Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Sweet, M.*; Mishima, Kenji*; 原田 正英; 栗田 圭輔; 飯倉 寛; 田崎 誠司*; 菊池 伯夫*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 9(2), p.11_1 - 11_17, 2025/04
中性子ビームは電気的に中性で透過性が高いため、植物、種子、微生物などの生物種への照射に独自の利点がある。われわれは、核破砕、原子炉、小型中性子源のJ-PARC BL10、JRR-3 TNRF、KUANSのシミュレーションを使用して、遺伝子変異を誘発する中性子照射の可能性を包括的に調査した。
 H to
H to  U
UParisi, A.*; Furutani, K. M.*; 佐藤 達彦; Beltran, C. J.*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 8(3), p.18_1 - 18_16, 2024/09
The analytical microdosimetric function (AMF) implemented in the Monte Carlo code PHITS is a unique tool that bridges the gap between macro- and microscopic scales of radiation interactions, enabling accurate microdosimetric calculations over macroscopic bodies. This study compares the older and newer AMFs in computing microdosimetric probability distributions, mean values, and the relative biological effectiveness (RBE). The newer AMF was found to offer superior performance, particularly for very heavy ions, producing results that align more closely with published in vitro clonogenic survival experiments. These findings suggest that the updated AMF provides a more reliable tool for microdosimetric calculations and RBE modeling, essential for ion radiation therapy and space radiation protection.
Costantini, J.-M.*; 小川 達彦
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 8(3), p.20_1 - 20_16, 2024/08
本研究では、不導体材料における放射線照射損傷の発生メカニズムを、クーロンスパイク法に基づいて説明する理論を構築した。ほぼ同じ密度(2.65)を持つフッ化リチウムと二酸化ケイ素を標的とし、ほぼ同じLETを持つ核子辺り1MeVのNiイオンとKrイオンを照射した場合について、PHITSの飛跡構造解析機能ITSARTとETS-for-Siを用いて電離の空間分布を計算し、電離(カチオン)の間に生じる静電気エネルギーを推定した。この静電気エネルギーが運動エネルギー、ひいては標的中の熱に変換されると仮定すると、二酸化ケイ素の中では、運動するカチオンの核的衝突によって付与される熱で、結晶の溶融が発生することを説明できた。また、フッ化リチウムではフォノンが付与される熱を受け取るが、それが十分でないため溶融に至らないことを説明できた。実験的な観測によると、二酸化ケイ素でのみ溶融後の冷却によって生じたと思われるアモルファス相が見られることから、本研究の理論解析は実験的事実と符合する妥当なものと判断される。
山崎 大; 丸山 龍治; 青木 裕之; 花島 隆泰*; 阿久津 和宏*; 宮田 登*; 曽山 和彦
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 9(2), p.20_1 - 20_12, 2024/06
This study developed a neutron-beam focusing supermirror for grazing-incidence small-angle neutron scattering (GISANS) measurements. It was fabricated by depositing NiC/Ti supermirror film with ion-beam sputtering on a precise elliptic surface of fused quartz figured using the elastic emission machining technique. Neutron measurements at a pulsed neutron reflectometer BL17 of MLF, J-PARC successfully demonstrated that the focusing supermirror enhances a beam intensity twentyfold compared with an optimally collimated beam, achieving the signal-to-background ratio of the focal spot as high as 500. The mirror can be readily installed and used at BL17.
