Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Morishita, Takatoshi; Ito, Takashi; Oguri, Hidetomo
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.946 - 949, 2019/10
J-PARC linac has finalized its precise alignment in 2006 and started a beam operation. Since the alignment error should be a cause of beam loss, a precise survey has been performed periodically to ensure the alignment accuracy. In the SDTL section, slight displacements occurred in the position restoration of the seismic isolation structure of the tank support. Along with continuing the smoothing alignment annually, we are taking measures to reduce the external force on the cavity. A local floor elevation continues at the upstream part of the straight section. The realignment of this section has been performed to restore the beam-line linearity every several years. In the downstream part of the linac, step-like floor displacements at the expansion joints and local settlements were observed for a few years from 2011, however, there have been stabilized in recent years. In this paper, we will report on the results of the precise survey as well as the realignment activities.
Kuriyama, Yasutoshi*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Hirota, Katsuya*; Hayano, Hitoshi*; Fuwa, Yasuhiro
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.32 - 35, 2019/10
Research and development of gradient enhancement of superconducting RF accelerating cavity is carried out by accelerator research institute in the world, but defects on the cavity surface limit accelerating electric field. Therefore, development of "Inside inspection system for superconducting accelerated cavity" that optically visualizes the state of the inner surface of the superconducting cavity has been carried out, and results have been achieved. In this research, we apply image processing technology that has developed remarkably in recent years to the internal inspection system, and advanced the defect recognition method. Extraction of depth information and image synthesis were performed from images obtained with different focal positions with the camera for internal surface inspection. Also, by performing pattern recognition processing on the images, automatic detection of defects has become possible. By integrating these techniques into the cavity inner surface inspection system, it becomes possible to shorten the scan time for defect search and acquire the defect shape.
Abe, Masashi*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Terunuma, Nobuhiro*; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Yako, Tomoki*
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.700 - 702, 2019/10
Application of permanent magnets to the damping ring of International Linear Collider (ILC) is investigated. Replacing electromagnets with permanent magnets can reduce not only electricity for exciting the coils and maintenance cost of power supplies but also leakage accidents of cooling water. Bending magnets and correction magnets are used in damping ring, but we tried to calculate magnetic field distributions in a correction magnets using permanent magnets with 3D magnetic field code CST studio. The orbit correction magnet requires that the polarity and the intensity of the generated magnetic field be variable in order to correct the beam orbit error. In this research, adjustment of the generated magnetic field was made possible by mounting the rotation mechanism on the permanent magnet in the magnetic circuit in the correction magnet. In addition, in order to suppress deterioration of beam quality due to an incorrect multipole magnetic field, optimization of the shape of the magnetic circuit was performed, and a magnet design that could be installed on a accelerator was established.
Yako, Tomoki*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Abe, Masashi*; Kurihara, Toshikazu*; Fukuda, Masafumi*; Sato, Masaharu*; Sugimura, Takashi*; Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Takamiya, Koichi*; Iinuma, Yuto*
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1003 - 1005, 2019/10
Permanent magnets are used as materials for beam optics elements, but it is known that radiation demagnetization occurs in neodymium magnets and samarium cobalt magnets. However, there is not enough information on the radiation demagnetization of ferrite magnets which is weak in strength but inexpensive. In order to verify the suitability of the ferrite magnet as a beam optics element, radiation demagnetization experiments by neutron irradiation of the ferrite magnet were carried out at the Kyoto University Research Reactor (KUR). In the experiment, neutron fluence up to 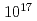 cm
cm was irradiated, and no significant demagnetization was detected on the fluence.
was irradiated, and no significant demagnetization was detected on the fluence.
Sako, Hiroyuki; Aoki, Kazuya*
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.344 - 347, 2019/10
no abstracts in English
Fuwa, Yasuhiro; Shinozaki, Shinichi; Chishiro, Etsuji; Hirane, Tatsuya; Fang, Z.*; Fukui, Yuji*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Mizobata, Satoshi*; Iwama, Yuhei*; Sato, Yoshikatsu*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.611 - 613, 2019/10
In the J-PARC linac, a proton accelerator is operated using 45 units of 324 MHz and 972 MHz klystrons. In the future stabilization and advancement of the accelerator, it is important to acquire the klystron output characteristics near the maximum output accurately. In order to understand this characteristics, measurement of the characteristics of the replaced klystron for some reason such as discharge, as well as the new klystron. However, such measurements have not been performed because of the risk of damage including peripheral equipment due to discharge and the temporal interference with the operation of the accelerator. Therefore, we set up a klystron test stand in the linac building and measured the high-voltage characteristics and input/output characteristics of the klystron under various operating parameters. By using this measurement result, the characteristics of klystron can be obtained before installation, and it becomes possible to determine the optimum operation parameters and make effective plan of klystron replacements. In addition, basic data for predicting the degradation tendency of klystron was acquired by comparing the characteristics of the used and used klystron.
