Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Matsukawa, Makoto; JA-EU Satellite Tokamak Working Group; JT-60SA Design Team
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Urano, Hajime; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Koide, Yoshihiko; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Takizuka, Tomonori; Yoshida, Maiko; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
The pedestal pressure and energy confinement of H-mode plasmas were improved by the reduction of toroidal field (TF) ripple with the installation of ferritic steel tiles (FSTs) in JT-60U. The profile of toroidal rotation 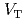 became less counter and the pedestal pressure
became less counter and the pedestal pressure 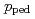 is increased with FSTs particularly in case where co-NBI was used at a large volume configuration. ELM frequency
is increased with FSTs particularly in case where co-NBI was used at a large volume configuration. ELM frequency 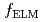 was reduced and ELM energy loss
was reduced and ELM energy loss 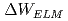 was increased. For increased
was increased. For increased 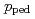 due to
due to 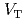 enhanced in co-direction and the reduction of TF ripple, the spatial width of H-mode pedestal became wider. The energy confinement was improved by enhancing
enhanced in co-direction and the reduction of TF ripple, the spatial width of H-mode pedestal became wider. The energy confinement was improved by enhancing 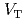 in co-direction and by the reduction of TF ripple.
in co-direction and by the reduction of TF ripple.
Shinohara, Koji; Sakurai, Shinji; Ishikawa, Masao; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro*; Suzuki, Yutaka; Masaki, Kei; Naito, Osamu; Kurihara, Kenichi; Suzuki, Takahiro; Koide, Yoshihiko; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Ferritic steel plates have been installed to improve the energetic ion confinement through reducing a toroidal magnetic field ripple. Aiming at cost-effective installation, orbit following calculations of energetic ions were performed for a design of ferritic installation on JT-60U by using the Fully three Dimensional magnetic field Orbit-Following Monte-Carlo (F3D OFMC) code. The installed ferritic steel adds the non-linear magnetic field on magnetic sensors for a plasma control and an equilibrium calculation. The code for a real-time control have been modified to take into account the magnetic field by ferritic steel. The plasma operation was successfully resumed and a real-time plasma control was successfully carried out after usual preparation processes. The heat load measurement indicates the improved confinement of energetic ions. These results are important for practical application of ferritic steel which is a leading candidate of a structural material on a demo reactor.
Horiike, Hiroshi*; Kondo, Hiroo*; Nakamura, Hiroo; Miyamoto, Seiji*; Yamaoka, Nobuo*; Matsushita, Izuru*; Ida, Mizuho; Ara, Kuniaki; Muroga, Takeo*; Matsui, Hideki*
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Ioki, Kimihiro; Chuyanov, V.*; Elio, F.*; Garkusha, D.*; Gribov, Y.*; Lamzin, E.*; Morimoto, Masaaki; Shimada, Michiya; Sugihara, Masayoshi; Terasawa, Atsumi; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Two important design updates have been made in the ITER VV and in-vessel components recently. One is the introduction of limiters moveable during a plasma discharge, and the other is optimization of the ferromagnetic insert configuration to minimize the toroidal field ripple. In the new limiter concept, the limiters are retracted by 8 cm during the plasma flat top phase in the divertor configuration. This concept gives important advantages: (1) the particle and heat loads due to disruptions, ELMs and blobs on the limiters will be mitigated approximately by a factor 1.5 or more; (2) the gap between the plasma and the ICRH antenna can be reduced to improve the coupling of the ICRH power. The ferromagnetic inserts have previously not been planned to be installed in the outboard midplane region between equatorial ports due to irregularity of tangential ports for NB injection. The result is a relatively large ripple (1 %) in a limited region of the plasma, which nevertheless seems acceptable from the plasma performance viewpoint. However, toroidal field flux lines fluctuate 10 mm due to the large ripple in the FW region. To avoid problems due to the large TF flux line fluctuation, additional ferromagnetic inserts are now planned to be installed in the equatorial port region.
