Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kubo, Shinji; Kasahara, Seiji; Sato, Hiroyuki; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Iwatsuki, Jin; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Miyashita, Reiko*; Tago, Yasuhiro*; Onuki, Kaoru
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/12
A stable hydrogen production via the IS process is relatively difficult because of the unique characteristics of the closed-cycle condition involved. This issue is therefore a high targeted priority when industrializing the process as feasible in a chemical plant. In system of IS process coupled with helium gas heat source, a process control method to maintain mass balance of the process was devised. The method is equipped with measurements of Bunsen reaction composition and allocation of heat for the O and H
and H production sections in strict proportion. Via computer simulation for closed-cycle and fully multi-section driven by high-temperature helium gas, the system worked automatically to maintain stoichiometric production ratio in response to shifts of helium gas conditions.
production sections in strict proportion. Via computer simulation for closed-cycle and fully multi-section driven by high-temperature helium gas, the system worked automatically to maintain stoichiometric production ratio in response to shifts of helium gas conditions.
Suzuki, Mitsutoshi; Namekawa, Takashi; Asano, Takashi; Niita, Koji*
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
The advanced MOX fabrication process in FaCT project has been studies to investigate an overall characteristic of nuclear material accounting of Pu in the proposed confinement box. Flow field induced by a forced convection inside the box is numerically simulated to evaluate the MOX particle behavior and a radiation field due to the spontaneous and induced neutrons emitted from Cm and Pu is calculated using PHITS code. The possibility of remote-monitoring techniques using non-destructive assay to apply to a future safegurads measure is invetigated.
 -rays from energy-recovery linacs
-rays from energy-recovery linacsHajima, Ryoichi; Kikuzawa, Nobuhiro; Hayakawa, Takehito; Minehara, Eisuke
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
Nondestructive assay of nuclear materials is one of the most urgent research issues for the management of nuclear waste. We apply nuclear resonant fluorescence (NRF), a fingerprint of each isotope, to the nondestructive detection. Detection of NRF signals from objectives irradiated by quasi-monochromatic  -rays enables one to make quantitative assay of nuclear materials in a nondestructive manner. In order to obtain high-flux
-rays enables one to make quantitative assay of nuclear materials in a nondestructive manner. In order to obtain high-flux  -rays for the above purpose, we propose to utilize an energy-recovery linac (ERL), which produces a high-brightness electron beam with high-average current. A design study of high-flux
-rays for the above purpose, we propose to utilize an energy-recovery linac (ERL), which produces a high-brightness electron beam with high-average current. A design study of high-flux  -ray source based on an ERL shows that a
-ray source based on an ERL shows that a  -ray flux of
-ray flux of 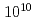 ph/sec/keV is obtained and detection of U-238 of 1 Bq/g in a concrete drum is possible within 1 second. In this paper, we present a design of the assay system and results of Monte Carlo simulations of NRF.
ph/sec/keV is obtained and detection of U-238 of 1 Bq/g in a concrete drum is possible within 1 second. In this paper, we present a design of the assay system and results of Monte Carlo simulations of NRF.
Morizono, Koji; Takeuchi, Norihiko; Takayama, Koichi; Deshimaru, Takehide; Mukai, Kazuo
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2008/10
Prototype fast breeder reactor Monju is the first power generating FBR in Japan which is a plant for research & development to demonstrate reliability of fast breeder reactor as a power plant and establish sodium handling technology etc. Monju started construction in 1985, achieved initial criticality in 1994 and attained 40% output in 1995, however the sodium leak accident occurred during the test operation at the end of that year. Since then, the plant remained shut down for 12 years. In this subject, our efforts for the restart of this long term shut down plant will be presented.
Kobayashi, Tsuguyuki*; Namba, Takashi*; Kawabe, Yukinari*; Washiya, Tadahiro
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
Japan Atomic Power Company (JAPC) and Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) have been developing fuel disassembly and fuel pin chopping systems for a future Japanese commercial FBR. At first, the wrapper tube is cut by the slit-cut to pull it out, then the fuel pins are cut by the crop-cut at their end-plugs to separate them from the entrance nozzle. The pins are transferred to the magazine of the chopping machine. A series of tests were performed to develop this procedure. As the result of mechanical cutting tests, the CBN wheel was selected. The slit-cut tests were carried out to evaluated the cutting performance of the wheel. Fuel pin handling tests were performed to transfer them from the disassembly machine to the chopping machine. The Saucer tray was selected to receive the disassembled pins. All the pins were transferred and loaded into a magazine of the chopping machine.