三浦 靖史*; 鈴木 賢治*; 諸岡 聡; 菖蒲 敬久
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 8(1), p.1_1 - 1_14, 2024/03
Probabilistic fracture mechanics (PFM) is expected as a reasonable structural integrity assessment method for nuclear components such as piping, whose main degradation phenomenon is stress corrosion cracking (SCC). Some input parameters are necessary for PFM analysis, and welding residual stress is one of the most important parameters because welding residual stress affects SCC initiation and propagation. Recently, a double exposure method (DEM) with synchrotron X-ray has been proposed, and the method is an expected candidate for the measurement of welding residual stress with a high spatial resolution. In this paper, the DEM was applied to measure the residual stress of the plate specimen, which was cut from the welded pipe using electrical discharge machining, and detailed stress maps under a plane stress state were obtained. Furthermore, the residual stress distributions of the welded pipe under a triaxial stress state were also evaluated using neutron diffraction. From these results, the method for obtaining a detailed stress map of the welded pipe by the complementary use of high-energy synchrotron radiation X-rays and neutrons was proposed.
徐 平光; Zhang, S.-Y.*; Harjo, S.; Vogel, S. C.*; 友田 陽*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 8(1), p.7_1 - 7_13, 2024/01
Comprehensive information about the  microstructure and crystal structure evolution during the preparation/production processes of various materials is in great demand in order to precisely control the microstructure morphology and the preferred orientation characteristics for the excellent strength-ductility-toughness balance of advanced engineering materials.
microstructure and crystal structure evolution during the preparation/production processes of various materials is in great demand in order to precisely control the microstructure morphology and the preferred orientation characteristics for the excellent strength-ductility-toughness balance of advanced engineering materials.  isothermal annealing experiments of cold rolled 17Ni-0.2C (mass %) martensitic steel sheets were carried out by using the TAKUMI and ENGIN-X time-of-flight neutron diffractometers, respectively. The inverse pole figures based on full-profile refinement were extracted to roughly evaluate the preferred orientation features along three principal sample directions of investigated steel sheets using the General Structure Analysis System (GSAS) software with built-in generalized spherical harmonic functions. The consistent rolling direction (RD) inverse pole figures from TAKUMI and ENGIN-X have confirmed that the time-of-flight neutron diffraction has high repeatability and statistical reliability, revealing that the principal preferred orientation evaluation of steel materials is available through 90
isothermal annealing experiments of cold rolled 17Ni-0.2C (mass %) martensitic steel sheets were carried out by using the TAKUMI and ENGIN-X time-of-flight neutron diffractometers, respectively. The inverse pole figures based on full-profile refinement were extracted to roughly evaluate the preferred orientation features along three principal sample directions of investigated steel sheets using the General Structure Analysis System (GSAS) software with built-in generalized spherical harmonic functions. The consistent rolling direction (RD) inverse pole figures from TAKUMI and ENGIN-X have confirmed that the time-of-flight neutron diffraction has high repeatability and statistical reliability, revealing that the principal preferred orientation evaluation of steel materials is available through 90 TD
TD  ND (transverse direction
ND (transverse direction  normal direction) rotation of the investigated specimen on the sample stage during two neutron diffraction experiments. Moreover, these RD, TD and ND inverse pole figures before and after in situ experiments were compared with the corresponding inverse pole figures recalculated respectively from the MUSASI-L complete pole figure measurement and the HIPPO in situ microstructure evaluation. The similar orientation distribution characteristics suggested that the principal preferred orientation evaluation method can be applied to in situ microstructure evolution of bulk orthorhombic materials and spatially resolved principal preferred orientation mappings of large engineering structure parts.
normal direction) rotation of the investigated specimen on the sample stage during two neutron diffraction experiments. Moreover, these RD, TD and ND inverse pole figures before and after in situ experiments were compared with the corresponding inverse pole figures recalculated respectively from the MUSASI-L complete pole figure measurement and the HIPPO in situ microstructure evaluation. The similar orientation distribution characteristics suggested that the principal preferred orientation evaluation method can be applied to in situ microstructure evolution of bulk orthorhombic materials and spatially resolved principal preferred orientation mappings of large engineering structure parts.
