Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Misawa, Takeharu; Takase, Kazuyuki
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2008/05
Zhang, W.; Yoshida, Hiroyuki; Takase, Kazuyuki
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/05
Liu, W.; Kureta, Masatoshi
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2008/05
R&D project to investigate thermal-hydraulic performance in the tight-lattice rod bundles for Innovative Water Reactor for Flexible Fuel Cycle (FLWR) has been progressed at Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA). The basic thermal-hydraulic characteristics about the critical power and the pressure drop, under both steady and transient conditions, have been ascertained with using 37-rod tight lattice bundle. The effect of the spacer on the critical power has also been ascertained. However, as to the axial power distribution, the severest one - which is called as the basic heating case in this research - is selected in these experiments, with no considering to the change of the axial power distribution with the proceeding of the burnup. Therefore, an experimental research on the effect of the axial power distribution on the critical power is necessary. In this paper, an experimental research on the effect of the axial power distribution on the critical power is performed under the atmospheric pressure with using a circular tube, which is axially divided into 3 insulated levels and is heated separately by 3 DC power supplies. The test section is capable to simulate the power distribution in the double-humped core. Axial uniform heating condition, the upper 3 layers simulation and the center 3-layers simulation of the basic heating case are selected as the cases for the detailed evaluation. The effects of relative power ratio on the critical power, critical quality and critical boiling length under different heating conditions are ascertained for the detailed evaluation cases. With using the experimental data, existed correlating methods for the boiling transition are evaluated. As the result, a combination of the critical quality - boiling length method and the critical heat flux - critical quality method is found a good correlating to the present data with a changed axial power distribution.
Sato, Hiroyuki; Kobayashi, Jun; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki; Kamide, Hideki
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2008/05
A sodium cooled fast reactor is designed to attain a high burn-up core in a feasibility study on commercialized fast reactor cycle systems. In high burn-up fuel subassemblies, deformation of fuel pin due to the swelling and thermal bowing may decrease flow rate via change of flow area in the sub-assembly and influence the heat removal capability. A 2.5 times enlarged 7-pin bundle water model was applied to investigate the influence of pin bowing and wrapping wire. The test section consisted of a hexagonal acrylic duct tube and fluorinated resin pins which had the refractive index nearly the same with water and high light transmission rate. This enabled to visualize around the central pin through the outer pins. Velocity distribution was measured by using PIV in sub-channels around the central pin in reference and deformation condition. Velocity distribution around the wrapping wire was measured and the wire influenced to the velocity and RMS in the wide region near the pin surface.
Tanaka, Masaaki; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Monji, Hideaki*
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2008/05
In Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), a numerical simulation program "MUGTHES (MUlti Geometry simulation code for THErmal-hydraulic and Structure heat conduction analysis in boundary fitted coordinate)" has been developed to evaluate thermal striping phenomena. MUGTHES can deal with three-dimensional transient thermal-hydraulic problem coupled with three-dimensional transient heat conduction in the surrounding structure in consideration of conjugated heat transfer. In this paper, numerical schemes for thermal-hydraulic simulation employed in MUGTHES are described including LES model. As the validation of MUGTHES, a numerical simulation of thermal striping phenomena in a T-junction piping system was conducted. The results were in good agreement with the experimental data.
Ioka, Ikuo; Kato, Chiaki; Kiuchi, Kiyoshi; Nakayama, Jumpei
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2008/05
Austenitic stainless steels suffer intergranular attack in boiling nitric acid with oxidants. The intergranular corrosion is mainly caused by the segregation of impurities to grain. An extra high purity austenitic stainless steel (EHP alloys) was developed with conducting the new multiple refined melting technique in order to suppress the total harmful impurities less than 100ppm. The basically corrosion behavior of type 310 EHP alloy with respect to nitric acid solution with highly oxidizing ions was investigated. The straining, aging and recrystallizing (SAR) treated type 310 EHP alloy showed superior corrosion resistance for intergranular attack. The segregated boron along the grain boundaries was one of main factor of intergranular corrosion from fission track etching results. The SAR treatment was effective to restrain the intergranular attack for type 310 EHP alloy with B less than 7ppm.
