Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Ueki, Taro
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 173, p.105236_1 - 105236_10, 2024/08
The theme of this paper is how to efficiently analyse extreme realizations of neutron effective multiplication factor (keff) over random media replicas modelled by incomplete randomized Weierstrass function (IRWF). To this end, a new bounded amplification (BA) technique is applied to IRWF. Numerical results indicate that the BA-applied IRWF reduces a required number of random media replicas at least by an order of magnitude. To validate this efficiency gain, generalized extreme value (GEV) analysis is applied to a data set of keff values obtained without applying BA. It turns out that the extreme values of these keff values follow the Weibull distribution. Therefore, the theory of GEV guarantees the existence of the upper limit of these keff values, and the actually computed upper limit is indeed smaller than the top two keff values obtained from an order-of magnitude reduced number of BA-applied IRWF random media replicas. This means that the efficiency gain via BA has been confirmed by GEV analysis.
Nakahara, Masaumi; Watanabe, So; Kimura, Shuya; Sasaki, Misa*; Inagaki, Hiromitsu*; Moriguchi, Tetsuji*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 172, p.105195_1 - 105195_8, 2024/07
A novel removal technique with ultrafine bubbles has been proposed for decommissioning of nuclear facilities. The performance of removal technology with ultrafine bubbles was evaluated in the removal experiments with non-radioactive materials, simulated contaminants precipitated Co oxides. To investigate the influence of difference in the chemical forms, the decontamination experiments were carried out with the fuel pin end plugs contaminated radioactive materials in a hot cell.
 C powder and B
C powder and B C pellet regarding the eutectic reaction with stainless steel
C pellet regarding the eutectic reaction with stainless steelHong, Z.*; Ahmed, Z.*; Pellegrini, M.*; Yamano, Hidemasa; Erkan, N.*; Sharma, A. K.*; Okamoto, Koji*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 171, p.105160_1 - 105160_13, 2024/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.05In this study, it is found that the eutectic reaction between B C powder and stainless steel (SS) is considerably more rapid than that between the B
C powder and stainless steel (SS) is considerably more rapid than that between the B C pellet and SS. The derived reaction rate constant values for powder and pellet cases are consistently based on the reference values. Also, a composition analysis using SEM/EDS was conducted for the detailed microstructures of the powder and pellet samples. In the powder case, only one thick layer is found as the reaction layer consisting of (Fe, Cr)B precipitate, including B
C pellet and SS. The derived reaction rate constant values for powder and pellet cases are consistently based on the reference values. Also, a composition analysis using SEM/EDS was conducted for the detailed microstructures of the powder and pellet samples. In the powder case, only one thick layer is found as the reaction layer consisting of (Fe, Cr)B precipitate, including B C powder. In the pellet case, two layers are found in the reaction layer.
C powder. In the pellet case, two layers are found in the reaction layer.
Hirose, Yoshiyasu; Abe, Satoshi; Ishigaki, Masahiro*; Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Hibiki, Takashi*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 169, p.105085_1 - 105085_13, 2024/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.05(Nuclear Science & Technology)Hirose, Yoshiyasu; Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Hibiki, Takashi*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 168, p.105027_1 - 105027_17, 2024/03
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:63.33(Nuclear Science & Technology)Shi, W.*; Machida, Masahiko; Yamada, Susumu; Yoshida, Toru*; Hasegawa, Yukihiro*; Okamoto, Koji*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 162, p.104792_1 - 104792_19, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Predicting radioactive source distributions inside reactor building rooms based on monitoring air dose rates is one of the most essential steps towards decommissioning of nuclear power plants. However, the attempt is rather a difficult task, because it can be generally mapped onto mathematically ill-posed problem. Then, in order to successfully perform the inverse estimations on radioactive source distributions even in such ill-posed conditions, we suggest that a machine learning method, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) minimizing the loss function, 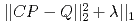 is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
is a promising scheme. For the purpose of its feasibility demonstrations in real building rooms, we employ PHITS code to make LASSO input as the above matrix C connecting the radioactive source vector P defined on surface meshes of structural materials with the air dose rate vector Q measured at internal positions inside the rooms. We develop a mathematical criterion on the number of monitoring points to correctly predict source distributions based on the theory of Candes and Tao. Then, we confirm that LASSO actually shows extremely high possibility for source distribution reconstructions as far as the number of detection points satisfies our criterion. Moreover, we verify that radioactive hot spots can be truly reconstructed in an experiment setup. At last, we examine an influence factor like detector-source distance to enhance the predicting possibility in the inverse estimation. From the above demonstrations, we propose that LASSO scheme is a quite useful way to explore hot spots as seen in damaged nuclear power plants like Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plants.