Saha, P. K.; Harada, Hiroyuki; Kinsho, Michikazu; Sato, Atsushi*; Yoneda, Hitoki*; Michine, Yurina*
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.841 - 845, 2019/07
Suganuma, Kazuaki; Hiroki, Fumio; Ito, Takashi; Yamazaki, Yoshio
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.846 - 848, 2019/07
In the past, water flow decreased at water cooling system in J-PARC Linac. Contamination get mixed in cooling water. The problem was resolved by changing the system of the circulation pumps and reducing the tiny metal in water cooling system. However, suppression of occurring tiny metal is unresolved. The tiny metal is the unique problem of accelerator. It is caused by heavy using oxygen free copper and phosphorus deoxidized copper. The two copper is used for the part of accelerator and purified water. The object of the report is investigation of tiny metal contamination of water cooling system in J-PARC Linac.
Otani, Masashi*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Tamura, Jun
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.566 - 568, 2019/07
A muon linac has been developed to generate a low emittance muon beam. Because muons have finite life time of 2.2  sec and the beam current is negligible, a superconducting radio-frequency (SRF) accelerator is suitable for accelerating the muon beam. Basic designs of an SRF linac with 1.3 GHz elliptical cavities to accelerate muons from
sec and the beam current is negligible, a superconducting radio-frequency (SRF) accelerator is suitable for accelerating the muon beam. Basic designs of an SRF linac with 1.3 GHz elliptical cavities to accelerate muons from  = 0.69 to 0.94 was carried out. Although the emittance growth is about 20 to 70%, the SRF muon linac is feasible.
= 0.69 to 0.94 was carried out. Although the emittance growth is about 20 to 70%, the SRF muon linac is feasible.
Sue, Yuki*; Iijima, Toru*; Inami, Kenji*; Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Shimomura, Koichiro*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.55 - 60, 2019/07
The result of bunch size measurement of muon accelerated by RFQ up to 89 keV is presented in this paper. A four-stage muon linac for precise measurement of muon property is under construction in the J-PARC. The demonstration of the first muon RF acceleration with an RFQ linac was conducted and the transverse profile of the accelerated muons was measured in 2017. As one of the remaining issues for the beam diagnostic system, the longitudinal beam profile after the RFQ should be measured to match the profile to the designed acceptance of the subsequent accelerator. For this purpose, the new longitudinal beam monitor using the microchannel plate is under development. The time resolution of the monitor aims to be around 30 to 40 ps corresponding to 1% of a period of an operating frequency of the accelerator, which is 324 MHz. On November 2018, the bunch size of accelerated negative muonium ion of 89 keV with the RFQ was measured using this monitor at the J-PARC MLF. The measured bunch width is 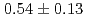 ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
ns, which is consistent with the simulation.
Yotsuzuka, Mai*; Iijima, Toru*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Inami, Kenji*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Saito, Naohito; Shimomura, Koichiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.814 - 817, 2019/07
The J-PARC E34 experiment aims to measure the muon anomalous magnetic moment and the electric dipole moment with a high precision. In this experiment, thermal muonium is produced and ionized by laser resonance to generate ultra-slow muons, which are then accelerated in a multistage muon linac. In order to satisfy the experimental requirements, suppression of the emittance growth during the acceleration is necessary. Because the main cause of the emittance growth is beam mismatching between the accelerating stages, the transverse and longitudinal beam monitoring is important. The longitudinal beam monitor has to measure the bunch length with the resolution equivalent to tens of picoseconds, which is 1% of the acceleration phase of 324 MHz. In addition, it should be sensitive to single muon because the beam intensity is limited during the commissioning phase. To realize above requirements, we are developing a longitudinal beam monitor with a micro channel plate, and the test bench to evaluate the monitor performance. So far, the time resolution of the beam monitor was obtained to be 65 ps in RMS including the jitter on the test bench. We also succeeded in measuring the longitudinal bunch size of the muon beam accelerated by RFQ using the beam monitor. In this paper, the results of the performance evaluation for this beam monitor are reported.