Naito, Morimasa; Saito, Yuya; Tanai, Kenji; Yui, Mikazu
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/05
An experimental approach is introduced for understanding how the engineered barriers of a deep geological repository system are affected by fault movement. The experiments are conducted using laboratory simulation test equipment. So far, the experiments indicate that the metal overpack is rotated within the bentonite buffer due to its plasticity, but not breached. Numerical analyses are also carried out to supplement the range of the experiments, which is limited by the capability of the test equipment.
Tsujita, Yuichi*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Suzuki, Yoshio; Kimura, Hideo
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2008/05
Shibata, Akira; Nakano, Junichi; Omi, Masao; Kawamata, Kazuo; Saito, Takashi; Hayashi, Koji; Saito, Junichi; Nakagawa, Tetsuya; Tsukada, Takashi
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/05
Irradiation assisted stress corrosion cracking (IASCC) is considered to be one of the key issues in the aged Light Water Reactors. To simulate IASCC behavior by the in-pile or post-irradiation experiment, it is necessary to irradiate specimens up to a neutron fluence that is higher than the so-called IASCC threshold fluence. There are, however, some technical hurdles to be overcome for the experiments. The techniques assembling pre-irradiated specimens into a in-pile test capsule in a hot cell and the eveluation of material integrity of the capsule during a long term irradiation are necessary. To evaluate material integrity on capsules during a long term irradiation, tensile test and SSRT using specimens which was previously irradiated to 1.0 3.9
3.9 10
10 n/m
n/m were performed. In this paper, technical developments required for IASCC test, e.g. the development of assembling techniques for IASCC capsules and the evaluation of stainless steels which dosed high-fluence neutron were described.
were performed. In this paper, technical developments required for IASCC test, e.g. the development of assembling techniques for IASCC capsules and the evaluation of stainless steels which dosed high-fluence neutron were described.
Kobayashi, Noboru; Ogawa, Takashi; Oki, Shigeo; Mizuno, Tomoyasu; Ogata, Takanari*
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2008/05
The metal fuel core is superior to the mixed oxide fuel core because of its higher breeding ratio and compact core size resulting from neutron economics, hard neutron spectrum, and high content of heavy metal nuclides. Utilizing the advantage of the metal fuel core, conceptual sodium-cooled fast breeder reactor designs have been pursued for the attractive core properties of high breeding ratio, small inventory, compact size, low sodium void reactivity, and high transmutation ratio of the minor actinides. Among attractive cores, a conceptual design for a high breeding ratio was performed without blanket fuels. The design conditions were set so a sodium void reactivity of less than 8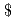 , a core height of less than 150 cm, a maximum cladding temperature of 650
, a core height of less than 150 cm, a maximum cladding temperature of 650  C, and a fuel pin bundle pressure drop of 0.4 MPa. The breeding ratio of the resultant core was 1.34 without blanket fuels.
C, and a fuel pin bundle pressure drop of 0.4 MPa. The breeding ratio of the resultant core was 1.34 without blanket fuels.
Suzuki, Yoshio; Nakajima, Norihiro; Araya, Fumimasa; Hazama, Osamu; Nishida, Akemi; Kushida, Noriyuki; Akutsu, Taku; Teshima, Naoya; Nakajima, Kohei; Kondo, Makoto; et al.
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2008/05
Yamano, Hidemasa; Tobita, Yoshiharu
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/05
This paper describes experimental analyses using SIMMER-III, which were precedently carried out for the integral verification of the COMPASS code. Two topics of key phenomena in CDAs were here presented: molten fuel freezing and dispersion; and boiling behavior of molten fuel pool. To analyze the fuel freezing behavior, the GEYSER out-of-pile and the CABRI-EFM1 in-pile experiments were selected. The SIMMER-III calculation well agreed with fuel penetration length measured in GEYSER. The freezing behavior in CABRI-EFM1 was also reasonably simulated by SIMMER-III. The boiling pool consisting of molten fuel/steel mixtures is characterized by the heat transfer between fuel and steel. The CABRI-TPA2 experiment has suggested less transient heat flux from fuel to steel due to a steel vapor blanketing around a steel droplet. SIMMER-III well simulated the steel boiling behavior observed in the CABRI-TPA2 experiment by reducing the heat transfer coefficients between fuel and steel.