Ueki, Taro
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 159, p.104630_1 - 104630_9, 2023/05
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)In this work, the methodology of Generalized Extreme Value (GEV) is applied to criticality tallies in Monte Carlo fission source cycles in order to evaluate the utility value of the distribution tail ends. Numerical results obtained under a sufficiently large number of particles per cycle show that the extreme value index (EVI) in GEV falls within the range of Weibull distribution including the EVI of Gumbel distribution as the role of a boundary value layer. GEV is also applied to a historically-challenging loosely-coupled system for demonstrating population diagnosis under an insufficient number of particles per cycle. It turns out that the transition from one equilibrium to other equilibrium makes the EVIs of upper and lower distribution tail ends depart from each other so that one of them falls in the range of Weibull distribution and the other in that of Frechet distribution.
Sakasegawa, Hideo; Nomura, Mitsuo; Sawayama, Kengo; Nakayama, Takuya; Yaita, Yumi*; Yonekawa, Hitoshi*; Kobayashi, Noboru*; Arima, Tatsumi*; Hiyama, Toshiaki*; Murata, Eiichi*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 153, p.104396_1 - 104396_9, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)When dismantling centrifuges in uranium-enrichment facilities, decontamination techniques must be developed to remove uranium-contaminated surfaces of dismantled parts selectively. Dismantled uranium-contaminated parts can be disposed of as nonradioactive wastes or recycled after decontamination appropriate for clearance. previously, we developed a liquid decontamination technique using acidic electrolyzed water to remove uranium-contaminated surfaces. However, further developments are still needed for its actual application. Dismantled parts have various uranium-contaminated surface features due to varied operational conditions, inhomogeneous decontamination using iodine heptafluoride gas, and changes in long-term storage conditions after dismantling. Here, we performed liquid decontamination on specimens with varying uranium-contaminated surfaces cut from a centrifuge made of low-carbon steel. From the results, the liquid decontamination can effectively remove the uranium-contaminated surfaces, and radioactive concentrations fell below the target value within twenty minutes. Although the required time should also depend on dismantled parts' sizes and shapes in their actual application, we demonstrated that it could be an effective decontamination technique for uranium-contaminated steels of dismantled centrifuges.
Hamdani, A.; Abe, Satoshi; Ishigaki, Masahiro; Shibamoto, Yasuteru; Yonomoto, Taisuke
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 153, p.104415_1 - 104415_16, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:63.91(Nuclear Science & Technology)Ueki, Taro
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 144, p.104099_1 - 104099_7, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Randomized Weierstrass function (RWF) has been under development for evaluating the uncertainty of random media criticality due to the material mixture under disorder. In this work, the modelling capability of RWF is refined so that the spectrum range can be controlled by specifying its lower and upper ends of the frequency domain variable. As a result, it becomes possible to make fair criticality comparison among replicas of random media under inverse power law power spectra. Technically, the infinite sum of trigonometric terms in RWF is extended to cover the arbitrarily low frequency domain and then truncated to finite terms for the sole purpose of spectrum range control. This means that the refinement is free of the convergence issue towards a fractal characteristic of Weierstrass function and thus termed Incomplete Randomized Weierstrass function (IRWF). As a demonstration, a three-dimensional version of IRWF is applied to the mixture of three fuels with different burnups in a water-moderated environment. Monte Carlo criticality calculations are carried out to evaluate the uncertainty of neutron effective multiplication factor due to the indeterminacy of the fuel mixture formation.
