Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sato, Hiroyuki; Park, H.*; Knoll, D.*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
Multiphysics core simulations for a prismatic-type VHTR are performed in this study. Our solution scheme is based on the JFNK method. As a preliminary example, a thermal-fluid calculation is performed with an idealized two-dimensional symmetric representation of the GT-MHR and compared with the RELAP5-3D simulation results. Also, a neutronics calculation is conducted using the same geometry as the thermal-fluid calculation, and using cross section data obtained from an HTGR benchmark problem. In addition, a coupled steady-state thermal-fluids neutronics calculation is performed. The calculation results showed that the developed prismatic VHTR core simulator can perform tightly-coupled multiphysics simulations efficiently.
Onoe, Hironori; Takeuchi, Ryuji; Saegusa, Hiromitsu; Daimaru, Shuji; Karino, Tomoyuki
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2011/10
Kurisaka, Kenichi; Okamura, Shigeki*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been developing the Japan Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (JSFR) in the Fast Reactor Cycle Technology Development (FaCT) Project. Risk targets were set out as part of the safety-related design requirement: i.e., the quantitative safety design requirements on the core damage frequency (CDF) and the containment failure frequency (CFF). This paper describes a preliminary evaluation of achievement level of JSFR to the risk targets at the FaCT project phase-I: JFY2006 to JFY2010. A Level-1 PSA has been implemented preliminarily to evaluate the CDF related to internal initiators in power operation. The calculated CDF became lower than the both requirements on CDF and CFF. For seismic events, the seismic fragility of principal structures and components was evaluated in terms of core damage prevention. This evaluation was based on the seismic response analysis, which considered the seismic isolation effect and the hardening effect of the laminated rubber bearing in the isolation devices. As a result, we confirmed that the principal structures and components of JSFR have sufficient seismic margin. Based on this, we judged the risk target could be achieved against the seismic event.
Furukawa, Tomohiro; Kato, Shoichi; Inagaki, Yoshiyuki; Aritomi, Masanori*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 5 Pages, 2011/10
A key problem in the application of a supercritical carbon dioxide (CO ) turbine cycle to a fast breeder reactor is the corrosion of structural materials brought about by supercritical CO
) turbine cycle to a fast breeder reactor is the corrosion of structural materials brought about by supercritical CO at high temperatures. In this study, high-temperature oxidation tests on the structural materials were performed in carbon dioxide pressurized at 0.2 and 1 MPa, and in air, and the oxidation behavior were compared. Results of investigating the effect of CO
at high temperatures. In this study, high-temperature oxidation tests on the structural materials were performed in carbon dioxide pressurized at 0.2 and 1 MPa, and in air, and the oxidation behavior were compared. Results of investigating the effect of CO pressure including the previous reports tested at 10 MPa and at 20 MPa, the effect was hardly observed for all steels. In air environment, weight gain caused by high temperature oxidation was much lower than that in CO
pressure including the previous reports tested at 10 MPa and at 20 MPa, the effect was hardly observed for all steels. In air environment, weight gain caused by high temperature oxidation was much lower than that in CO .
.
Kamiji, Yu; Terada, Atsuhiko; Sugiyama, Hitoshi*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2011/10
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has been conducting R&D on heat utilizing system of High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR). Toward the lower energy consumption and cost reduction of system, we think it is effective to develop waste heat recovery technology. For hydrogen production by thermochemical iodine sulfur process (IS process) which is considered as one of the heat utilization, temperature control unit is an important factors for stable process system driving. Authors focused gas-mixing temperature control and proceeded to design high performance compact unit for process recuperators. From experimental results, in the case of door opening inclining toward flow, there was quite high turbulent kinetic energy up to 3.0U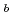
 because of effects of turbulence from separation at tip of the door. Additionally in that door opening, heated flow partially goes to door, so that mixture starts in upstream of mixing region and temperature diffusion gets quite active.
because of effects of turbulence from separation at tip of the door. Additionally in that door opening, heated flow partially goes to door, so that mixture starts in upstream of mixing region and temperature diffusion gets quite active.