Harjo, S.; Gong, W.; 川崎 卓郎
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(4), p.32_1 - 32_13, 2023/12
Tensile deformation in situ neutron diffraction of an extruded AZ31 alloy was performed to validate conventional procedures and to develop new procedures for stress evaluation from lattice strains by diffraction measurements of HCP-structured magnesium alloys. Increases in the lattice strains with respect to the applied true stress after yielding largely vary among [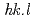 ] grains. The newly proposed procedure of stress evaluation from the lattice strains shows very high accuracy and reliability by weighting the volume fraction of [
] grains. The newly proposed procedure of stress evaluation from the lattice strains shows very high accuracy and reliability by weighting the volume fraction of [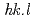 ] grains and evaluating them in many [
] grains and evaluating them in many [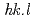 ] orientations in addition to multiplication by the diffraction elastic constant. When multiple
] orientations in addition to multiplication by the diffraction elastic constant. When multiple 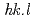 peaks cannot be obtained simultaneously, we recommend to use the 12.1 peak for stress evaluation.
peaks cannot be obtained simultaneously, we recommend to use the 12.1 peak for stress evaluation.
 B-enriched MgB
B-enriched MgB wire using a pulsed neutron source
wire using a pulsed neutron source町屋 修太郎*; 長村 光造*; 菱沼 良光*; 谷口 博康*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(4), p.34_1 - 34_17, 2023/10
Measuring the actual strain on the MgB filaments are of paramount importance, since tensile stress and strain diminish the critical current. In this study, the strain measurement using neutron diffraction during tensile loading was established. We fabricated a MgB
filaments are of paramount importance, since tensile stress and strain diminish the critical current. In this study, the strain measurement using neutron diffraction during tensile loading was established. We fabricated a MgB wire enriched with boron-11, an isotope having a smaller neutron absorption cross- section than natural boron, and succeeded in obtaining changes in the lattice constant under tensile loading through Rietveld analysis.
wire enriched with boron-11, an isotope having a smaller neutron absorption cross- section than natural boron, and succeeded in obtaining changes in the lattice constant under tensile loading through Rietveld analysis.
安江 歩夢*; 川上 真由*; 小林 謙祐*; Kim, J.*; 宮津 裕次*; 西尾 悠平*; 向井 智久*; 諸岡 聡; 兼松 学*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(2), p.15_1 - 15_14, 2023/05
Neutron diffraction is a noncontact method that can measure the rebar strain inside concrete. In this method, rebar strain and stress are calculated using the diffraction profile of neutrons irradiated during a specific time period. In general, measurement accuracy improves with the length of the measurement time. However, in previous studies, the measurement time was determined empirically, which makes the accuracy and reliability of the measurement results unclear. In this study, the relationship between the measurement time and the measurement standard deviation was examined for reinforced concrete specimens under different conditions. The aim was to clarify the accuracy of the measurement of rebar stress using the neutron diffraction method. It was found that if the optical setup of the neutron diffractometer and the conditions of the specimen are the same, there is a unique relationship between the diffraction intensity and the rebar stress standard deviation. Furthermore, using this unique relationship, this paper proposes a method for determining the measurement time from the allowable accuracy of the rebar stress, which ensures the accuracy of the neutron diffraction method.
山崎 泰広*; 篠宮 啓介*; 奥村 忠晴*; 鈴木 賢治*; 菖蒲 敬久; 中村 唯我*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(2), p.14_1 - 14_12, 2023/05
The suspension plasma spray (SPS) technique has attracted attention because of its various microstructures, which can be achieved by mixing submicron spray particles with a solvent to form a suspension. Thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) with a columnar structure, which might achieve high strain tolerance, can be obtained using the SPS technique. In this study, the internal stress distribution of the SPS-TBC with different columnar structures was evaluated by hybrid measurement using high-energy synchrotron X-ray diffraction analysis and laboratory low-energy X-rays. The effect of microstructure on the internal stress distribution of the SPS-TBC was discussed on the basis of the experimental results. In addition, the in-plane internal stress was decreased by decreasing the column diameter. The thin columnar microstructure of the SPS-TBC has superior strain tolerance. The internal stresses in the column of the SPS-TBC are periodic decrements caused by stress relaxation in porous layers.