Nagaoki, Yoshihiro; Kikuchi, Shin; Ichimiya, Masakazu
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
"Fast Reactor Cycle Technology Development (FaCT)" project has been conducted since 2006. In this project, design study and research and development (R&D) on innovative technologies for fast reactor (FR) cycle system are implemented in order to present the conceptual designs of commercial and demonstration facilities by 2015 and start operating demonstration fast reactor in 2025. The R&Ds has been stepped forward into the development stage to establish the realization of innovative technologies which bring excellent performance to fast reactor cycle system. The purpose of R&D by 2010 is to decide weather innovative technologies shall be adopted. So promoting R&D of FR, the project governance was organized. Furthermore, several possible R&D have been effectively carried out within the frameworks of international cooperation, such as GNEP, GIF, and INPRO.
Enoeda, Mikio; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Tsuru, Daigo; Hirose, Takanori; Ezato, Koichiro; Yokoyama, Kenji; Dairaku, Masayuki; Seki, Yohji; Suzuki, Satoshi; Mori, Kensuke*; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
Ezato, Koichiro; Akiba, Masato; Enoeda, Mikio; Suzuki, Satoshi; Seki, Yohji; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Tsuru, Daigo; Mori, Hideo*; Oka, Yoshiaki*
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Satoshi; Ezato, Koichiro; Yokoyama, Kenji; Dairaku, Masayuki; Enoeda, Mikio; Tanigawa, Hisashi; Tsuru, Daigo; Seki, Yohji; Mori, Kensuke*; Nishi, Hiroshi; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
This paper presents the present status of R&D activities on plasma facing components (PFCs) for fusion reactors, such as ITER and fusion demonstration reactor (DEMO). The PFCs as typified by divertor and first wall components are subjected to high heat flux and particle flux from fusion plasma. It is essential to have sufficient heat removal capability and robust structure against those loadings. JAEA has been carried out to develop the ITER-PFCs which consist of copper alloys and armor materials with high thermal conductivity, such as carbon fiber composites, tungsten and beryllium. The demonstration of the thermomechanical performance has successfully been made under close mutual cooperation between the participant countries of ITER. Currently, the activity on the development of the ITER-PFCs is in a qualification phase prior to the bulk production for construction. In JAEA, the R&Ds on the DEMO-PFCs is being made in parallel with the development activity of the ITER-PFCs.
Sano, Kazuya; Kitamura, Koichi; Tezuka, Masashi; Mizui, Hiroyuki; Kiyota, Shiko; Morishita, Yoshitsugu
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
The operation of Advanced Thermal Reactor Fugen was terminated on Mar. 29th, 2003. After the operation, the preparative works and R&D have been conducted strenuously for the planning of the rational and safe decommissioning. The decommissioning program for Fugen was planed, based on the results of above works and R&D, and was applied to the government as a first case under the revised nuclear reactor regulation law. As a result, the program was approved on Feb. 12th, 2008. In this paper, the decommissioning program for Fugen was outlined, which are the dismantling process consists of four periods; (1) Spent fuel transportation, (2) Periphery facilities dismantlement, (3) Reactor dismantlement and (4) Building demolition, the amount of radioactive waste, the safety assessment etc.
Nakano, Masanao; Takeishi, Minoru
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
The liquid effluent has been discharged from each nuclear fuel cycle facility in mainly industrially advanced nations with authorization. Since the safety assessment confirms that environmental impact from each facility would be small enough, it was not necessary to assess the effect of the multilateral radioactive effluents. But it will be necessary to quantify the radiological impact between plural countries due to the increase of interest to the global environment and of demand on nuclear energy in the world. In this study, the long-term and multilateral environmental radiological assessment from tritium discharge by effluents from nuclear fuel cycle facilities in the world was carried out. Then, collective and effective doses were evaluated in case of intake of marine products. Additionally, an assessment from the nuclear testing in the atmosphere was carried out. As a result, the concentration and dose level was confirmed not to become an issue for global scale, even if Rokkasho reprocessing plant operates with full scale.
Seo, Toshihiro; Sasao, Eiji; Notoya, Shin; Shimizu, Kazuhiko
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
JAEA has promoted research and development of HLW disposal technology to contribute to both implementation and safety regulation. This R&D covers the geological environment, repository engineering and performance assessment. At two underground laboratories (Mizunami and Horonobe), surface-based investigations have been completed, and the excavation of shafts and drifts is underway. A complementary study of natural disruptive phenomena, such as volcanism and faulting, has also been conducted. In the ENTRY and QUALITY research facilities, the development of engineering technologies with associated advanced models and databases for quantification of the long-term evolution of the near-field has been carried out. To integrate these R&D activities and manage the huge amount of data that they produce, JAEA has initiated a novel project to develop an advanced knowledge management system which will provide a technical knowledge base for supporting both implementers and regulators.