Goto, Minoru; Shimakawa, Satoshi; Tachibana, Yukio
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2011/10
In the past, benchmark calculations of criticality approach for the HTTR, which is a Japanese HTGR, were performed by research institutes in several countries, and almost all of the calculations overestimated the excess reactivity. In Japan, the benchmark calculations were performed by JAEA, and were also resulted in overestimation. JAEA improved the calculations by revising the geometric model and replacing the nuclear data library with JENDL-3.3, which was the latest JENDL at that time. However, the overestimation remained and this problem has not been resolved until today. We performed calculations of the HTTR criticality approach with several nuclear data libraries, and found that slight difference in the neutron capture cross section of carbon at thermal energy among the libraries causes significant difference in the 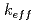 values. The cross section value of carbon was not concerned in reactor neutronics calculation because of its small value of the order of 1E-3 burn, and consequently the cross section value had not been revised for a long time even in the major nuclear data libraries: JENDL, ENDF/B and JEFF. We thought that the cross section should be revised based on the latest measurement data to improve the accuracy of the HTGR criticality analysis. In May 2010, the latest JENDL (JENDL-4.0) was released by JAEA, and the capture cross section of carbon was revised. JENDL-4.0 yielded 0.4-0.9%
values. The cross section value of carbon was not concerned in reactor neutronics calculation because of its small value of the order of 1E-3 burn, and consequently the cross section value had not been revised for a long time even in the major nuclear data libraries: JENDL, ENDF/B and JEFF. We thought that the cross section should be revised based on the latest measurement data to improve the accuracy of the HTGR criticality analysis. In May 2010, the latest JENDL (JENDL-4.0) was released by JAEA, and the capture cross section of carbon was revised. JENDL-4.0 yielded 0.4-0.9% k/k smaller
k/k smaller 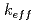 values than JENDL-3.3 in the criticality calculations for the HTTR critical approach, and consequently the problem of the overestimation of the excess reactivity in the HTTR benchmark calculation was resolved by replacing the nuclear data libraries with JENDL-4.0.
values than JENDL-3.3 in the criticality calculations for the HTTR critical approach, and consequently the problem of the overestimation of the excess reactivity in the HTTR benchmark calculation was resolved by replacing the nuclear data libraries with JENDL-4.0.
Takeda, Takeshi; Maruyama, Yu; Watanabe, Tadashi; Nakamura, Hideo
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2011/10
Experiments simulating PWR intermediate-break loss-of-coolant accidents (IBLOCAs) with 17% break at hot leg or cold leg were conducted in OECD/NEA ROSA-2 project using LSTF. In the hot leg IBLOCA test, core uncovery appeared simultaneously with loop seal clearing (LSC). Water remained on upper core plate in upper plenum due to CCFL. In the cold leg IBLOCA test, core dryout took place before LSC. Liquid was accumulated in upper plenum, SG U-tube upflow-side and SG inlet plenum before the LSC due to CCFL. The RELAP5/MOD3.2.1.2 post-test analyses were performed. In the hot leg IBLOCA case, cladding surface temperature was underpredicted due to overprediction of core liquid level after the core uncovery. In the cold leg IBLOCA case, the cladding surface temperature was underpredicted too due to later core uncovery than in the experiment. These may suggest that the code has remaining problems in proper prediction of primary coolant distribution.
Ohno, Shuji; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Tajima, Yuji*; Oki, Hiroshi*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
Conceptual design study of the JSFR needs the evaluation of thermodynamic consequences in hypothetical sodium fire accident. The authors are therefore initiating systematic V&V activity for sodium fire evaluation tools. The activity is in progress with the main focuses on already developed sodium fire analysis codes SPHINCS and AQUA-SF. The present paper describes that a preliminary "PIRT" is developed at first, and an "assessment matrix" is proposed which summarizes both separate effect tests (SET) and integral effect tests (IET) for validating the computational models or whole code for important phenomena. Furthermore, the paper shows an individual validation with SET in which the spray droplet combustion model of SPHINCS and AQUA-SF predicts the burned amount of a falling sodium droplet with the error mostly less than 30%.
