ginges, J. S. M.*; Heylen, H.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 847, p.138278_1 - 138278_9, 2023/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:79.71(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Meng, Q.*; Hiyama, Emiko*; Oka, Makoto*; Hosaka, Atsushi; Xu, C.*
Physics Letters B, 846, p.138221_1 - 138221_6, 2023/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:92.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
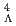 H hypernucleus using in-flight
H hypernucleus using in-flight  He
He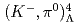 H reaction
H reactionAkaishi, Takaya; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Tanida, Kiyoshi; 35 of others*
Physics Letters B, 845, p.138128_1 - 138128_4, 2023/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:25.07(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Nakayama, Katsumasa*; Suzuki, Kei
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138017_1 - 138017_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:79.71(Astronomy & Astrophysics)The Casimir effect is a quantum phenomenon induced by the zero-point energy of relativistic fields confined in a finite-size system. This effect for photon fields has been studied for a long time, while the realization of counterparts for fermion fields in Dirac/Weyl semimetals is an open question. We theoretically demonstrate the typical properties of the Casimir effect for relativistic electron fields in Dirac/Weyl semimetals and show the results from an effective Hamiltonian for realistic materials such as Cd As
As and Na
and Na Bi. We find an oscillation of the Casimir energy as a function of the thickness of the thin film, which stems from the existence of Dirac/Weyl nodes in momentum space. Experimentally, such an effect can be observed in thin films of semimetals, where the thickness dependence of thermodynamic quantities is affected by the Casimir energy.
Bi. We find an oscillation of the Casimir energy as a function of the thickness of the thin film, which stems from the existence of Dirac/Weyl nodes in momentum space. Experimentally, such an effect can be observed in thin films of semimetals, where the thickness dependence of thermodynamic quantities is affected by the Casimir energy.
 Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of
Ne at the transition into the island of inversion; Detailed structure study of  Ne
NeWang, H.*; Yasuda, Masahiro*; Kondo, Yosuke*; Nakamura, Takashi*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Yoshida, Kazuki; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138038_1 - 138038_9, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:67.28(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Detailed  -ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope
-ray spectroscopy of the exotic neon isotope  Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from
Ne has been performed using the one-neutron removal reaction from  Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for
Ne. Based on an analysis of parallel momentum distributions, a level scheme with spin-parity assignments has been constructed for  Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
Ne and the negative-parity states are identified for the first time. The measured partial cross sections and momentum distributions reveal a significant intruder p-wave strength providing evidence of the breakdown of the N = 20 and N = 28 shell gaps. Only a weak, possible f-wave strength was observed to bound final states. Large-scale shell-model calculations with different effective interactions do not reproduce the large p-wave and small f-wave strength observed experimentally, indicating an ongoing challenge for a complete theoretical description of the transition into the island of inversion along the Ne isotopic chain.
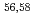 Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic
Ca cast doubt on a doubly magic  Ca
CaChen, S.*; Browne, F.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Lee, J.*; Obertelli, A.*; Tsunoda, Yusuke*; Otsuka, Takaharu*; Chazono, Yoshiki*; Hagen, G.*; Holt, J. D.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 843, p.138025_1 - 138025_7, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:89.00(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Gamma decays were observed in  Ca and
Ca and  Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from
Ca following quasi-free one-proton knockout reactions from 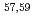 Sc. For
Sc. For  Ca, a
Ca, a  ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for
ray transition was measured to be 1456(12) keV, while for  Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the
Ca an indication for a transition was observed at 1115(34) keV. Both transitions were tentatively assigned as the 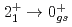 decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for
decays. A shell-model calculation in a wide model space with a marginally modified effective nucleon-nucleon interaction depicts excellent agreement with experiment for 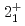 level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the
level energies, two-neutron separation energies, and reaction cross sections, corroborating the formation of a new nuclear shell above the N = 34 shell. Its constituents, the 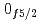 and
and 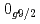 orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic
orbitals, are almost degenerate. This degeneracy precludes the possibility for a doubly magic  Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to
Ca and potentially drives the dripline of Ca isotopes to  Ca or even beyond.
Ca or even beyond.