Sakamoto, Keishi; Kasugai, Atsushi; Takahashi, Koji; Minami, Ryutaro*; Kariya, Tsuyoshi*; Mitsunaka, Yoshika*; Kobayashi, Noriyuki
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Sato, Satoshi; Verzilov, Y.*; Ochiai, Kentaro; Wada, Masayuki*; Kubota, Naoyoshi; Kondo, Keitaro; Yamauchi, Michinori; Nishitani, Takeo; Konno, Chikara
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Asakura, Nobuyuki; Ono, Noriyasu*; Kawashima, Hisato; Miyoshi, Hideaki*; Matsunaga, Go; Oyama, Naoyuki; Takamura, Shuichi*; Uesugi, Yoshihiko*; Takechi, Manabu; Nakano, Tomohide; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Radial transport of the SOL plasma was recently studied in order to understand heat and particle loading to the first wall and the SOL formation mechanism. Fast propagation of the ELM plasma and fluctuation properties in H- and L-modes were determined at low-field-side (LFS) SOL using reciprocating Mach probes in JT-60U. Large and short peaks were found in ELM plasma flux, which was regularly enhanced after each ELM event. Transport dynamics of the first large 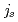 peak was determined, i.e. it propagated to near the first wall with the fast velocity of 1.3-2.5 km/s. Statistical analysis of a probability distribution function was applied to describe intermittent (non-diffusion) transport in SOL plasma fluctuations. It was found that the positive bursty events appeared in a wide SOL region, where the flow reversal of the SOL plasma was observed. Influences of the radial transport of the convective blobby plasma on the SOL formation and the flow reversal were investigated.
peak was determined, i.e. it propagated to near the first wall with the fast velocity of 1.3-2.5 km/s. Statistical analysis of a probability distribution function was applied to describe intermittent (non-diffusion) transport in SOL plasma fluctuations. It was found that the positive bursty events appeared in a wide SOL region, where the flow reversal of the SOL plasma was observed. Influences of the radial transport of the convective blobby plasma on the SOL formation and the flow reversal were investigated.
Kubo, Hirotaka; Nakano, Tomohide; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Tsuzuki, Kazuhiro; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kawashima, Hisato; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Urano, Hajime; Fujimoto, Kayoko; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Aiba, Nobuyuki; Tokuda, Shinji; Takizuka, Tomonori; Kurita, Genichi; Ozeki, Takahisa
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Stabilities of peeling, ballooning and peeling-ballooning modes, which relate to edge-localized modes (ELMs), are investigated numerically with the linear ideal magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) stability code MARG2D. Effects of "sharpness" on the stability of the peeling-ballooning mode are examined, where the sharpness is defined in terms of the curvature at the top and bottom of the outermost flux surface. It is found for the first time that the stable pressure gradient significantly improves as the sharpness increases even when the ellipticity and the triangularity are unchanged. The sharpness is an important parameter for high performance H-mode operations with high pedestal pressure.
Yoshida, Maiko; Koide, Yoshihiko; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Urano, Hajime; Oyama, Naoyuki; Kamiya, Kensaku; Sakamoto, Yoshiteru; Kamada, Yutaka; JT-60 Team
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Nakano, Tomohide; Kubo, Hirotaka; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Shimizu, Katsuhiro; Konoshima, Shigeru; Fujimoto, Kayoko; Kawashima, Hisato; Higashijima, Satoru
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Volume recombination of C and
and 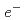 into C
into C is observed for the first time in detached plasmas with MARFE. It is found that the recombination flux of C
is observed for the first time in detached plasmas with MARFE. It is found that the recombination flux of C to C
to C is comparable to the ionization flux of C
is comparable to the ionization flux of C to C
to C , and that the recombination zone is above an X-point and beneath the ionization zone. This result suggests that this volume recombination predominantly produces C
, and that the recombination zone is above an X-point and beneath the ionization zone. This result suggests that this volume recombination predominantly produces C ions, which contribute 60-80 % to the total radiation power in the divertor plasma.
ions, which contribute 60-80 % to the total radiation power in the divertor plasma.