Kurikami, Hiroshi; Niizato, Tadafumi; Yasue, Kenichi
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
Description of system evolution is an important task in safety and investigation strategies. This paper showed the method to describe system evolution based on safety functions and FEPs and its application to the Horonobe site. Based on the SDM and the Horonobe-specific FEPs, the important FEPs were put in a timeline with the main safety functions. According to the FEPs, we defined thermal and resaturation phase, steady geology phase and geologically evolution phase. In the steady geology phase, the functions of retardation and dilution in the deeper part of the Wakkanai Formation are important, therefore, advection, dispersion and sorption in the domain should be assessed based on the nuclide migration scenario. In the geologically evolution phase, the uplift and denudation are important. Thus, the uplift, denudation and the consequent THMC processes were involved in the reference evolution. Through the application and the discussion, the method was found to be applied to other sites.
Maeda, Shigetaka; Ito, Chikara; Sekine, Takashi; Aoyama, Takafumi
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
The verification of calculated core characteristics of the Joyo MK-III core using the JUPITER fast reactor standard analysis method was conducted by comparing with the measured values through the core physics tests. The purpose is to upgrade the core performance to increase the driver fuel burn-up and to increase the excess reactivity necessary for conducting various irradiation tests in the core region. Most of the C/Es are within 5% of unity. Through the comparisons, the calculation accuracy of the JUPITER standard analysis method for a small size sodium cooled fast reactor with a hard neutron spectrum like Joyo was clarified. As a result of this study, more irradiation tests can be performed with appropriate safety margin and the efficient core and fuel management can be achieved to save the number of refueling.
Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Nagae, Masahiro*; Ioka, Ikuo; Iwatsuki, Jin; Kubo, Shinji; Onuki, Kaoru
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 4 Pages, 2011/10
The Thermochemical water-splitting cycle IS process constitutes severe environments to the materials of construction because of the corrosive chemicals. This paper discusses corrosion resistance of novel metallic materials in high temperature sulfuric and hydriodic acid. As for the sulfuric acid environment, corrosion resistances of MoN, Mo-Ta-N, and Mo-Cr-N alloys were examined. The experiments were performed for the duration of 5 hour in 90wt% sulfuric acid at 300 C. Although no material showed satisfactory corrosion resistance (ca. 1.5 mm/y in the case of MoN), the addition of Ta or Cr was found to be effective to improve the corrosion resistance. As for the hydriodic acid environment, corrosion resistance of Nb-W alloy was examined by immersing the test pieces for up to 100 hours in the test solutions of 200
C. Although no material showed satisfactory corrosion resistance (ca. 1.5 mm/y in the case of MoN), the addition of Ta or Cr was found to be effective to improve the corrosion resistance. As for the hydriodic acid environment, corrosion resistance of Nb-W alloy was examined by immersing the test pieces for up to 100 hours in the test solutions of 200 C. It was observed that the corrosion rates lowered with the progress of immersion time and reached to a stable value of lower than 0.1 mm/y.
C. It was observed that the corrosion rates lowered with the progress of immersion time and reached to a stable value of lower than 0.1 mm/y.
Sugiyama, Katsuteru*; Noguchi, Hiroki; Takegami, Hiroaki; Onuki, Kaoru; Kaneko, Akiko*; Abe, Yutaka*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2011/10
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has been conducting R&D on thermo-chemical IS process, which is one of most attractive water-splitting hydrogen production methods using nuclear heat of a high temperature gas-cooled reactor. The present study concerns with development of IS process equipment utilizing direct contact heat exchanger (DCHX). The application of DCHX to the sulfuric acid decomposition step of IS process has been proposed such that the decomposed gas contacts with the sulfuric acid solution supplied from the Bunsen reaction step. The concept is very attractive in terms of the development of compact and efficient sulfuric acid concentrator. However, little is known on the behavior of sulfuric acid in the DCHX, which is required for the equipment design. Therefore, we considered an experimental acquisition of essential design parameter of the DCHX, the gas-phase mass transfer coefficient.