Sun, L. J.*; Fry, C.*; Davids, B.*; Esker, N.*; Wrede, C.*; Smallcombe, J.; 27 of others*
Physics Letters B, 839, p.137801_1 - 137801_8, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.87(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Xia, C.-J.*; Maruyama, Toshiki; Yasutake, Nobutoshi*; Tatsumi, Toshitaka*; Zhang, Y.-X.*
Physics Letters B, 839, p.137769_1 - 137769_5, 2023/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:43.87(Astronomy & Astrophysics) Ne at the boundary of the island of inversion
Ne at the boundary of the island of inversionRevel, A.*; Wu, J.*; Iwasaki, Hironori*; Ash, J.*; Bazin, D.*; Brown, B. A.*; Chen, J.*; Elder, R.*; Farris, P.*; Gade, A.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 838, p.137704_1 - 137704_7, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:57.48(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
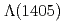 measured in
measured in 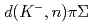 reactions
reactionsAikawa, Shu*; Hashimoto, Tadashi; Tanida, Kiyoshi; 73 of others*
Physics Letters B, 837, p.137637_1 - 137637_8, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:79.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics) isomer in
isomer in 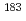 Hg and
Hg and  (
(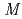 2) systematics of neutron transitions across the nuclear chart
2) systematics of neutron transitions across the nuclear chartHuang, H.*; Zhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, Z.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Li, Z. H.*; Guo, C. Y.*; Barzakh, A. E.*; Van Duppen, P.*; Andel, B.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 833, p.137345_1 - 137345_8, 2022/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:17.31(Astronomy & Astrophysics) Pb
PbZhang, W. Q.*; Andreyev, A. N.; Liu, Z.*; Seweryniak, D.*; Huang, H.*; Li, Z. H.*; Li, J. G.*; Guo, C. Y.*; 34 of others*
Physics Letters B, 829, p.137129_1 - 137129_7, 2022/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:65.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics) Ca; Spectroscopy of
Ca; Spectroscopy of  K,
K,  Ca, and
Ca, and  Ca
CaKoiwai, Takuma*; Wimmer, K.*; Doornenbal, P.*; Obertelli, A.*; Barbieri, C.*; Duguet, T.*; Holt, J. D.*; Miyagi, Takayuki*; Navr til, P.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; et al.
til, P.*; Ogata, Kazuyuki*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 827, p.136953_1 - 136953_7, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:71.48(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
Meng, Q.*; Harada, Masayasu*; Hiyama, Emiko; Hosaka, Atsushi; Oka, Makoto
Physics Letters B, 824, p.136800_1 - 136800_5, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:97.52(Astronomy & Astrophysics)Spectrum of the doubly heavy tetraquarks, 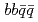 , is studied in a constituent quark model. Four-body problem is solved in a variational method where the real scaling technique is used to identify resonant states above the fall-apart decay thresholds. In addition to the two bound states that were reported in the previous study we have found several narrow resonant states above the
, is studied in a constituent quark model. Four-body problem is solved in a variational method where the real scaling technique is used to identify resonant states above the fall-apart decay thresholds. In addition to the two bound states that were reported in the previous study we have found several narrow resonant states above the 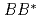 and
and 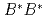 thresholds. Their structures are studied and are interpreted by the quark dynamics. A narrow resonance with spin-parity
thresholds. Their structures are studied and are interpreted by the quark dynamics. A narrow resonance with spin-parity 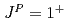 is found to be a mixed state of a compact tetraquark and a
is found to be a mixed state of a compact tetraquark and a 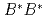 scattering state. This is driven by a strong color Coulombic attraction between the
scattering state. This is driven by a strong color Coulombic attraction between the 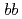 quarks. Negative-parity excited resonances with
quarks. Negative-parity excited resonances with 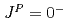 ,
, 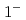 and
and 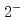 form a triplet under the heavy-quark spin symmetry. It turns out that they share a similar structure to the
form a triplet under the heavy-quark spin symmetry. It turns out that they share a similar structure to the  -mode of a singly heavy baryon as a result of the strongly attractive correlation for the doubly heavy diquark.
-mode of a singly heavy baryon as a result of the strongly attractive correlation for the doubly heavy diquark.
Maruyama, Tomoyuki*; Baha Balantekin, A.*; Cheoun, M.-K.*; Kajino, Toshitaka*; Kusakabe, Motohiko*; Mathews, G. J.*
Physics Letters B, 824, p.136813_1 - 136813_8, 2022/01
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:65.93(Astronomy & Astrophysics) Mg
MgKitamura, Noritaka*; Wimmer, K.*; Poves, A.*; Shimizu, Noritaka*; Tostevin, J. A.*; Bader, V. M.*; Bancroft, C.*; Barofsky, D.*; Baugher, T.*; Bazin, D.*; et al.
Physics Letters B, 822, p.136682_1 - 136682_7, 2021/11
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:71.33(Astronomy & Astrophysics)no abstracts in English
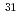 P and
P and 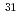 S; A Test for isospin symmetry
S; A Test for isospin symmetryTonev, D.*; De Angelis, G.*; Deloncle, I.*; Orlandi, R.; 27 of others*
Physics Letters B, 821, p.136603_1 - 136603_6, 2021/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:57.44(Astronomy & Astrophysics)