渡辺 真朗; 木原 工*; 野尻 浩之*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(1), p.1_1 - 1_10, 2023/03
J-PARC物質・生命科学実験施設において、ユーザーが使いやすく、かつ新しい試料環境装置として35Tまで発生可能なパルスマグネットシステムを開発した。これは、真空チャンバー、GM冷凍機、小型ソレノイドコイルを挿入したSUS管で構成されている。コイルは液体窒素自動供給装置から供給される液体窒素で冷却され、試料はGM冷凍機で冷却される。この組み合わせにより、ユーザー操作のための自動運転可能な強磁場回折測定が容易になる。散乱角は最大42度で、これまでの装置よりも大幅に広くなっている。中性子回折実験は、マルチフェロイック物質(TbMnO )を用いて、回折ピークの磁場依存性が明確に観察された。このようにユーザープログラム用の実用的な強磁場回折のための、新しいパルスマグネットシステムが確立された。
)を用いて、回折ピークの磁場依存性が明確に観察された。このようにユーザープログラム用の実用的な強磁場回折のための、新しいパルスマグネットシステムが確立された。
西田 真之*; Harjo, S.; 川崎 卓郎; 山下 享介*; Gong, W.
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(1), p.8_1 - 8_15, 2023/03
In this study, the thermal stress alterations generated in a tungsten fiber reinforced titanium composite (W/Ti composite) were evaluated by the neutron stress measurement method at cryogenic temperatures. The W/Ti composite thermal loads were repeated from room temperature to the cryogenic temperature (10 K), and alterations in thermal residual stress were evaluated using the neutron in situ stress measurement method. In this measurement, the stress alterations in the titanium matrix and the tungsten fibers were measured. This measurement was carried out by TAKUMI (MLF-BL19) of J-PARC, a neutron research facility in the Japan Atomic Agency. The measurement method of TAKUMI is the time-of-flight (TOF) method. Owing to this measurement method, the measurement time was significantly shortened compared to the angle-dispersion type measurement by a diffractometer. As a result of the measurement, large compressive stresses of about 1 GPa were generated in the tungsten fibers, and tensile stresses of about 100 MPa existed in the titanium matrix. The thermal stresses due to the temperature change between room temperature and cryogenic temperature is caused by the difference of thermal expansions between the tungsten fibers and the titanium matrix, and these stress values can be approximated by a simple elastic theory equation.
Constantini, J.-M.*; 小川 達彦
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 7(1), p.7_1 - 7_16, 2023/03
イオンなどを物体に照射し、物体の構成原子や分子を放出させるスパッタリングは、工学的に重要な技術として様々な分野で利用されている。このスパッタリングで放出される原子や分子の運動では、入射粒子の運動と真逆に放出される成分があることが実験的に知られていた。従来、照射効果の予測に標準的に用いられてきたサーマルスパイクモデルでは、伝導により平衡に達した熱統計集団が蒸発して粒子を放出する。ただし、この放出は等方的であり、指向性のある成分は説明が付かない。本研究では、イオン照射で発生する電離が飛跡に沿って直線状に配置され、それらの間に働く電気的斥力がイオン照射方向に指向性を持つことに着想を得て、スパッタリングの角度分布をイオン照射で発生する静電気力により表現した。具体的な手法として、イオン照射によって発生する電離を飛跡構造解析コードRITRACKSを使用して計算し、その電離で発生する陽イオンの幾何的配置から、静電気力によるイオンの運動を計算した。その結果、1MeVの陽子や1MeV/uの炭素イオンを水に照射した場合、照射と逆方向 にイオンの噴出が確認できた他、スパッタリングの放出収量も先行研究の実験と矛盾ない結果が得られた。