Chikazawa, Yoshitaka; Kato, Atsushi; Obata, Hiroyuki*; Nishiyama, Noboru; Uzawa, Masayuki*; Tozawa, Katsuhiro*; Chishiro, Ryo*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2011/10
A preliminary design of the JSFR fuel handling system has been proposed. FaCT phase I results of key technology evaluations on preliminary safety assessment, a pantograph fuel handling machine, a sodium pot with two core component positions, dry spent fuel cleaning and minor actinide-bearing fresh fuel shipping cask are provided.
Noguchi, Akira; Kishi, Hirokazu; Hatanaka, Koichiro; Naito, Morimasa
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2011/10
A standardized method for choosing a mix design of low pH shotcrete is proposed for their intended use in the construction of a High Level Radioactive Waste (HLW) repository in order to be applied to the various geological environment of the location of the HLW repositories. There are two improvement in this method. One is estimating binder composition to satisfy low pH. The other is estimating water bender ratio to satisfy the strength of sprayed concrete. The method uses a sequential development process with consideration given to a number of physicochemical requirements, incorporates current shotcrete technology. The method is demonstrated in its entirety through a series of experiments and tests using a low pH cement binder comprised of a mixture of ordinary Portland cement, fly ash (FA) and silica fume (SF), referred to here as high-volume FA SF cement (HFSC). Moreover, the method is referred from the demonstration of HFSC shotcrete in Horonobe underground research laboratory.
Iwamoto, Yukiharu*; Kondo, Manabu*; Yasuda, Kazunori*; Sogo, Motosuke*; Tanaka, Masaaki; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
Tani, Akihiro*; Shimakawa, Yoshio*; Kubo, Shigenobu*; Fujimura, Ken; Yamano, Hidemasa
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
Baba, Takeo*; Hirota, Kazuo*; Sago, Hiromi*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Aizawa, Kosuke; Xu, Y.*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 9 Pages, 2011/10
Kikuchi, Shin; Ohshima, Hiroyuki; Hashimoto, Kenro*
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/10
In a sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), liquid sodium is used as heat transfer fluid to carry the energy from the reactor core to the steam generation (SG) system for power generation. If the heat transfer tube in the SG is failed, high pressurized water vapor blows into the liquid sodium and the sodium-water reaction (SWR) takes place. The extremely high temperature reaction jet formed by the SWR causes damage to the surface of the neighboring heat transfer tubes by thermal and chemical effects. Therefore, it is important to clearly understand the SWR for safety assessment of SG. In this work, we studied the surface reaction in the SWR by using ab initio calculations. The successive OH cleavages of a water molecule at the liquid sodium surface were focused. The possible reaction path and the related energies including the barrier heights were reported. The relative rates of the OH cleavages were also discussed.
Obayashi, Hironari; Sugawara, Takanori; Nishihara, Kenji
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2011/10
Takamatsu, Kuniyoshi; Ueta, Shohei; Sawa, Kazuhiro
Proceedings of 19th International Conference on Nuclear Engineering (ICONE-19) (CD-ROM), 10 Pages, 2011/10
The three gas circulators trip test and the vessel cooling system stop test as the safety demonstration test by using the High Temperature engineering Test Reactor (HTTR) are under planning to demonstrate inherent safety features of High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR). All three gas circulators to circulate the helium gas as the coolant are stopped to simulate the loss of forced cooling in the three gas circulators trip test. The stop of the vessel cooling system located outside the Reactor Pressure Vessel (RPV) to remove the residual heat of the reactor core follows the stop of all three gas circulators in the vessel cooling system stop test. The analysis of the reactor transient for such tests and abnormal events postulated during the test is performed. From the result of analysis, it is confirmed that the three gas circulators trip test and the vessel cooling system stop test can be performed within the region of the normal operation in the HTTR.