Onuki, Kaoru; Kubo, Shinji; Terada, Atsuhiko; Iwatsuki, Jin; Takegami, Hiroaki; Okuda, Hiroyuki; Kasahara, Seiji; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Imai, Yoshiyuki
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been conducting R&D on thermochemical water-splitting Iodine-Sulfur (IS) process for hydrogen production. Closed-cycle operation of the process was demonstrated for one week with hydrogen production rate of about 30NL/h. Components in H SO
SO section were designed featuring a heat exchanger made of silicon carbide. Flowsheet process analysis is now in progress. For higher thermal efficiency, a Bunsen reactor and an EED cell are investigated. Vapor-liquid equilibrium of HI-H
section were designed featuring a heat exchanger made of silicon carbide. Flowsheet process analysis is now in progress. For higher thermal efficiency, a Bunsen reactor and an EED cell are investigated. Vapor-liquid equilibrium of HI-H O-I
O-I for high pressure is measured.
for high pressure is measured.
Murakami, Haruko*; Ahn, J.*
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
Yokoyama, Kenji; Numata, Kazuyuki*; Hazama, Taira; Ishikawa, Makoto
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
The new solver for cross section adjustment and design accuracy evaluation has been developed for the new reactor physics analysis code system, MARBLE. In this development, object-oriented design was applied for achieving software extendibility. The new solver was successfully designed to easily add a uncertainty prediction method. This extendibility was confirmed by implementing the extended bias method. The new solver reproduces all functions of the conventional code system and can be used as standard solver for cross section adjustment and design accuracy evaluation in MARBLE.
Takamine, Jun; Haruyama, Mitsuo; Takase, Misao; Yamaguchi, Satoshi
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
When an object including a lot of hydrogen atoms such as the cemented waste is measured by using the conventional active neutron method, radial sensitivity distribution in the region of surface and center is different more than 100 times. Then we developed the method to detect a nuclear fission neutron induced by the neutron which slowed down in the matrix itself, and so performed a position sensitivity difference of 10%. Furthermore, we understood that the background neutron in nuclear fission neutron counting area is great decrease by using SUS-304 instead of graphite as a moderator of conventional detection system. And then, this new system enabled to measure clearance level activity included in cemented waste. Besides, we modified the optimum structure of the detector bank, which enabled to measure precisely even metal compaction waste (the density is 3 4 g/cm
4 g/cm ). In this session, we introduce the process of the past research, applied examples, recent results of the research.
). In this session, we introduce the process of the past research, applied examples, recent results of the research.
Tamaki, Hitoshi; Yoshida, Kazuo; Hamaguchi, Yoshikane*
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
A PSA is a comprehensive and structured method for assessing the safety of a nuclear facility. This method also provides risk information that could be applied to effective regulatory activities for nuclear facilities and so on. A PSA procedure for MOX fuel fabrication facility has been developed at JAEA. This procedure consists of two steps. One is called as preliminary PSA using simple methods for likelihood and consequence evaluation through whole processes in the facility. The other step is called as detailed PSA and is carried out to evaluate risk of the significant events using methods corresponding to level 1 PSA and level 2 PSA for nuclear power plants. The procedure was applied to a practical model facility based on process information and handling quantities of materials from the planned MOX fabrication plant to understand risks at whole processes in the model facility. A risk-profile, which consisted of dominant accident sequences, was also obtained through this analysis.
Rintsu, Yuko*; Serizawa, Shigeru*; Yamazaki, Tetsuo*; Umeyama, Nobuaki*; Moriuchi, Shigeru*; Handa, Hiroyuki*; Onishi, Ryoichi*; Takemura, Morio*; Chino, Masamichi; Nagai, Haruyasu; et al.
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
no abstracts in English
Takahashi, Saburo; Kikuno, Hiroshi; Shiromo, Hideo; Kuba, Meiji; Abe, Tomoyuki; Takeda, Seiichiro
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been accumulating various experience and knowledge on development of MOX fuel technologies for more than 40 years since 1966. Plutonium Fuel Production Facility (PFPF) has introduced a fully automated and remote operation in 1988 as a pioneer in the world, based on the operational and technical experience obtained in the existing facilities. The PFPF has fabricated MOX fuel assemblies for a fast reactor "JOYO" and a fast breeder reactor "MONJU" so far. Through MOX fuel fabrication for JOYO and MONJU, many operational experiences such as a hold-up material problem have been gained. Based on the experiences, process equipments have been newly developed and a process technology has been improved. As the results, fully automated and remote fabrication technologies including easy contact maintenance of process equipments for FBR MOX fuel have been demonstrated in the PFPF on a large scale.
Yamamura, Osamu
Proceedings of 16th Pacific Basin Nuclear Conference (PBNC-16) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2008/10
Tokai reprocessing plant (TRP) has been processing over 1,123 tons of spent fuels from the beginning of its active operation in Sept. 1977. For 30 years operation of TRP, many technological problems have been overcome to obtain the stable and reliable operation. The process for establishments of maintenance technology in TRP was evaluated through the analysis of significant plant equipment failures reported to the authorities concerned. Through these troubles and its solution, following knowledge could be obtained.