 single crystal by ion irradiation; A Molecular dynamics study
single crystal by ion irradiation; A Molecular dynamics study篠嶋 妥*; 神長 龍一*; 石川 法人; 岩瀬 彰宏*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 5(4), p.32_1 - 32_14, 2021/11
分子動力学法に基づく計算手法により、高速重イオンを照射したCeO 単結晶において、ナノスケールの穿孔が形成される様子をシミュレーションした。蛍石型結晶構造の中央位置のナノスケールの柱状領域に高い熱エネルギーを投入し、その後の結晶構造の変化を追った結果、照射後0.3ピコ秒に突然ナノ穿孔が発生し、0.5ピコ秒で最大の大きさになるまで成長した。その後は1.0ピコ秒にかけて収縮現象が見られた。阻止能(イオン照射によって投入されたエネルギー密度)の増加とともに、ナノ穿孔の大きさが増加する傾向が見られた。本結果は、ナノ穿孔を作成し、かつ大きさを制御する際の有用な知見を与える。
単結晶において、ナノスケールの穿孔が形成される様子をシミュレーションした。蛍石型結晶構造の中央位置のナノスケールの柱状領域に高い熱エネルギーを投入し、その後の結晶構造の変化を追った結果、照射後0.3ピコ秒に突然ナノ穿孔が発生し、0.5ピコ秒で最大の大きさになるまで成長した。その後は1.0ピコ秒にかけて収縮現象が見られた。阻止能(イオン照射によって投入されたエネルギー密度)の増加とともに、ナノ穿孔の大きさが増加する傾向が見られた。本結果は、ナノ穿孔を作成し、かつ大きさを制御する際の有用な知見を与える。
大久保 成彰; 藤村 由希; 友部 政勝*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 5(3), p.27_1 - 27_9, 2021/09
加速器駆動システム(ADS)において、核破砕ターゲットの隔壁であるビーム窓の材料は、過酷な条件下で重照射に晒される。ビーム窓材では、鉛ビスマス流れ環境下で高エネルギー中性子、あるいは陽子線照射により、弾き出し損傷と腐食とが同時に起こる。ADSで用いられる材料には、液体鉛ビスマス合金(LBE)内での液体金属脆化(LME)や液体金属腐食(LMC)に耐えるための共存性が必要である。本研究では、自己イオン照射した316Lに対して、照射後LBE中腐食試験によりLMC挙動を調べた。316L試料に対して、10.5MeVまで加速した鉄イオンを、450 Cにて最大50dpaまで照射を行った。低酸素濃度のLBE中、450
Cにて最大50dpaまで照射を行った。低酸素濃度のLBE中、450 Cで腐食試験を行った結果、未照射部では、酸化皮膜は観察されずに局所腐食が見られた一方で、照射部は鉄/クロム系の酸化皮膜で覆われていた。また、高い酸素濃度のLBEの場合、未照射部は、鉄/クロム系酸化物の1層であった一方で、照射部は鉄酸化物と鉄/クロム系酸化物の2層酸化皮膜で覆われていた。316Lにおいて、自己イオン照射による残存空孔等の照射損傷が試料表面での鉄と酸素の拡散が促進されたことにより、酸化層の形成が促進したと考えられる。
Cで腐食試験を行った結果、未照射部では、酸化皮膜は観察されずに局所腐食が見られた一方で、照射部は鉄/クロム系の酸化皮膜で覆われていた。また、高い酸素濃度のLBEの場合、未照射部は、鉄/クロム系酸化物の1層であった一方で、照射部は鉄酸化物と鉄/クロム系酸化物の2層酸化皮膜で覆われていた。316Lにおいて、自己イオン照射による残存空孔等の照射損傷が試料表面での鉄と酸素の拡散が促進されたことにより、酸化層の形成が促進したと考えられる。
徐 平光; Liss, K.-D.*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 5(2), p.11_1 - 11_14, 2021/06
In contrast to conventional angle dispersive neutron diffractometers with a single-tube detector or a small-size linear position-sensitive detector, the WOMBAT diffractometer at Australian Nuclear Science and Technology Organisation (ANSTO) is equipped with a large-area curved position-sensitive detector, spanning 120 for the scattering angle 2
for the scattering angle 2 and 15
and 15 for the azimuth