Nakazawa, Yuga*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Iwashita, Yoshihisa*; Iwata, Yoshiyuki*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Saito, Naohito; Sue, Yuki*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.404 - 407, 2019/07
An inter-digital H-mode drift-tube linac (IH-DTL) is developed in a muon linac at the J-PARC E34 experiment. IH-DTL will accelerate muons from 0.34 MeV to 4.5 MeV at a drive frequency of 324 MHz. Since IH-DTL adopts an APF method, with which the beam is focused in the transverse direction using the rf field only, the proper beam matching of the phase-space distribution is required before the injection into the IH-DTL. Thus, an IH-DTL prototype was fabricated to evaluate the performance of the cavity and beam transmission. As a preparation of the high-power test, tuners and coupler are designed and fabricated. In the low power measurement, we decided the loop structure with witch the VSWR = 1.01 and field distortion of within 7%. In this paper, the development of the tuner and the coupler and the result of the low-power measurement will be presented.
Yasuda, Hiromasa*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Kitamura, Ryo; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Saito, Naohito; Sue, Yuki*; Nakazawa, Yuga*; Matoba, Shiro*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.371 - 375, 2019/07
Muon linac is developed for the muon g-2/EDM experiment at J-PARC. In this experiment, ultra slow muon is accelerated to a momentum of 300 MeV/c with the four linac structures. This scheme offers new opportunity for precise measurements; it enables us to reverse muon polarization at early stage of acceleration. The reversal of polarization is a common method of precision polarization measurements as it can be used to identify or reduce systematic uncertainties dependent on time. It is necessary to accelerate muons and flip its spin without substantial emittance growth for the experimental requirement. As one of the candidates for our spin rotator, we are developing the Wien-filter type. The emittance growth is +64% in x-x' plane and +56% in y-y' plane, but it is revealed it would be reduced by tuning electric field to + 47% in x-x' plane and + 2% in y-y' plane. In this paper, the design of the Wien-filter type spin rotator for the low emittance muon beam will be presented.
Matsuda, Makoto; Osa, Akihiko; Ishizaki, Nobuhiro; Tayama, Hidekazu; Kabumoto, Hiroshi; Nakamura, Masahiko; Kutsukake, Kenichi; Otokawa, Yoshinori; Asozu, Takuhiro; Matsui, Yutaka; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1270 - 1273, 2019/07
The JAEA-Tokai tandem accelerator was operated over a total of 138 days, and delivered 16 different ions to the experiments in the research fields of nuclear physics, nuclear chemistry, atomic physics, solid state physics and radiation effects in material in FY2018. Maximum acceleration voltage was 16.6 MV. A new beam attenuator was installed at the entrance beam line of the tandem accelerator to facilitate control of the beam current and minimize stripper foil consumption. The main maintenance items included replacing the pellet chain used for about 68,000 hours and the drive motor for the high voltage terminal generator used for about 9 years. A fault has occurred in the building's oxygen deficiency monitor. This paper describes the operational status of the accelerators and the major technical developments of our facility.
Hatakeyama, Shuichiro*; Yamamoto, Kazami; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Hayashi, Naoki
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.789 - 793, 2019/07
The J-PARC Rapid Cycling Synchrotron (RCS) accelerates 400 MeV LINAC beams up to 3 GeV, and distributes them to the Materials Life Science Experiment Facility (MLF) and the Main Ring Synchrotron (MR) in 25 Hz cycle. To prevent radiation damages from the beam loss and also to detect failures of machines an interlock mechanism called the Machine Protection System (MPS) is introduced. If the beam is stopped by the MPS we should recover it quickly for the users of experiment facilities. The MPS related to the beam dynamics is usually diagnosed by beam loss monitors (BLM), beam position monitors (BPM) and current transformers (CT). Data of these monitors should be distinguished MLF or MR since the parameters for the magnet and the RF systems are different between MLF and MR. We confirmed validity of the method to distinguish the beam destination by using the information of the beam synchronized tag from the reflective memory (RFM) when taking the monitor data in 25 Hz.
