Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
仲吉 彬; 小山 真一; 鷲谷 忠博
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/10
PreADESプロジェクトの活動は、多くの国際機関との連携の下で実施され、有用な知見を蓄積してきた。そのPreADESプロジェクトでは以下のタスクが議論された。(1)1F, TMI2,チェルノブイリの燃料デブリの特性を様々な分析と実験から明らかにした「燃料デブリ特性表」、(2)燃料デブリ分析に関する情報を整理した「燃料デブリ分析表」、「主要な問題と方法論の表」、「ホット施設の分析機能の表」。これらは、取得すべき分析データを特定し、燃料デブリのハンドリングのための実用的な適切かつ最適な方法論を示す。(3)将来の国際的な研究開発の枠組み。これらの活動や多くの議論を通じて、参加機関は将来の国際協力の成功にとって重要なことは、関連する組織間の柔軟な対話と情報交換であることを再認識した。現在、ポストPreADESプロジェクト「Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station Accident Information Collection and Evaluation (FACE)」プロジェクトが発足し、活発な議論が行われている。
Pshenichnikov, A.; 倉田 正輝; 永江 勇二
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/10
CLADS-MADE-04は、下部コア領域での溶融伝播挙動の理解を目的としたシリーズの次のテストである。この寄稿では、電子プローブ マイクロアナライザー(EPMA)によって調査された金属破片の微細構造を含む試験後分析の最近の結果について説明する。テスト中、制御棒ブレードの溶融は、比較的ゆっくりと(数cm/分)急激な強い熱放出の波で発生し、最も高温の領域から、劣化しつつある制御棒ブレードとチャネルボックスに沿って下方に広がり、ジルカロイ-4で作られた壁を消費した。サンプル支持板にも大きな損傷が発生した。このような金属リッチ破片の微細構造の調査により、強化された局所コア劣化のメカニズムを理解できるようになる。EPMAによる相同定を徹底した上で、放熱性が高く周囲への拡散の可能性があることを確認する必要がある。Fe-B共晶デブリとZr-Fe共晶デブリの違いについて概説する。これは、下部炉心プレートのメルトスルーと、下部プレナムへのZr-Fe溶融材料の進行の可能性を理解するために特に重要である。
鈴木 健太; 八代 大*; 川端 邦明
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/10
This paper describes a development of PHITSPlugin for the radiation behavior calculation. The developed plugin calculates a dose distribution in conjunction with Choreonoid which is a physical simulator. It was developed to contribute to estimate an integral radiation dose on the robots. We discuss a procedure for calculating the dose distribution. Also, we demonstrate to calculate the dose distribution by utilizing experimental examples.
Porcheron, E.*; Leblois, Y.*; Journeau, C.*; Delacroix, J.*; Molina, D.*; Suteau, C.*; Berlemont, R.*; Bouland, A.*; Lallot, Y.*; Roulet, D.*; et al.
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2022/10
福島第一原子力発電所(1F)の事故炉廃止措置における重要な課題の一つが、燃料デブリの取り出しである。ONET Technologies, CEA, IRSNからなるフランスのコンソーシアムがJAEA/CLADSのために実施したURASOLプロジェクトは、燃料デブリ模擬物質の熱的・機械的加工による放射性エアロゾルの生成と特性に関する科学的基礎データの取得に取り組んでいる。VITAE施設で行われる加熱試験はレーザーによる熱的切断の代表的な条件を模擬している。機械的切断では、FUJISAN施設においてコアボーリング試験を実施した。燃料デブリ模擬物質は、非放射性試験と放射性試験のために開発されている。化学的特性評価と粒径情報の取得は、デブリ取り出しで発生する可能性のある放射性粒子の特性推定のために実施された。これらの情報は1Fにおける燃料デブリ取り出し作業において放射線防護上の対策を評価するうえで重要な情報である。
Journeau, C.*; Molina, D.*; Brackx, E.*; Berlemont, R.*; 坪田 陽一
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 5 Pages, 2022/10
CEAは、劣化ウランを使用したUO またはHfO
またはHfO を(核燃料としての)UO
を(核燃料としての)UO の 代替として用いて、福島第一原子力発電所の模擬燃料デブリを製造した。溶融燃料-コンクリート相互作用によって生じたEx-vessel模擬燃料デブリでは、酸化物相の密度が金属相の密度より軽くなる。それゆえ重い金属質の相が底に偏析する。このうち3つの金属質試料を、CEAカダラッシュ研究所でのハンドソー切断、及び同研究所のFUJISAN施設でコアボーリング装置により機械的に切断された。これらの金属ブロックのうち、2つは非常に切断しにくく(1つはUO
の 代替として用いて、福島第一原子力発電所の模擬燃料デブリを製造した。溶融燃料-コンクリート相互作用によって生じたEx-vessel模擬燃料デブリでは、酸化物相の密度が金属相の密度より軽くなる。それゆえ重い金属質の相が底に偏析する。このうち3つの金属質試料を、CEAカダラッシュ研究所でのハンドソー切断、及び同研究所のFUJISAN施設でコアボーリング装置により機械的に切断された。これらの金属ブロックのうち、2つは非常に切断しにくく(1つはUO 試料、もう1つはHfO
試料、もう1つはHfO 試料)、最後の1つはより簡単に切断可能であった。これらの3つの金属ブロックの金相分析(SEM-EDSとXRD)の類似点/相違点に関して議論する予定である。この経験は、福島第一原子力発電所の燃料デブリの切断・回収を視野に入れた場合、有益な学びとなる。
試料)、最後の1つはより簡単に切断可能であった。これらの3つの金属ブロックの金相分析(SEM-EDSとXRD)の類似点/相違点に関して議論する予定である。この経験は、福島第一原子力発電所の燃料デブリの切断・回収を視野に入れた場合、有益な学びとなる。
芝 知宙; 冠城 雅晃; 能見 貴佳; 鈴木 梨沙; 小菅 義広*; 名内 泰志*; 高田 映*; 長谷 竹晃; 奥村 啓介
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 3 Pages, 2022/10
A technique that can easily determine the presence of nuclear material in removed object from Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant site is important from the viewpoint of sorting fuel debris from radioactive waste. In the case of fresh uranium, the amount of nuclear material in the waste generated from nuclear facilities can be determined by measuring 1001 keV gamma-rays emitted by 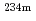 Pa, which is a daughter nuclide of
Pa, which is a daughter nuclide of  U. However, it has been pointed out that such gamma-ray measurement cannot be used for fuel debris that contains a large portion of fission products (FPs) emitting various energies of gamma-rays. In this study, we focus on prompt fission gamma-rays that are directly emitted from nuclear materials and those energy exists in a higher energy region than those of FPs, and aim to measure them in simple manners.