Miyato, Naoaki; Kishimoto, Yasuaki; Li, J. Q.*
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
Zonal flow behaviour and its effect on turbulent transport in tokamak plasmas are investigated by global fluid simulations of electrostatic ion temperature gradient (ITG) driven turbulence. It is found that oscillatory zonal flows called geodesic acoustic modes (GAMs) appearing in a high  (safety factor) region have the same frequency in a certain radial region whose width is almost proportional to
(safety factor) region have the same frequency in a certain radial region whose width is almost proportional to 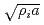 in positive shear tokamaks, and the radial wavelength of the GAMs is proportional to
in positive shear tokamaks, and the radial wavelength of the GAMs is proportional to 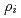 , where
, where 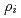 is an ion Larmor radius and
is an ion Larmor radius and  is a minor radius of a plasma. The turbulent transport is affected by the nonlocal behaviour of the GAMs. It seems that the radial width of the region connecting a low tranport region where the stationary zonal flows are dominant with a high transport region where the GAMs are dominant is related with the nonlocal width of the GAMs. In reversed shear tokamaks with high
is a minor radius of a plasma. The turbulent transport is affected by the nonlocal behaviour of the GAMs. It seems that the radial width of the region connecting a low tranport region where the stationary zonal flows are dominant with a high transport region where the GAMs are dominant is related with the nonlocal width of the GAMs. In reversed shear tokamaks with high  , turbulent transport is high even in a minimum
, turbulent transport is high even in a minimum  region because the GAMs are dominant. The turbulent transport is reduced in the minimum
region because the GAMs are dominant. The turbulent transport is reduced in the minimum  region when
region when  is enough low to damp the GAMs. The difference of zonal flow behaviour causes the difference of the turbulent transport and may trigger formation of ion internal transport barriers in both positive and reversed shear tokamaks.
is enough low to damp the GAMs. The difference of zonal flow behaviour causes the difference of the turbulent transport and may trigger formation of ion internal transport barriers in both positive and reversed shear tokamaks.
Tsuchiya, Kunihiko; Hoshino, Tsuyoshi; Kawamura, Hiroshi; Mishima, Yoshinao*; Yoshida, Naoaki*; Terai, Takayuki*; Tanaka, Satoru*; Munakata, Kenzo*; Kato, Shigeru*; Uchida, Munenori*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Kubota, Naoyoshi; Ochiai, Kentaro; Kutsukake, Chuzo; Hayashi, Takao; Shu, Wataru; Kondo, Keitaro; Verzilov, Y.*; Sato, Satoshi; Yamauchi, Michinori; Nishi, Masataka; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 7 Pages, 2007/03
Fuel and impurity particles show complicated behavior on the surface of plasma facing components (PFC) in fusion devices. The study is important for the design of the fuel recycling, safety management of the tritium inventory, etc. Quantitative measurements of hydrogen and lithium isotopes together with other impurities on the PFC surface exposed to D-T plasmas in TFTR were performed using the deuteron-induced nuclear reaction analysis, imaging plate method, full combustion method and activation analysis. The tritium depth profile was different from deuterium one. The surface tritium largely contributed to the whole tritium in the sample. On the other hand, the retained amount of lithium-6 was lager than that of lithium-7. This relates to the injection of enriched lithium-6 pellets in some campaigns. No other impurities were detected. So the large amount of tritium remained near the surface and did not diffuse more deeply, which gives a bright prospect for tritium safety.