Harada, Hiroyuki; Saha, P. K.; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.179 - 182, 2019/07
Recently, humankind had big discovery about neutron star, which is great big nuclear in the space. They are discovery of neutron star with twice mass of solar in 2010 and observation of gravity wave when two neutron start incorporate in 2017. In order to understand the high dense matter like the neutron star, project of experimental researches by using accelerated heavy ion beams become heated in the world, such RHIC-BES-II program, FAIR project, NICA project, etc. The J-PARC provides MW class high intensity proton beams to many experiments and researches. We have study of the heavy ion beam in J-PARC to fully utilize high intensity ability of J-PARC. We propose the accelerator scheme of the beam in J-PARC and the intensity will reach to the world record. In our talk, we will report the current status of proton beam and the accelerator scheme for the high-intensity heavy ion beam in J-PARC.
Ono, Ayato; Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Ueno, Tomoaki*; Horino, Koki*; Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.399 - 403, 2019/07
J-PARC uses an ignitron switch as the klystron power source clover device and a thyratron switch as the kicker power system. Ignitron uses mercury, which is of limited use worldwide, and is expected to be discontinued in the future. Therefore, a semiconductor switch for ignitron substitution using a MOS gate thyristor is designed. In order to be used as a crowbar device, a switch capable of resisting an operating output of 120 kV, 40 kA, 50 us is required. We have realized an oval type substrate module that achieves an operating output of 3 kV, 40 kA, 50 us per substrate. In addition, we adopted a LTD circuit using SiC-MOSFET as an alternative switch for thyratron, and produced a radially symmetric pulse power supply circuit to which this circuit was applied. This circuit board achieves a rise of 250 ns or less, and a flat top of 1.5 us or more necessary for the RCS kicker power supply system, with a pulse output of 800 V and 2 kA per circuit board. We report on the power test results at 20 kV.
Hasegawa, Kazuo; Kinsho, Michikazu; Oguri, Hidetomo; Yamamoto, Kazami; Hayashi, Naoki; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Naito, Fujio*; Yoshii, Masahito*; Toyama, Takeshi*; Yamamoto, Noboru*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.1235 - 1239, 2019/07
After the summer shutdown in 2018, the J-PARC restarted user operation in late October. While beam power to the Materials and Life Science Experimental Facility (MLF) was 500 kW as before the summer shutdown, linac beam current was increased from 40 to 50 mA. Operation of the Main Ring (MR) was suspended due to the modification and/or maintenance of the Superkamiokande (neutrino detector) and Hadron experimental facility. The user operation was resumed in the middle of February for the Hadron experimental facility at 51 kW. But on March 18, one of the bending magnets in the beam transport line to the MR had a failure. It was temporary recovered and restored beam operation on April 5, but the failure occurred again on April 24 and the beam operation of the MR was suspended. In the fiscal year of 2018, the availabilities for the MLF, neutrino and hadron facilities are 94%, 86%, and 74%, respectively.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Takei, Hayanori; Matsuda, Hiroki; Yuri, Yosuke*; Yuyama, Takahiro*
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.515 - 519, 2019/07
no abstracts in English
Takayanagi, Tomohiro; Ono, Ayato; Ueno, Tomoaki*; Horino, Koki*; Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 16th Annual Meeting of Particle Accelerator Society of Japan (Internet), p.75 - 79, 2019/07
We will replace the Thyratron and Ignitron discharge type switch with a semiconductor switch capable of more stable operation. The thyratron alternative switch used by the kicker power supply manufactured the radial symmetric module substrate of the 800V/2kA output which was built by LTD circuit using SiC-MOSFET. By making the power transfer structure between module substrates stacked for high voltage output into a coaxial ring type, a further reduction in inductance is realized. We report the results of evaluating a pulse output of 20kV/1kA (final specification is 40kV/2kA). Ignitron, which is used as a high-power klystron clover switch, has the potential to be discontinued in the future because it uses mercury, which has limited use worldwide. LINAC's klystron clover switches require a working output of 50kV at 120kV/40kA. We fabricated 3kV/40kA oval type module substrate using MOS gate thyristor. Report on preliminary test results.