U. However, it has been pointed out that such gamma-ray measurement cannot be used for fuel debris that contains a large portion of fission products (FPs) emitting various energies of gamma-rays. In this study, we focus on prompt fission gamma-rays that are directly emitted from nuclear materials and those energy exists in a higher energy region than those of FPs, and aim to measure them in simple manners.
名内 泰志*; 能見 貴佳; 鈴木 梨沙; 小菅 義広*; 芝 知宙; 高田 映*; 冠城 雅晃; 奥村 啓介
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/10
As one of the identification techniques for materials in fuel debris, the neutron induced gamma ray spectroscopy (NIGS) is focused on since the gamma ray spectrum is intrinsic to isotopes. The energy of the target gamma ray in NIGS is often higher than that of most of fission products. To demonstrate feasibility of NIGS for the identification, we have measured and analyzed the HPGe response of isotopes for Cf-252 neutron irradiation for plutonium samples and several structural materials. As a result, we confirmed the possibility to identify light water, boron, concrete, sea water, structural material, signal lines and coils, fuel cladding, gadolinium, uranium, and plutonium contained in the retrieved materials from Fukushima Daiichi NPPs.
 /Fe(0) by bacteria
/Fe(0) by bacteriaLiu, J.; 土津田 雄馬; 北垣 徹; 高野 公秀; 大貫 敏彦; 香西 直文
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 2 Pages, 2022/10
福島第一原子力発電所の事故では、核燃料と原子炉内の構造材を主成分とする燃料デブリが形成され、大部分は原子炉格納容器内の水中に存在しており、地下水中に生息する微生物と相互作用を生じる可能性がある。燃料デブリの経年変化を評価するためには、微生物と燃料デブリとの相互作用の知識が不可欠である。本研究では、燃料デブリの重要な成分であるUO とFe(0)の粉末試料を作り、自然界に広く存在し、事故現場にも生息すると考えられる枯草菌(Bacillus subtilis)との相互作用を検討した。粉末試料と枯草菌を静置して時間的な変化を分析したうえで、枯草菌によってU(IV)とFe(0)の酸化溶解が促進されることを確認した。溶解したU(VI)の一部は、非晶質のFe(III)水酸化物と思われる鉄の沈殿物とともに沈殿していた。これらの結果から、微生物が燃料デブリの経年変化の促進に寄与する可能性が示唆された。
とFe(0)の粉末試料を作り、自然界に広く存在し、事故現場にも生息すると考えられる枯草菌(Bacillus subtilis)との相互作用を検討した。粉末試料と枯草菌を静置して時間的な変化を分析したうえで、枯草菌によってU(IV)とFe(0)の酸化溶解が促進されることを確認した。溶解したU(VI)の一部は、非晶質のFe(III)水酸化物と思われる鉄の沈殿物とともに沈殿していた。これらの結果から、微生物が燃料デブリの経年変化の促進に寄与する可能性が示唆された。
多木 寛; 永江 勇二; 倉田 正輝
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/10
The analysis of small samples retrieved from the inside of Primary Containment Vessel (PCV) of Units 1, 2, and 3 at Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station detected various types of U-bearing particles. Elucidation of the formation mechanism of these particles is expected to be good practice for real debris characterization. In this study, we attempted to analyze the solidification path of U-bearing particles by the thermodynamic approach. From the thermodynamic solidification path patterns analysis, pattern II (at low oxidation condition) was identified as the available one for Units 1 & 2 particles, whereas pattern IV (at high oxidation condition) would be additionally possibly for Unit 3. From these thermodynamic analyzes, the following characteristic are speculated for the debris in PCV: 1) The debris are likely to have been solidified by gradual cooling from high temperatures to intermediate temperatures and solid-solid transition at lower temperatures may be limited. 2) Units 1 & 2 debris might be exposed to slightly hypo-stoichiometric conditions than Unit 3, and whereas Unit 3 debris might have a wider variation in the oxidation degree.