Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; Morishita, Takatoshi; Otani, Masashi*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Yoshida, Mitsuhiro*; Kitamura, Ryo*; et al.
Proceedings of 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '18) (Internet), p.5041 - 5046, 2018/06
J-PARC is developing the reacceleration system of the ultra slow (30 meV) muon (USM) obtained by two-photon laser resonant ionization of muonium atoms. The muon beam thus obtained has low emittance, meeting the requirement for the g-2/EDM experiment. J-PARC E34 experiment aims to measure the muon anomalous magnetic moment (g-2) with a precision of 0.1 ppm and search for EDM with a sensitivity to 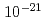 e cm. The USM's are accelerated to 212 MeV by using a muon dedicated linac to be a ultra cold muon beam. The muon LINAC consists of an RFQ, a inter-digital H-mode DTL, disk and washer coupled cell structures, and disk loaded structures. Proof of the slow muon acceleration scheme is an essential step to realize the world first muon linac. In October 2017, we have succeeded to accelerate slow negative muoniums generated using a simpler muonium source to 89 keV. In this talk, present design of the muon linac and the result of the world first muon acceleration experiment are reported.
e cm. The USM's are accelerated to 212 MeV by using a muon dedicated linac to be a ultra cold muon beam. The muon LINAC consists of an RFQ, a inter-digital H-mode DTL, disk and washer coupled cell structures, and disk loaded structures. Proof of the slow muon acceleration scheme is an essential step to realize the world first muon linac. In October 2017, we have succeeded to accelerate slow negative muoniums generated using a simpler muonium source to 89 keV. In this talk, present design of the muon linac and the result of the world first muon acceleration experiment are reported.
Miura, Akihiko; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Miyao, Tomoaki*
Proceedings of 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '18) (Internet), p.5022 - 5025, 2018/06
A wire-scanner monitor using metallic wire is reliably employed for the beam-profile measurement in the J-PARC linac. Because the loading of negative hydrogen (H ) ion beam on a wire increases under high-current beam operation, we focus on using a high-durability beam profile monitors by attaching another wire material. Carbon nanotubes (CNT) are made of graphite in a cylindrical shape and have a tensile strength not less than 100 times that of steel. The electric conductivity has higher than that of metals, and hardness is endured thermally around 3000
) ion beam on a wire increases under high-current beam operation, we focus on using a high-durability beam profile monitors by attaching another wire material. Carbon nanotubes (CNT) are made of graphite in a cylindrical shape and have a tensile strength not less than 100 times that of steel. The electric conductivity has higher than that of metals, and hardness is endured thermally around 3000 C in a vacuum circumstance. We applied the wires made from CNT to WSM and measured transverse profiles with a 3-MeV H
C in a vacuum circumstance. We applied the wires made from CNT to WSM and measured transverse profiles with a 3-MeV H beam. As a result, we obtained the equivalent signal levels taken by carbon wire made of polyacrylonitrile without any damage. In this paper, the signal response when the CNT is irradiated with an H
beam. As a result, we obtained the equivalent signal levels taken by carbon wire made of polyacrylonitrile without any damage. In this paper, the signal response when the CNT is irradiated with an H beam and the result of beam profile measurement. In addition, the surface of CNT after 3-MeV beam operation was observed.
beam and the result of beam profile measurement. In addition, the surface of CNT after 3-MeV beam operation was observed.
Saha, P. K.; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Hotchi, Hideaki; Harada, Hiroyuki; Hayashi, Naoki; Tamura, Fumihiko
Proceedings of 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '18) (Internet), p.620 - 623, 2018/06
Yamamoto, Kazami; Saha, P. K.
Proceedings of 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '18) (Internet), p.1045 - 1047, 2018/06
The 3 GeV rapid cycling synchrotron (RCS) at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) provides more than 500 kW beams to the Material and Life Science Facility (MLF) and Main Ring (MR). In such a high-intensity hadron accelerator, even losing less than 0.1% of the beam can cause many problems. Such lost protons can cause serious radio-activation and accelerator component malfunctions. Therefore, we have conducted a beam study to achieve high-power operation. In addition, we have also maintained the accelerator components to enable stable operation. This paper reports the status of the J-PARC RCS over the last two years.
