Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 and Br
and Br and its effect on corrosion of a low-alloy steel
and its effect on corrosion of a low-alloy steelHata, Kuniki; Inoue, Hiroyuki*; Kojima, Takao*; Kasahara, Shigeki; Hanawa, Satoshi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Tsukada, Takashi; Iwase, Akihiro*
Proceedings of Symposium on Water Chemistry and Corrosion in Nuclear Power Plants in Asia 2017 (AWC 2017) (USB Flash Drive), p.304 - 314, 2017/09
A model simulation of  radiolysis of mixed solutions of NaCl and NaBr was carried out. The simulation result agreed well with the experimental result, and Br
radiolysis of mixed solutions of NaCl and NaBr was carried out. The simulation result agreed well with the experimental result, and Br played an important role in determining the amounts of products from water radiolysis. The simulation result also showed that, in highly pure NaCl solutions, the steady-state concentration of a radolytic product, H
played an important role in determining the amounts of products from water radiolysis. The simulation result also showed that, in highly pure NaCl solutions, the steady-state concentration of a radolytic product, H O
O , was mainly controlled by three reactions (Cl
, was mainly controlled by three reactions (Cl +
+  OH
OH  ClOH
ClOH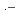 , ClOH
, ClOH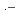
 Cl
Cl +
+  OH, and ClOH
OH, and ClOH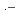 + H
+ H
 Cl
Cl + H
+ H O), which indicated that accurate evaluation of the rate constants of these reactions was very important in improving the radiolysis simulation of solutions containing Cl
O), which indicated that accurate evaluation of the rate constants of these reactions was very important in improving the radiolysis simulation of solutions containing Cl . An immersion test using a low-alloy steel, SQV2A, in the mixed solutions was also carried out under irradiation. The corrosion rate increased or decreased depending on the pH or the concentrations of the halide ions in a similar way to the change in concentration of H
. An immersion test using a low-alloy steel, SQV2A, in the mixed solutions was also carried out under irradiation. The corrosion rate increased or decreased depending on the pH or the concentrations of the halide ions in a similar way to the change in concentration of H O
O produced from water radiolysis, which is affected by the presence of Cl
produced from water radiolysis, which is affected by the presence of Cl and Br
and Br . However, at high pH values (
. However, at high pH values ( 12), the corrosion rate was almost zero even though the concentration of H
12), the corrosion rate was almost zero even though the concentration of H O
O was high. This could be attributed to enhancement of the passivity of test specimens at higher pH values.
was high. This could be attributed to enhancement of the passivity of test specimens at higher pH values.
Hidaka, Akihide; Yokoyama, Hiroya
Proceedings of Symposium on Water Chemistry and Corrosion in Nuclear Power Plants in Asia 2017 (AWC 2017) (USB Flash Drive), p.29 - 42, 2017/09
no abstracts in English