for the azimuth 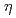 , respectively. Here, WOMBAT was employed to establish a texture measurement environment for complex textured samples, through measuring neutron diffractograms at two selected wavelengths on a typical reference sample of martensite-austenite multilayered steel sheet. All neutron patterns were simultaneously Rietveld analyzed using the software, Materials Analysis Using Diffraction (MAUD). The shorter wavelength enabled to collect the martensite diffraction peaks 110, 200, 211, 220, 310, 222 as well as the austenite diffraction peaks 111, 200, 220, 311, 222, 331 diffraction peaks simultaneously by pre-setting the detector range to 2
, respectively. Here, WOMBAT was employed to establish a texture measurement environment for complex textured samples, through measuring neutron diffractograms at two selected wavelengths on a typical reference sample of martensite-austenite multilayered steel sheet. All neutron patterns were simultaneously Rietveld analyzed using the software, Materials Analysis Using Diffraction (MAUD). The shorter wavelength enabled to collect the martensite diffraction peaks 110, 200, 211, 220, 310, 222 as well as the austenite diffraction peaks 111, 200, 220, 311, 222, 331 diffraction peaks simultaneously by pre-setting the detector range to 2 = 30
= 30 150
150 . The longer wavelength enabled to separate the overlapping strong martensite peak 110 and austenite peak 111 more reliably. Moreover, the detector panel division along the vertical direction covers a good stereographic coverage in the azimuthal angle. Such combination of multiple wavelength neutron diffraction combined with simultaneous Rietveld texture analysis was confirmed much valuable to realize high precision measurements for complex textured samples at an orientation distribution function (ODF) graticule of 5
. The longer wavelength enabled to separate the overlapping strong martensite peak 110 and austenite peak 111 more reliably. Moreover, the detector panel division along the vertical direction covers a good stereographic coverage in the azimuthal angle. Such combination of multiple wavelength neutron diffraction combined with simultaneous Rietveld texture analysis was confirmed much valuable to realize high precision measurements for complex textured samples at an orientation distribution function (ODF) graticule of 5 , and in a much shorter beam time than the conventional angle dispersive method.
, and in a much shorter beam time than the conventional angle dispersive method.