Meigo, Shinichiro; Matsuda, Hiroki; Iwamoto, Yosuke; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Hasegawa, Shoichi; Maekawa, Fujio; Yoshida, Makoto*; Ishida, Taku*; Makimura, Shunsuke*; Nakamoto, Tatsushi*
Proceedings of 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '18) (Internet), p.499 - 501, 2018/06
no abstracts in English
Kitamura, Ryo*; Otani, Masashi*; Fukao, Yoshinori*; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Miyake, Yasuhiro*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Kazuo; et al.
Proceedings of 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '18) (Internet), p.1190 - 1193, 2018/06
Muon acceleration using radio-frequency accelerators makes it possible to precisely measure the muon anomalous magnetic moment and the electric dipole moment. The first muon acceleration was demonstrated using a radio-frequency quadrupole (RFQ) linac. A negative muonium ion (Mu ) with less than 2 keV energy was produced from an incident muon with 3 MeV energy using a thin aluminum foil target in order to cool the muon beam for the acceleration, because the designed input energy of the RFQ is 5.6 keV. The Mu
) with less than 2 keV energy was produced from an incident muon with 3 MeV energy using a thin aluminum foil target in order to cool the muon beam for the acceleration, because the designed input energy of the RFQ is 5.6 keV. The Mu was first accelerated to 5.6 keV using an electrostatic accelerator, and was subsequently accelerated to 90 keV using the RFQ. This accelerated Mu
was first accelerated to 5.6 keV using an electrostatic accelerator, and was subsequently accelerated to 90 keV using the RFQ. This accelerated Mu was selected using a diagnostic beam line and was identified based on Time-Of-Flight measurements.
was selected using a diagnostic beam line and was identified based on Time-Of-Flight measurements.
 ion beam derived from the ultraviolet light
ion beam derived from the ultraviolet lightNakazawa, Yuga*; Iinuma, Hiromi*; Otani, Masashi*; Kawamura, Naritoshi*; Mibe, Tsutomu*; Yamazaki, Takayuki*; Kitamura, Ryo*; Kondo, Yasuhiro; Saito, Naohito; Sue, Yuki*
Proceedings of 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '18) (Internet), p.997 - 1000, 2018/06
A muon LINAC is under research and development for a precise measurement of muon g-2/EDM at J-PARC. We conducted an experiment of a muon RF acceleration on October and December, 2017. The surface muon beam is irradiated to a metal degrader to generate slow negative muonium. The slow muoniums are accelerated to 90keV with an electrostatic accelerator and an RFQ. Prior to muon RF acceleration, we conducted a commissioning of the diagnostic beam line consisting of two quadrupole magnets and a bending magnet. The ultraviolet light is irradiated to an aluminum foil and forms H ion. It is accelerated with the electrostatic accelerator and can be detected as a pseudo muon beam. This system allowed us to check operation for the diagnostic beam line, which is essential task for transportation and momentum selection of the negative muonium. In this presentation, I would like to report the performance evaluation of the diagnostic beam line by H
ion. It is accelerated with the electrostatic accelerator and can be detected as a pseudo muon beam. This system allowed us to check operation for the diagnostic beam line, which is essential task for transportation and momentum selection of the negative muonium. In this presentation, I would like to report the performance evaluation of the diagnostic beam line by H ions.
ions.
Takahashi, Hiroki; Miura, Akihiko; Sawabe, Yuki; Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Suzuki, Takahiro*; Kawase, Masato*
Proceedings of 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '18) (Internet), p.2180 - 2182, 2018/06
The stepping motor control system used in the profile monitor and RCS collimator of J-PARC is configured by VME-based. Most of these pieces of control equipment are in use for more than 10 years. Therefore, countermeasures against aging of equipment are necessary. In addition, it is necessary to implement countermeasures against malfunction of the control system, which is thought to be caused by radiation. In 2016, a malfunction occurred in the motor control system of the RCS collimator. Taking this as a starting point, we began developing a motor control system that can ensure equipment safety even if a malfunction occurs. In this paper, we show the inference of the cause of this malfunction and present details of the developed high-safety motor control system.