Tanigawa, Hiroyasu; Shiba, Kiyoyuki; Hirose, Takanori; Kasada, Ryuta*; Wakai, Eiichi; Jitsukawa, Shiro; Kimura, Akihiko*; Koyama, Akira*
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2007/03
The status of research and development of reduced activation martensitic steels (RAMs) in Japan are reviewed and key issues suggested from recent achievements in Japan since the last conference are highlighted, with the aim of the fabrication for the ITER Test Blanket Module (TBM) and application for the DEMO reactor. It was pointed out that international collaboration would be desirable for research on key issues such as precipitate stability under irradiation or Ta effects which are common for all RAMs and require an extensive research effort.
Kobayashi, Kazuhiro; Isobe, Kanetsugu; Iwai, Yasunori; Hayashi, Takumi; Shu, Wataru; Nakamura, Hirofumi; Kawamura, Yoshinori; Yamada, Masayuki; Suzuki, Takumi; Miura, Hidenori*; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Isayama, Akihiko; Oyama, Naoyuki; Urano, Hajime; Suzuki, Takahiro; Takechi, Manabu; Hayashi, Nobuhiko; Nagasaki, Kazunobu*; Kamada, Yutaka; Ide, Shunsuke; Ozeki, Takahisa; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
no abstracts in English
Suzuki, Takahiro; Ide, Shunsuke; Oikawa, Toshihiro; Fujita, Takaaki; Ishikawa, Masao*; Seki, Masami; Matsunaga, Go; Takechi, Manabu; Naito, Osamu; Hamamatsu, Kiyotaka; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
For the first time, we have measured the current density profile for off-axis neutral beam current drive (NBCD), using motional Stark effect (MSE) diagnostic. A spatially localized NBCD profile was clearly observed at 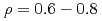 . The location was also confirmed by neutron emission profile measurement. The total amount of the driven current (0.15MA) was consistent with the decrease in the surface loop voltage. The off-axis current drive can raise safety factor (q) in the center and help to avoid instability that limits performance of the plasma. We have developed a real-time control system of the minimum q (qmin), using the off-axis current drive. Injection power of lower hybrid (LH) waves, and hence, its off-axis driven current controls qmin. In a high
. The location was also confirmed by neutron emission profile measurement. The total amount of the driven current (0.15MA) was consistent with the decrease in the surface loop voltage. The off-axis current drive can raise safety factor (q) in the center and help to avoid instability that limits performance of the plasma. We have developed a real-time control system of the minimum q (qmin), using the off-axis current drive. Injection power of lower hybrid (LH) waves, and hence, its off-axis driven current controls qmin. In a high  plasma (
plasma (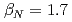 ,
, 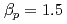 ), the system was adopted to control qmin. With the control, qmin was raised and MHD fluctuations were suppressed. The stored energy increased by 16% with the MHD fluctuations suppressed.
), the system was adopted to control qmin. With the control, qmin was raised and MHD fluctuations were suppressed. The stored energy increased by 16% with the MHD fluctuations suppressed.
Oyama, Naoyuki; Isayama, Akihiko; Suzuki, Takahiro; Koide, Yoshihiko; Takenaga, Hidenobu; Ide, Shunsuke; Nakano, Tomohide; Asakura, Nobuyuki; Kubo, Hirotaka; Takechi, Manabu; et al.
Proceedings of 21st IAEA Fusion Energy Conference (FEC 2006) (CD-ROM), 8 Pages, 2007/03
After installation of ferritic steel tiles (FSTs) which reduced fast ion losses due to toroidal field ripple, the performance of long-pulse ELMy H-mode plasmas was improved in terms of sustained duration time for both high normalized beta (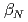 ) and high thermal confinement enhancement factor (
) and high thermal confinement enhancement factor (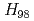 ). High
). High 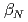
 2.3 together with
2.3 together with 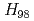
 1 was sustained for 23.1s (
1 was sustained for 23.1s ( 12
12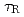 )
) 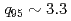 , which also provide high
, which also provide high 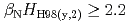 , which is higher than ITER reference scenario. These long-pulse plasmas are possible candidates for ITER hybrid operation scenario.
, which is higher than ITER reference scenario. These long-pulse plasmas are possible candidates for ITER hybrid operation scenario.