Aihara, Haruka; Watanabe, So; Shibata, Atsuhiro; Mahardiani, L.*; Otomo, Ryoichi*; Kamiya, Yuichi*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 139, p.103872_1 - 103872_9, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:29.53(Nuclear Science & Technology)Gou llo, M.*; Hokkinen, M.*; Suzuki, Eriko; Horiguchi, Naoki; Barrachin, M.*; Cousin, F.*
llo, M.*; Hokkinen, M.*; Suzuki, Eriko; Horiguchi, Naoki; Barrachin, M.*; Cousin, F.*
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 138, p.103818_1 - 103818_10, 2021/08
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:63.04(Nuclear Science & Technology)The present work aimed to study the transport of caesium iodide particles through a Thermal Gradient Tube (TGT) from 1023 K to 453 K. Retention inside the tube was evaluated for laminar flowrates composed of argon and steam. Higher retention of particles was highlighted for the experiments using higher steam content and lower flowrate. The second phase of the experiment aimed at identifying the possible revaporization or/and resuspension processes after the deposition. Three atmosphere compositions (Ar/H O, Ar/H
O, Ar/H and Ar/Air) were investigated. The particles removed from what was deposited on the surface walls during the sampling phase exhibited a similar GMD in Ar/H
and Ar/Air) were investigated. The particles removed from what was deposited on the surface walls during the sampling phase exhibited a similar GMD in Ar/H O and Ar/H
O and Ar/H and a bigger diameter in Ar/Air. The experimental results were then analysed with the SOPHAEROS module of the ASTEC code. Overall, the results obtained during the first phase were in agreement with the measured experimental results and during second phase led to no resuspension process.
and a bigger diameter in Ar/Air. The experimental results were then analysed with the SOPHAEROS module of the ASTEC code. Overall, the results obtained during the first phase were in agreement with the measured experimental results and during second phase led to no resuspension process.
Myagmarjav, O.; Tanaka, Nobuyuki; Nomura, Mikihiro*; Noguchi, Hiroki; Imai, Yoshiyuki; Kamiji, Yu; Kubo, Shinji; Takegami, Hiroaki
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 137, p.103772_1 - 103772_7, 2021/07
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:69.63(Nuclear Science & Technology)Atkinson, S.*; Aoki, Takeshi; Litskevich, D.*; Merk, B.*; Yan, X.
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 134, p.103689_1 - 103689_10, 2021/04
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:15.09(Nuclear Science & Technology)This article evaluates the safety features of the designed 10 MWth U-Battery concept with respect to a control rod withdrawal and a depressurised loss of coolant accident. This article provides the evaluation methodology for both transients, using a one-dimensional heat transfer model involving point reactor kinetic model to simulate reactor feedback in the control rod withdrawal. Overall, this work has shown that during the control rod withdrawal the fuel temperature rises by 110 K and at this point the excess reactivity is compensated by the negative temperature coefficient of the fuel. During the depressurised loss of coolant accident, the maximum fuel temperature reached 1455 K after 60 hours. This concludes that during both transients the temperatures maintained well below the maximum fuel operating temperature.
Herranz, L. E.*; Jacquemain, D.*; Nitheanandan, T.*; Sandberg, N.*; Barr , F.*; Bechta, S.*; Choi, K.-Y.*; D'Auria, F.*; Lee, R.*; Nakamura, Hideo
, F.*; Bechta, S.*; Choi, K.-Y.*; D'Auria, F.*; Lee, R.*; Nakamura, Hideo
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 127, p.103432_1 - 103432_14, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:20.53(Nuclear Science & Technology)Baron, P.*; Cornet, S. M.*; Collins, E. D.*; DeAngelis, G.*; Del Cul, G.*; Fedorov, Y.*; Glatz, J. P.*; Ignatiev, V.*; Inoue, Tadashi*; Khaperskaya, A.*; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 117, p.103091_1 - 103091_24, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:75 Percentile:94.03(Nuclear Science & Technology)The results of an international review of separation processes for spent nuclear fuel (SNF) recycling in future closed fuel cycles with the evaluation of Technology Readiness Level are reported. This study was made by the Expert Group on Fuel Recycling Chemistry (EGFRC) organised by the Nuclear Energy Agency (NEA) of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). A unique feature of this study was that processes were classified according to a hierarchy of separations aimed at different elements within spent fuel (uranium; uranium-plutonium co-recovery; minor actinides; high heat generating radionuclides) and also the Head-end processes, used to prepare the SNF for chemical separation, were included. Separation processes covered both wet (hydrometallurgical) and dry (pyro-chemical) processes.