Miura, Akihiko; Kawane, Yusuke*; Moriya, Katsuhiro; Futatsukawa, Kenta*; Miyao, Tomoaki*; Fukuoka, Shota*
Proceedings of 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '18) (Internet), p.2183 - 2186, 2018/06
In order to mitigate the beam loss during a beam transportation in the high-brilliant accelerator facilities, wire-based profile monitors are used to measure by both transverse and longitudinal beam profiles using wire-scanner monitors and bunch-shape monitors for the tuning of quadrupole magnets and buncher cavities. Signals are generated due to the direct interaction between a metallic wire and beam. We have used the tungsten wire as a high melting-point material by estimation of heat loading during the impact of beam particles. In addition, a spring is applied for the relaxing a flexure under wire's own weight. A tensile fracture test is conducted by supplying an electrical current as a simulated beam loading. As the results, we obtained the relation between the thermal limit to fracture and tension loading of tungsten wire.
Hotchi, Hideaki; Watanabe, Yasuhiro; Harada, Hiroyuki; Okabe, Kota; Saha, P. K.; Shobuda, Yoshihiro; Tamura, Fumihiko; Yoshimoto, Masahiro
Proceedings of 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '18) (Internet), p.1041 - 1044, 2018/06
Hasegawa, Kazuo; Hayashi, Naoki; Oguri, Hidetomo; Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu; Yamazaki, Yoshio; Naito, Fujio; Koseki, Tadashi; Yamamoto, Noboru; Yoshii, Masahito
Proceedings of 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '18) (Internet), p.1038 - 1040, 2018/06
Yoshimoto, Masahiro; Saha, P. K.; Kato, Shinichi; Okabe, Kota; Yamamoto, Kazami; Kinsho, Michikazu
Proceedings of 9th International Particle Accelerator Conference (IPAC '18) (Internet), p.1048 - 1050, 2018/06
The charge exchange multi-turn beam injection scheme is adopted in the J-PARC 3GeV Rapid Cycling Synchrotron Accelerator (RCS) due to achieve 1MW beam power operation. In the conventional multi-turn beam injection scheme, which is provided by only the septum and bump magnets, injecting turn numbers are limited by the beam losses at the septum. On the other hand, charge exchange multi-turn beam injection does not cause the beam losses at the septum; there is no restriction in principle on the injecting turn number. However, high residual doses are observed around the stripper foil. During the charge exchange multi-turn beam injection, not only the injecting beam but also circulating beam hit the foil, and then a large number of secondary particles, namely protons and neutrons, are generated. PHITS simulation results indicate that the secondary particles cause the high residual doses around the foil. To verify this examination, secondary particles measurement is key issue. Then, a new independent type foil introducing device is installed in the 100-deg dump beam transport line in order to construct a simple experimental system for secondary particle measurements. We plan the two experiments by using this system; one is a directly secondary particle detecting method, and the other is a radioactivation analysis method with metal sample pieces. Now, we started the study of how the identification of species and energies of the secondary particles with PHITS code. Irradiation target of Cu is adopted and irradiated proton or neutron beam with various energy range. Then radio-nuclides emitted the  -ray are picked up. Moreover, the radio-nuclides, whose reaction efficiencies due to beam species or energy are different, are searched for the indicator of the secondary particles. From the simulation results,
-ray are picked up. Moreover, the radio-nuclides, whose reaction efficiencies due to beam species or energy are different, are searched for the indicator of the secondary particles. From the simulation results,  Zn is extremely suitable for a proton beam indicator, and
Zn is extremely suitable for a proton beam indicator, and  Co and
Co and  Co are also suited for a neutron and proton indicator respectively.
Co are also suited for a neutron and proton indicator respectively.