菖蒲 敬久; 城 鮎美*; 河野 史明*; 村松 壽晴; 山田 知典; 永沼 正行; 小澤 隆之
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 5(2), p.17_1 - 17_9, 2021/06
自動車産業は、照射面の反対側に照射痕を発生させることなく高エネルギー密度を実現するため、レーザービーム溶接を採用している。ひずみゲージや管球X線などの一般的な測定手法では、接合部の溶接部での局所的なひずみを評価できない。本研究では、高エネルギー放射光X線回折を使用して、高温かつ荷重下でのレーザー重ね継手PNC-FMS鋼(厚さ2および5mm)の内部ひずみ分布を計測した。その結果、引張荷重が増加すると、局所的な引張ひずみと圧縮ひずみが界面近くで増加した。これらの分布は、有限要素解析の結果とよく一致した。ただし、当該分布はレーザー加工によって発生する欠陥に依存するため、X線透過イメージングによる内部欠陥観察を補完的に利用することが不可欠であることもわかった。
石川 法人; 田口 富嗣*; 小河 浩晃
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 4(4), p.43_1 - 43_14, 2020/12
LiNbO , ZrSiO
, ZrSiO , Gd
, Gd Ga
Ga O
O , SrTiO
, SrTiO について、200MeV Auイオンを照射し、透過型電子顕微鏡で、照射損傷組織(イオントラックとヒロック)を詳細に観察した。その結果、LiNbO
について、200MeV Auイオンを照射し、透過型電子顕微鏡で、照射損傷組織(イオントラックとヒロック)を詳細に観察した。その結果、LiNbO , ZrSiO
, ZrSiO , Gd
, Gd Ga
Ga O
O は、イオントラックとヒロックともにアモルファス化していることが確認され、耐照射性の低い「アモルファス化可能材料」に分類されることが確認された。一方で、CaF
は、イオントラックとヒロックともにアモルファス化していることが確認され、耐照射性の低い「アモルファス化可能材料」に分類されることが確認された。一方で、CaF などのフッ化物は、耐照射性の高い「非アモルファス化可能材料」に分類されることが、我々の前回の研究で判明している。ところが、本研究で調べたSrTiO
などのフッ化物は、耐照射性の高い「非アモルファス化可能材料」に分類されることが、我々の前回の研究で判明している。ところが、本研究で調べたSrTiO は、2つの分類の中間に当たることが判明した。耐照射性の観点から区別される2つの材料分類を分ける材料基準が何なのか従来から問題となっていたが、本研究により、イオン結合性の強さ、結晶対称性の高さが、その材料基準となることが示唆された。
は、2つの分類の中間に当たることが判明した。耐照射性の観点から区別される2つの材料分類を分ける材料基準が何なのか従来から問題となっていたが、本研究により、イオン結合性の強さ、結晶対称性の高さが、その材料基準となることが示唆された。
雨倉 宏*; Li, R.*; 大久保 成彰; 石川 法人; Chen, F.*
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 4(4), p.39_1 - 39_11, 2020/12
200MeV Xeイオンビームを照射したY Al
Al O
O (YAG)の屈折率変化の深さ分布測定を行った。その結果、3
(YAG)の屈折率変化の深さ分布測定を行った。その結果、3 mまでの浅い領域では電子的エネルギー付与に起因した屈折率変化が見られ、さらに深い6
mまでの浅い領域では電子的エネルギー付与に起因した屈折率変化が見られ、さらに深い6 mまでの中間領域では電子的エネルギー付与と弾性衝突によるエネルギー付与の重畳効果がみられ、さらに深い13
mまでの中間領域では電子的エネルギー付与と弾性衝突によるエネルギー付与の重畳効果がみられ、さらに深い13 mでは弾性衝突によるエネルギー付与に起因する屈折率変化が見られた。これらの光学特性の深さ分布は、必ずしも照射損傷の量と一致しないため、損傷の質(照射で誘起される材料歪みなど)も光学特性変化に影響を及ぼしている可能性が示唆された。
mでは弾性衝突によるエネルギー付与に起因する屈折率変化が見られた。これらの光学特性の深さ分布は、必ずしも照射損傷の量と一致しないため、損傷の質(照射で誘起される材料歪みなど)も光学特性変化に影響を及ぼしている可能性が示唆された。
鈴木 賢治*; 城 鮎美*; 豊川 秀訓*; 佐治 超爾*; 菖蒲 敬久
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 4(3), p.25_1 - 25_14, 2020/09
粗大粒で構成される材料の2次元回折パターンはリング状とはならずスポット状となるため、従来の回折計と0次元検出器を利用したひずみスキャンニング法では応力評価が困難である。この課題を解決するために2次元検出器を利用した2重露光法を提案した。本研究ではこの技術を白色X線に対して適用するための技術開発を行った。粗大粒で構成される材料に白色X線を照射すると得られる回折はラウエスポットとなる。そこで検出するエネルギーを制限できるCdTeピクセル2次元検出器の開発とそれを利用した応力評価を行った。その結果、オーステナイト系ステンレス鋼を供試材とする曲げ試験片に対して、ほぼ理論値通りのひずみ分布を計測することに成功した。今後、当該技術の向上を図り、実機材料に適用していきたいと考えている。