Watanabe, So; Ogi, Hiromichi*; Arai, Yoichi; Aihara, Haruka; Takahatake, Yoko; Shibata, Atsuhiro; Nomura, Kazunori; Kamiya, Yuichi*; Asanuma, Noriko*; Matsuura, Haruaki*; et al.
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 117, p.103090_1 - 103090_8, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:79.16(Nuclear Science & Technology)Sugawara, Takanori; Takei, Hayanori; Iwamoto, Hiroki; Oizumi, Akito; Nishihara, Kenji; Tsujimoto, Kazufumi
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 106, p.27 - 33, 2018/07
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:85.89(Nuclear Science & Technology)The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has investigated an accelerator-driven system (ADS) to transmute minor actinides which will be partitioned from the high level waste. There are various inherent issues for the research and development on the ADS. The recent two activities to realize a feasible and reliable ADS concept are introduced in this paper. For the feasibility, the design of a beam window which is a boundary of the accelerator and the subcritical core, is one of the most important issues. To mitigate the design condition of the beam window, namely to reduce the proton beam current, the subcritical core concept with subcriticality adjustment rods were investigated. For the reliability, the beam-trip is the inherent and serious issue for the ADS design because it induces rapid temperature change to coolant and structures in the subcritical core. To improve the beam-trip frequencies, a double-accelerator concept was proposed and its beam-trip frequency was estimated.
Taninaka, Hiroshi; Takegoshi, Atsushi; Kishimoto, Yasufumi*; Mori, Tetsuya; Usami, Shin
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 101(Part C), p.329 - 337, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)The present paper describes the evaluation of the power reactivity loss data obtained in the Japanese prototype fast breeder reactor Monju. The most recent analysis on the power reactivity loss measurement (Takano, et al., 2008) is updated considering the following findings: (a) in-core temperature distribution effect, (b) crystalline binding effect, (c) logarithmic averaging of the fuel temperature, (d) localized fuel thermal elongation effect, (e) updated Japanese Evaluated Nuclear Data Library, JENDL-4.0, and (f) refined corrections on the measured value. The influences of the updates are quantitatively identified and the most precise and probable C/E value is derived together with a thorough uncertainty evaluation. As a result, it is revealed that the analysis overestimates the measurement by 4.6% for the measurement uncertainty of 2.0%. The discrepancy is reduced to as small as 1.1% when the core bowing effect is considered, which implies the importance of the core bowing effect in the calculation of the power reactivity loss.
Gunji, Satoshi; Tonoike, Kotaro; Izawa, Kazuhiko; Sono, Hiroki
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 101(Part C), p.321 - 328, 2017/11
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:28.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)Criticality safety of fuel debris, particularly MCCI (Molten-Core-Concrete-Interaction) products, is one of the major safety issues for decommissioning of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Criticality or subcriticality condition of the fuel debris is still uncertain; its composition, location, neutron moderation, etc. are not yet confirmed. The effectiveness of neutron poison in cooling water is also uncertain for use as a criticality control of fuel debris. A database of computational models is being built by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), covering a wide range of possible conditions of such composition, neutron moderation, etc., to facilitate assessing criticality characteristics once fuel debris samples are taken and their conditions are known. The computational models also include uncertainties which are to be clarified by critical experiments. These experiments are planned and will be conducted by JAEA with the modified STACY (STAtic experiment Critical facilitY) and samples to simulate fuel debris compositions. Each of the samples will be cladded by a zircalloy tube whose outer shape is compatible with the fuel rod of STACY and loaded into an array of the fuel rods. This report introduces a study of experimental core configurations to measure the reactivity worth of samples simulating MCCI products. Parameters to be varied in the computation models for the experimental series are:(1) Uranium dioxide with  U enrichments of 3, 4, and 5 wt.%; (2) Concrete volume fraction in the samples of 0, 20, 40, 60, and 80%; and (3) Porosity of the samples filled from 0 to 80% where the sample void is filled with water. It is concluded that the measurement is feasible in both under- and over-moderated conditions. Additionally, the required amount of samples was estimated.
U enrichments of 3, 4, and 5 wt.%; (2) Concrete volume fraction in the samples of 0, 20, 40, 60, and 80%; and (3) Porosity of the samples filled from 0 to 80% where the sample void is filled with water. It is concluded that the measurement is feasible in both under- and over-moderated conditions. Additionally, the required amount of samples was estimated.