Saito, Junichi; Ara, Kuniaki; Sugiyama, Kenichiro*; Kitagawa, Hiroshi*; Nakano, Haruyuki*; Ogata, Kan*; Yoshioka, Naoki*
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2008/05
no abstracts in English
Aoshima, Atsushi; Ueno, Tsutomu; Shiotsuki, Masao
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2008/05
In TVF, concentrated high radioactive liquid waste produced in TRP has been vitrified since 1995. Because of very corrosive condition of melting glass, design life of a melter is limited five years and it requires interruption of plant operation and generation of high radioactive solid waste for melter change. To improve this situation, prolongation of melter design life time by increasing corrosion resistance of structural material is required strongly. Effective removal of noble metal from a melter is also required because accumulated noble metal cause shortening lifetime of a melter. So, JAEA tried to develop a melter which equipped with ability of high corrosion resistance and control temperature distribution for noble metal easy drain out. Mechanical removal technology of remained noble metal rich glass also used if necessary. Low temperature glassing technology and advance removal of noble metal from concentrated high radioactive liquid are also be studying.
Monji, Hideaki*; Shinozaki, Tatsuya*; Kamide, Hideki; Sakai, Takaaki
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2008/05
This paper deals with characteristics of surface vortex in a cylindrical vessel. One of the characteristics is a gas core length which is important to estimate the onset condition of the gas entrainment but influenced easily by the experimental condition. In the experiment using water, the effects of the water temperature, water level and the surface tension on the gas core length were investigated. The onset condition of the gas entrainment is sometimes estimated by using the Burgers vortex model but the real flow in the vessel is different from the model. The velocity fields were measured by PIV and the velocity gradient of the downward flow was discussed. The proper flow conditions for the Burgers vortex model are a high water level and a high flow rate.
Yamaguchi, Akira*; Takata, Takashi*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Kohara, Yoshitake*
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2008/05
Sodium-water reaction (SWR) is a design basis accident of a Sodium Fast Reactor (SFR). A breach of the heat transfer tube in a steam generator (SG) results in contact of liquid sodium with water. In this paper, a new computer program has been developed and the SWR in a counter-flow diffusion flame is studied by a numerical simulations and an experiment. The experiment is designed with the numerical simulation so that the stable reaction flame is maintained for long time and physical and chemical quantities are measured. From the comparison of analysis and experiment, there exist discrepancies that may be caused by the assumptions of chemical reaction. Hence, a new experiment is proposed to enhance the measurement accuracy and to investigate the reason of the disagreement. The authors propose a depressurized experiment. With the depressurization, it is expected the flame location can be controlled and the reaction region becomes thicker because of decrease in reactant gas density.
Tsuruoka, Hokuto*; Tamura, Takeshi*; Sugiyama, Kenichiro*; Narabayashi, Tadashi*; Ohshima, Hiroyuki
Proceedings of 16th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/05
The occurrence of secondary heat transfer tube failure due to overheating by sodium-water reaction in LMFBR steam generators has been concerned from the viewpoint of public acceptance. To evaluate the phenomena, a sophisticated computer code SERAPHIM has been developed by JAEA. For the purpose of obtaining fundamental data for the validation of the code, a sodium experiment was carried out, where the void fraction around a single rod set in a sodium pool without sodium-water reaction was measured. The void fraction was observed to somewhat increase with increasing the gas jet velocity. The increase rate was clearly smaller compared with that in the water experiment. The void fraction also showed more monotonous distribution from the stagnation point to the rear point than that in water pool. These results reflect the difference of surface tension between water and sodium. It is concluded that the entrainment of ambient sodium is easily caused and this leads monotonous distribution of void fraction in the sodium pool.